Aromatic hydrocarbons
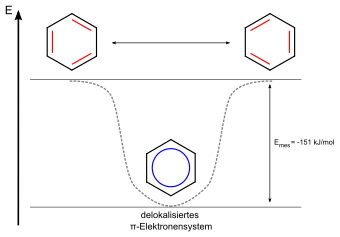
The aromatic hydrocarbons or benzoid hydrocarbons , called arenes according to IUPAC , are cyclic, planar hydrocarbons with an aromatic system . Due to their delocalized π-electron system , they are energetically more favorable than their non-aromatic mesomers and therefore more chemically stable. Aromatic hydrocarbons can be divided into mono- (mAh) or polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH).
Like all pure hydrocarbons, aromatic hydrocarbons are non-polar , lipophilic compounds. Since aromatic compounds are compared to the aliphatic carbon compounds and are thus defined by a negation, this means that all non-aliphatic organic compounds are aromatic. The classification of organic compounds into aliphatics and aromatics is based on the aromaticity criteria .
history
The first discovered was the aromatic 1825 by Michael Faraday in coal gas found benzene (C 6 H 6 ). Soon substances with similar properties were discovered that showed a different structure. It quickly became apparent that these formally unsaturated compounds, in spite of the double bonds, were not easy to induce into addition reactions .
Examples
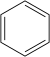
Examples of aromatic hydrocarbons Parent
compound
benzenealkylated arenes
( Alkylbenzenes )
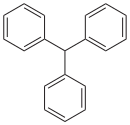
Arenes with multiple phenyl groups
(Polyarylalkanes)
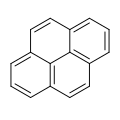
fused arenas
(PAK)

≡

Toluene xylenes ( o -, m -, p -xylene) ethylbenzene cumene






Biphenyl
Note: The structural formulas of aromatic compounds are usually shown in just one mesomeric form .
Annulenes , i.e. cyclic hydrocarbons with conjugated double bonds, can have aromaticity. After benzene, [14] -annulene is the smallest aromatic annulene, and annulenes with 18 and 22 carbon atoms are also aromatic.
Occurrence and extraction
Aromatic hydrocarbons are found in petroleum . There arenes can be found which have the structural elements of indane , tetrahydronaphthalene , fluorene , biphenyl and acenaphthene , as well as arenes with an isoprenoid structure. The majority of the technically important compounds are synthesized using petrochemical processes . In the coking plant , aromatics are a by-product and can be found in coal tar and coke oven gas . Important mass products are benzene, toluene, xylenes and ethylbenzene ( BTEX aromatics). They are themselves the raw materials for plastics and for other bulk chemicals. Important PAHs are naphthalene and anthracene, which are obtained from coal tar and petroleum.
| Procedure | Objective of the procedure | Process conditions | Other characteristics | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pressure (bar) | Temperature (T °) | catalyst | Encore | |||
| Refining process | ||||||
| Hydrogenation of pyrolysis gasoline | Hydrogenation of diolefins and desulfurization | 40-60 | 200-250 | Co , Mo , Ni , Pd | H 2 | Two-step process |
| Benzene pressure refining | Hydrogenation of crude benzene coking plant | 20-50 | 350 | Co, Mon | H 2 | Sulfur reduction below 0.5 ppm; Removal of unsaturated hydrocarbons which make it difficult to obtain benzene by distillation |
| Dealkylation processes | ||||||
| Houdry -Litol | Benzene production from toluene | 50 | 600 | Co, Mon | H 2 | Hydrogenation of unsaturates; hydrocracking cleavage of non-aromatics; Desulfurization, dealkylation and dehydrogenation of naphthenes lead to high benzene yields |
| Houdry dealkylation (HDA) | Benzene production from toluene | 45 | Max. 750 | H 2 | Benzene yield up to 99% | |
| Isomerization processes | ||||||
| Octafining | Increased proportion of p -xylene | 10-30 | 425-480 | Pt / zeolite | H 2 | Comparable to the Isomar ( UOP ), Isoforming ( Exxon ) and Isarom ( IFP ) processes |
| Transalkylation | ||||||
| Arco | Production of benzene and C 8 aromatics from toluene | 2 | 480-520 | Al 2 O 3 / SiO 2 | Fluidized bed process in the gas phase | |
| Tatoray | Production of benzene and C 8 aromatics from toluene | 10-50 | 350-530 | Zeolite | H 2 | adiabatic process |
| Mobil LTD | Production of benzene and C 8 aromatics from toluene | 46 | 260-315 | Zeolite | Contact life approx. 1.5 years | |
Derivatives
Aromatic hydrocarbons can form derivatives with organic or non-organic substituents.
literature
- Cornelsen: Chemistry Upper Level - Organic Chemistry , 1st Edition, ISBN 978-3-06-011174-9 .
Individual evidence
- ↑ Entry on arenes . In: IUPAC Compendium of Chemical Terminology (the “Gold Book”) . doi : 10.1351 / goldbook.A00435 Version: 2.3.3.
- ↑ Entry on aromatic . In: IUPAC Compendium of Chemical Terminology (the “Gold Book”) . doi : 10.1351 / goldbook.A00441 Version: 2.3.3.
- ^ FA Carey, RJ Sundberg: Organische Chemie , VCH, Weinheim 1995.
- ↑ Hans-Dieter Jakubke, Ruth Karcher (Ed.): Lexicon of Chemistry , Spectrum Academic Publishing House, Heidelberg, 2001.
- ^ Heinz-Gerhard Franck, Jürgen Walter Stadelhofer: Industrial Aromatic Chemistry: Raw Materials · Processes · Products . Springer, 1987, ISBN 978-3-662-07876-1 , pp. 135 .