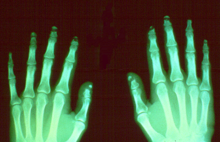
Acroosteolysis
| Classification according to ICD-10 | |
|---|---|
| M89.5 | Osteolysis |
| M89.8 | Other specified bone diseases |
| ICD-10 online (WHO version 2019) | |
The acro-osteolysis ( ancient Greek ἄκρος akros , extremely ' ὀστέον osteon , bone' and λύσις lysis , dissolution ', latin Acropathia ulcero-mutilans ) is an end members of fingers and toes and the distal end of the clavicle bone Resolution (relevant osteolysis ).
causes
The cause is not known. Most often it is a symptom of an underlying condition such as:
- Acropathia ulcero-mutilans familiaris (Acroosteopathia ulcero-mutilans familiaris; primary neuropathic acrodystrophy; familial acroosteolysis; Thévenard syndrome; congenital sensory neuropathy, Nélaton syndrome)
- Bureau-Barrière Syndrome (non-familial form)
- Primary hyperparathyroidism
- Scleroderma (" Madonna's finger ")
- Vinyl chloride disease
Classification
A classification is possible according to various criteria:
- Diffuse type of absorption in pycnodysostosis , autoimmune disease , vasculitis , Raynaud's syndrome , trauma , epidermolysis bullosa , psoriasis , frostbite , sarcoid , acromegaly and advanced leprosy
- Band-like type of absorption after exposure to vinyl chloride and in Hajdu-Cheney syndrome
- Congenital forms in Ehlers-Danlos syndrome , Rothmund-Thomson syndrome , analgesia syndrome, epidermolysis bullosa
- Acquired forms in secondary hyperparathyroidism , trauma, infection , frostbite, leprosy, psoriasis, hyperuricemia or polyvinyl intoxication
In the context of syndromes
- Hajdu-Cheney syndrome (acroosteolysis, autosomal dominant)
- Acro-osteolysis-keloid-like lesions-premature aging syndrome (premature aging syndrome type Penttinen)
- Neuropathy, autonomic hereditary sensory, type 2 (acroosteolysis, neurogenic; HSAN2; neuropathy, radicular sensory, autosomal recessive)
- Hypotrichosis-osteolysis-periodontitis-palmoplantar keratosis syndrome (HOPP syndrome; hypotrichosis-keratosis palmoplantaris striata-acroosteolysis-periodontitis syndrome)
- Idiopathic phalanges acroosteolysis
- Endangiitis obliterans
- Keutel syndrome
- Mandibuloacral dysplasia
- Hereditary idiopathic osteolysis type I Lamy-Maroteaux
- Hereditary idiopathic osteolysis type II Joseph
- Van Bogaert Hozay syndrome (hereditary idiopathic osteolysis type III Hozay)
- Hereditary idiopathic osteolysis type IV Thieffry-Shurtleff
diagnosis
The x-ray shows a defect in the nail process with erosion , rarefied cancellous bone .
literature
- Radiopaedia
- D. Weber-Klukkert: Acroosteolysis in the context of psoriasis. In: Deutsche Medizinische Wochenschrift (1946) , Volume 133, No. 31-32, August 2008, pp. 1625-1626, doi: 10.1055 / s-0028-1082778 , PMID 18651364 .
- H. Kleinsorge, G. Thiele: Acroosteolysis. In: Deutsche Medizinische Wochenschrift (1946) , Volume 81, No. 45, November 1956, pp. 1785-1790, doi: 10.1055 / s-0028-1115229 , PMID 13384109 .
- Les Acro-osteolyses. (PDF)
Individual evidence
- ↑ Encyclopedia Dermatology
- ^ W. Pschyrembel: Clinical dictionary. 266th, updated edition. de Gruyter, Berlin 2014, ISBN 978-3-11-033997-0, keyword acroosteolysis
- ↑ a b K. Ebel, E. Willich, E. Richter (eds.): Differential diagnostics in pediatric radiology . Volume I. Thieme 1995, ISBN 3-13-128101-4 , p. 348
- ↑ Acroosteolysis-keloid-like lesions-premature aging syndrome. In: Orphanet (Rare Disease Database).
- ↑ Hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy type 2. In: Orphanet (database for rare diseases).
- ↑ Hypotrichosis-osteolysis-periodontitis-palmoplantar keratoderma syndrome. In: Orphanet (Rare Disease Database).
- ↑ Idiopathic phalangeal acro-osteolysis. In: Orphanet (Rare Disease Database).
- ↑ Bernfried Leiber (founder): The clinical syndromes. Syndromes, sequences and symptom complexes . Ed .: G. Burg, J. Kunze, D. Pongratz, PG Scheurlen, A. Schinzel, J. Spranger. 7., completely reworked. Edition. tape 2 : symptoms . Urban & Schwarzenberg, Munich et al. 1990, ISBN 3-541-01727-9 .