(5335) Damocles
|
Asteroid (5335) Damocles |
|
|---|---|
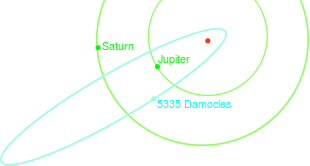
|
|
| Orbit of (5335) Damocles compared to the orbits of Saturn and Jupiter. | |
| Properties of the orbit ( animation ) | |
| Orbit type | Damocloid |
| Major semi-axis | 11.838 AU |
| eccentricity | 0.866 |
| Perihelion - aphelion | 1.582 AU - 22.095 AU |
| Inclination of the orbit plane | 61.95 ° |
| Length of the ascending node | 314.18 ° |
| Sidereal period | 40.73 a |
| Physical Properties | |
| Absolute brightness | 13.3 mag |
| history | |
| Explorer | Robert McNaught |
| Date of discovery | February 18, 1991 |
| Another name | 1991 DA |
| Source: Unless otherwise stated, the data comes from JPL Small-Body Database Browser . The affiliation to an asteroid family is automatically determined from the AstDyS-2 database . Please also note the note on asteroid items. | |
(5335) Damocles is an asteroid belonging to the group of Damocloids , which was discovered on February 18, 1991 by Robert McNaught at the Siding Spring Observatory . The asteroid was named after Damocles .
Properties of the orbit
The asteroid's orbit is highly elliptical with an eccentricity of 0.866. The perihelion lies with 1.582 AU in the inner solar system, the aphelion with 22.094 AU lies beyond the Uranus orbit. The asteroid takes 40.73 years to orbit the sun. Furthermore, the orbital plane is inclined at 61.95 degrees against the ecliptic .
Duncan Steel , Gerhard Hahn , Mark Bailey, and David Asher made projections of their long-term dynamic development.
Web links
- (5335) Damocles in the JPL Small-Body Database Browser
- Article about the damocloids on the website of the Kuffner observatory
Individual evidence
- ^ Lutz D. Schmadel: Dictionary of minor planet names . Vol. 1. Springer, Berlin & New York 2003
- ↑ Asher, DJ; Bailey, ME; Hahn, G .; Steel, DI: Asteroid 5335 Damocles and its implications for cometary dynamics. In: mnras.oxfordjournals.org. Royal Astronomical Society , May 27, 1993, archived from the original on July 17, 2016 ; accessed on July 17, 2016 (English).