Artesunate
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
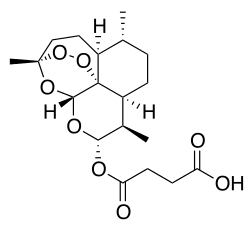
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Artesunate | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
(3 R , 5a S , 6 R , 8a S , 9 R , 10 S , 12 R , 12a R ) -decahydro-3,6,9-trimethyl-3,12-epoxy-12 H -pyrano [4.3 - j ] -1,2-benzodioxepin-10-ol-hydrogen succinate ( IUPAC ) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 19 H 28 O 8 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 384.421 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Artesunate is a from Artemisinin derived semi-synthetic drug for the treatment of by Plasmodium falciparum causing malaria . The active ingredient artesunate was added to the list of essential drugs of the World Health Organization by the World Health Organization (WHO) in 2002.
Pharmacological properties
Artesunate has a significantly improved bioavailability compared to artemisinin . Like all artemisinin derivatives, it acts via an endogenous peroxide group that presumably forms radicals that are toxic to the plasmodia in infected erythrocytes . The relatively short half-life is problematic. Artesunate is metabolized in the liver by the enzyme cytochrome P450 3A4 .
Preparations and Uses
Artesunate is mainly used as a combination preparation with other anti-malarial drugs such as amodiaquine for the treatment of malaria. An artesunate-amodiaquine combination preparation (ASAQ) was developed in collaboration between the Drugs for Neglected Diseases Initiative (DNDi) and sanofi-aventis and registered in several African countries. Artesunate preparations are not currently approved in Europe. However, approval is being sought for the ASAQ preparation; it is to be marketed under the brand name Coarsucam ® in the future. Other combination preparations of artesunate with mefloquine are currently under development.
The main focus for the application of artesunate is the treatment of the uncomplicated malaria tropica , especially with plasmodia, which are resistant to other drugs like chloroquine . The World Health Organization advises against using it as a single substance in order to reduce the risk of developing resistance to artemisinin derivatives. In complicated malaria (Falciparum malaria), however, the intravenous administration of artesunate is the drug of choice and should, if available, be preferred to the intravenous administration of quinine. It is not on the market in Germany, but can be obtained from import companies.
Manufacturing
Artesunate is produced by reacting dihydroartemisinin obtained from Artemisia annua with succinic anhydride in an alkaline medium. Pure artesunate is a colorless, water-soluble powder.
Individual evidence
- ↑ There is not yet a harmonized classification for this substance . A label for 4-oxo-4 - {[(1R, 4S, 5R, 8S, 9R, 10S, 12R, 13R) -1,5,9-trimethyl-11,14,15 is shown, which is derived from a self-classification by the distributor , 16-tetraoxatetracyclo [10.3.1.0 ^ {4,13} .0 ^ {8,13}] hexadecan-10-yl] oxy} butanoic acid in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed December 17 2019.
- ↑ Artesunate data sheet at Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on February 16, 2020 ( PDF ).
- ↑ WHO Model List of Essential Medicines (PDF; 442 kB) accessed on September 20, 2012.
- ↑ ASAQ to treat malaria. ( Memento of May 5, 2012 in the Internet Archive ) DNDi.org
- ↑ WHO on artemisinin monopreparations .
- ↑ Guideline 042/001 Diagnosis and Therapy of Malaria .