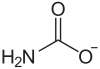
Ammonium carbamate
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Ammonium carbamate | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | H 2 NCOONH 4 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white solid with an ammonia-like odor |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 78.07 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.6 g cm −3 |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
152 ° C (in closed ampoule) |
||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
Decomposition from 35 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
117.70 h Pa (25 ° C) (decomposition) |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
good in water (790 g l −1 at 20 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Ammonium carbamate , formerly also called ammonium carbamate , is the ammonium salt of carbamic acid , which is not known in the free state. It is a minor ingredient in staghorn salt .
properties
Ammonium carbamate forms a colorless crystal powder that dissolves well in water (at 790 g / l). The solubility is increased by adding ammonia gas . In aqueous solution, ammonium carbamate partially hydrolyzes above 35 ° C, and above 60 ° C completely, with the formation of ammonium carbonate , which in turn can break down into ammonia and carbon dioxide .
The decay can be quantified via the corresponding dissociation pressures.
| Dissociation pressure of ammonium carbamate | ||||||||||||
| temperature | in ° C | 10.03 | 14.92 | 17.86 | 21.25 | 24.91 | 26.77 | 30.91 | 35.91 | 39.89 | 44.86 | |
| pressure | in kPa | 3.89 | 5.66 | 7.03 | 9.08 | 11.77 | 13.37 | 17.85 | 24.89 | 32.33 | 44.21 | |
When heated in a closed system, decomposition into urea and water can be observed at temperatures around room temperature . The rate of conversion increases sharply with increasing temperature, with the water formed having a catalytic effect.
synthesis
Ammonium carbamate is produced by the direct reaction of ammonia gas and CO 2 in a volume ratio of 2: 1 with the exclusion of water .
use
Ammonium carbamate is used in the cosmetics industry and in the manufacture of pesticides. It is also an important intermediate in the production of urea . It is also used as a cleaning, pickling and neutralizing agent, as well as in the deer horn salt mentioned above for baking. In Germany, the direct production of ammonium carbamate is only around 1000 t / a due to the low demand. The automotive industry is investigating ammonium carbamate as an alternative to the AUS 32 urea solution in SCR catalysts.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g Entry on ammonium carbamate in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 1, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ K.-H. Zapp, K.-H. Wostbrock, M. Schäfer, K. Sato, H. Seiter, W. Zwick, R. Creutziger, H. Head: Ammonium Componds. In: Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry . Wiley-VCH Verlag, Weinheim 2005, doi : 10.1002 / 14356007.a02_243 .
- ↑ a b c T. R. Briggs, V. Migrdishian: The Ammoniumn Carbamate Equilibrium. In: J. Phys. Chem. 28, 1923, pp. 1121-1135, doi: 10.1021 / j150245a001 .





