Büren (Westphalia)
| coat of arms | Germany map | |
|---|---|---|

|
Coordinates: 51 ° 33 ' N , 8 ° 34' E |
|
| Basic data | ||
| State : | North Rhine-Westphalia | |
| Administrative region : | Detmold | |
| Circle : | Paderborn | |
| Height : | 230 m above sea level NHN | |
| Area : | 170.99 km 2 | |
| Residents: | 21,515 (Dec 31, 2019) | |
| Population density : | 126 inhabitants per km 2 | |
| Postal code : | 33142 | |
| Primaries : | 02951, 02955, 02958 | |
| License plate : | PB, BÜR | |
| Community key : | 05 7 74 016 | |
| LOCODE : | DE BUQ | |
| City structure: | 12 localities | |
City administration address : |
Königstrasse 16 33142 Büren |
|
| Website : | ||
| Mayor : | Burkhard Schwuchow ( CDU ) | |
| Location of the city of Büren in the Paderborn district | ||
Büren is a medium -sized town in East Westphalia-Lippe in the south of the Paderborn district . The city of Büren was the district town of the Büren district until 1974 and has an international airport in the city area, Paderborn / Lippstadt Airport . The city is known for its many schools and educational institutions.
geography
Geographical location
Büren is located in the extreme southwest of the Ostwestfalen-Lippe region north of the Sauerland , on the southwestern edge of the Paderborn plateau and west of the Sintfeld in the heart of the Bürener Land . In the city the Afte flows into the Alme . The urban area includes altitudes of 190 to 360 meters above sea level .
The city belongs to the Bad Wünnenberg / Büren recreation area .
geology

The underground of the city is made up of solid rock from the Middle Ages and the ancient times . Sandstones are widespread , including, for example, the Rüthener sandstone from the Lower Cretaceous , as well as limestone (including the Anröchter Stone ) and marl stones from the Upper Cretaceous . The Paderborn plateau is built up from the marl stones of the Upper Cretaceous ; it is characterized by different rock hardnesses and the associated shallow collapse of the layers, which has resulted in a layered landscape . The landscape is characterized by sinkholes and dry valleys . Older rocks, dark clay , silt and sandstones from the Upper Carboniferous period can be found on the slopes of the Alme , Nette and Afte valley . They come to the surface under the Cretaceous layers. Since these rocks were mountainous at the end of the ancient world , they are folded . Boulders and deposited loess as deposits of the Ice Age are only present in small areas. Particularly noteworthy are the geologically young calcareous sinter formations at the sources of the streams.
The rocks of the Upper Cretaceous are capable of karstification and are good aquifers. They lie on the poorly permeable base made of rocks from the Upper Carboniferous. The seeping surface water flows in crevices and karst waters and reappears in Salzkotten- Upsprunge and Geseke . Since the interface between the carbon and chalk rocks is undercut in the Almetal above Weine and near the Afte, a large number of springs emerge on the slopes that were previously used to supply drinking water. Since the surface water is only slightly filtered by the soil due to the karstification, problems in particular have arisen with the nitrate pollution caused by agriculture . Around two-thirds of the city's drinking water has therefore been taken from the Aabach dam since 1983 .
The above-mentioned sandstones Anröchte Stein and Rüthener sandstone, as well as deposits of limestone, marl-lime and limestone marl, were formerly used as building blocks, bulk material and for lime or cement production. In the meantime, however, there is no longer any dismantling.
On the Paderborn plateau, brown soils developed from ice age, partly relocated loess. As shallow brown soils, they are widespread in combination with very stony, often still calcareous, rendzines of 10–30 cm in diameter in the northern urban area along the A 44 and in the southern urban area.
The rendzines form a layer of hard limestone on hilltops and saddles to the east and west of Büren. They are in great danger of dehydration, stony and difficult to work with. Gleye and pseudogleye are common south of Steinhausen and east of Büren. The foothills of the Sauerland between Siddinghausen and Ringelsteiner Wald are characterized by medium to deep, silty brown earth. They are creepy to very stony and consist of slope and plateau clay , which is based on silicate rock of the Upper Carboniferous. The river valleys of Alme and Afte are covered by floodplain soils. In some small side valleys, fens with high groundwater levels have developed.
Büren is well to very well suited for the use of geothermal heat sources by means of a geothermal probe and heat recovery through heat pump heating (see the adjacent map).
Expansion and use of the urban area
The city, classified as a "small town", covers an area of 170.97 km². The largest share of the area is made up of forest and agricultural areas with a total of approx. 87.6%, settlement and traffic areas cover a further 11.2%. The largest extension in north-south direction is approx. 18.8 km, in east-west direction approx. 17.1 km.
| Area according to type of use |
Agricultural area |
Forest area |
Building, open and operational space |
Traffic area |
Surface of water |
Sports and green space |
other use |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area in km² | 84.32 | 65.43 | 9.08 | 10.05 | 0.68 | 1.30 | 0.05 |
| Share of total area | 49.34% | 38.28% | 5.31% | 5.88% | 0.40% | 0.76% | 0.03% |
Neighboring cities
Starting in the north, Büren is bordered clockwise by the towns of Salzkotten and Bad Wünnenberg in the Paderborn district and, in the Arnsberg district, the towns of Brilon in the Hochsauerland district and Rüthen and Geseke in the Soest district .
City structure
According to Section 3 (1) of its main statute, the city of Büren is divided into twelve localities: The old town of Büren and eleven municipalities of the Büren Office that were independent until 1975 :
| Locality | Residents | surface | Mayor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ahden | 998 | 9.78 km² | Rainer Fischer ( SPD ) |
| Barkhausen | 128 | 6.15 km² | Johannes Wördehoff ( CDU ) |
| Brenken | 2239 | 27.41 km² | Jutta Schmidt (CDU) |
| Büren | 8609 | 26.43 km² | Wigbert Löper (CDU) |
| Eickhoff | 90 | 4.09 km² | Josef Püster (CDU) |
| Harth | 823 | 18.28 km² | Dirk Nölting (CDU) |
| Hegensdorf | 941 | 15.26 km² | Dirk Herbst (CDU) |
| Siddinghausen | 946 | 10.36 km² | Gerhard Helle (CDU) |
| Steinhausen | 3523 | 14.45 km² | Franz-Josef Borghoff (SPD) |
| Weiberg | 655 | 5.3 km² | Wilhelm Luis (CDU) |
| Wines | 567 | 6.88 km² | Norbert Steven (CDU) |
| Wewelsburg | 2190 | 26.48 km² | Günther Eggebrecht (CDU) |
history
| Capitals and cities of the Principality of Paderborn until 1802/03 (as of 1789): |
|---|
| Paderborn , Warburg , Brakel , Borgentreich | Beverungen , Borgholz , Bredenborn , Büren , Driburg , Dringenberg , Gehrden , Calenberg , Kleinenberg , Lichtenau , Lippspringe , Lügde , Nieheim , Peckelsheim , Salzkotten , Steinheim , Vörden , Willebadessen , Wünnenberg |
middle Ages

Before 1195, when the city was founded, Büren had been a farming settlement for 300 years. Büren (Buranon) was first mentioned in 1095. The noblemen of Büren applied for the city to be founded. The village was on the left bank of the Alme (today: Menkenberg / Bühl) and was quite insignificant. A church consecrated to Saint Gangolf was probably built in the second half of the 9th century. A cross on Menkenberg reminds of the church and the submerged village.
Around 1150, the nobles von Büren built a castle complex at the confluence of the Alme and Afte rivers . They came from the area north of Winterberg and Medebach (from Deifeld ) and came in the wake of the new high bailiffs of the Diocese of Paderborn, the Counts of Schwalenberg , as feudal lords of the so-called County of Wewelsburg .
The founding of the city of Büren was decided by a contract between the Bishop of Paderborn and the noblemen of Büren in 1195. The bishop gave his approval for the town and contributed to the fortification costs. He also granted the right to coin and customs as well as various tithe. For this he had the city enlisted as a fiefdom and the right to open it certified. About thirty house spaces were created on the south side of the castle.
The first expansion of the city of Büren took place between 1195 and 1220. The ascending ridge between Alme and Afte was opened up by three parallel streets running in north-south direction (today Rosenstrasse, Burgstrasse and Königsstrasse), which are connected by cross streets. Two of the resulting large squares were reserved for the church of St. Nicholas with churchyard and the market with the town hall. For topographical reasons, the city area was expanded to the west and east of the three streets to the edge of the Alme and Afte river valleys and gradually surrounded by a wall reinforced by nine towers. In 1238, the city of Büren received a constitution based on the Lippstadt town charter . A city judge was also on site.
In 1243 the noblemen von Büren founded the Cistercian monastery Holthausen , in which the von Fürstenberg family lives today and where the noblemen von Büren are buried.
A document from the Paderborn bishop spoke of two new towns in Büren in 1252. This second city expansion could be spread over the area south of the upper gate on both sides of the road to Siddinghausen (today: betweenBruchstrasse and Schanze). A city wall was also built at this time. A debt register from 1286 of the Livonian Hanseatic City of Riga suggests that Büren was actively involved in the Hanseatic trade until around 1336. After the reconciliation of the Bürener citizenship with Bishop Simon III. zu Lippe through the mediation of Berndt von Büren the St. Sebastian Brotherhood was founded in 1490.
Modern times
In 1588 the first Büren water pipe was put into operation. In 1661 the last nobleman from Büren , Moritz von Büren, died and established the Jesuit order as heir to the rule of Büren. The Bürener castles at the lower gate (Burgstrasse) were demolished between 1717 and 1728. On October 18, 1816, the Büren district was formed by ordinance of the royal government in Minden. A second rifle club, the Bürgererschützenverein, was founded in Büren in 1828. The two communities Oberntudorf and Niederntudorf came from the Paderborn district to the Büren district in 1832. Since then they have belonged to the Bürener Land . In 1895 the railway line from Paderborn through the Almetal to Büren was completed, and in 1900 the Almetalbahn was extended to Brilon . In 1898 the Geseke – Büren railway via Steinhausen was built.
In 1908 Büren got its own power grid. The district of Wewelsburg was the location of the Niederhagen concentration camp when Heinrich Himmler had the Wewelsburg converted into a National Socialist cult center from 1940 . Adolf von Oeynhausen , who had drawn Himmler's attention to the Wewelsburg in 1933, was made an honorary citizen of the city. In 1945, before the end of the war, large parts of the facility were blown up. The Americans liberated the city and district of Büren from National Socialism in 1945 . Before that, around 80 members of the SS had been expelled from the city by the city's residents in order to save Büren from destruction.
In 1946, the Sisters of Our Lady founded the Liebfrauengymnasium as the second Büren grammar school. In 1971 the Büren Airport Paderborn / Lippstadt was put into operation by the Büren district in Ahden. Due to the local reorganization, the Büren district was dissolved in 1975 and added to the neighboring districts. In 1980 passenger traffic on the Almetalbahn Paderborn-Büren-Brilon was stopped and in 1984 the line was finally closed. The JVA Büren started operations in 1994.
Religions
Due to its affiliation to the former Paderborn Monastery, the majority of the population in Büren is traditionally Catholic . The denominational affiliation of the students in Büren can be an indication of the distribution of religions. Accordingly, in the 2006/2007 school year, 16.8% of the students stated Protestant, 72.9% Catholic and 0.8% Islamic as their religious affiliation. 4.9% said they belonged to another religion and 4.6% had no denomination. In addition to the Catholic parishes there are two Protestant churches , including one in Buren and in Wewelsburg. But also congregations of the New Apostolic Church, Baptists , Jehovah's Witnesses and the Free Church congregation are represented in Büren. The Apostle Ministry of Jesus Christ also has a local church.
Incorporations
On January 1, 1975, the Sauerland / Paderborn law not only dissolved the Büren district and added the neighboring districts, but also the communities of Ahden, Barkhausen, Brenken, Eickhoff, Hardt, Hegensdorf, Siddinghausen, Steinhausen, Weiberg, Weine and Wewelsburg, which previously belonged to the office of Büren , incorporated into the city of Büren. These formerly independent communities are still characterized by their lively club life and their autonomy .
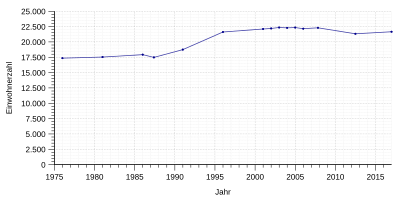
Population development
|
|
¹ census result
politics
The political landscape in Büren is formed by the nationwide parties CDU , SPD , FDP and Bündnis'90 Die Grünen . Since two councilors left the SPD in 2010 and 2011 until the 2014 local elections, there was also the SFWG (Social Free Voting Community).
With the Junge Union (CDU), the Jusos (SPD) and the Julis (FDP), three youth organizations are active in the city. The CDU has also formed a representative for senior citizens with the Seniors Union .
City council
The city council has 38 members. In addition, the mayor is the council chairman. The following table shows the local election results since 1975:
| 2014 | 2009 | 2004 | 1999 | 1994 | 1989 | 1984 | 1979 | 1975 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Political party | Seats | % | Seats | % | Seats | % | Seats | % | Seats | % | Seats | % | Seats | % | Seats | % | Seats | % |
| CDU | 22nd | 57.06 | 22nd | 58.73 | 23 | 60.43 | 25th | 65.30 | 23 | 58.11 | 23 | 58.05 | 25th | 62.95 | 27 | 65.71 | n / a | 66.06 |
| SPD | 11 | 29.90 | 10 | 25.79 | 11 | 29.44 | 12 | 31.67 | 16 | 41.17 | 16 | 41.95 | 14th | 34.96 | 12 | 30.66 | n / a | 23.47 |
| FDP | 3 | 6.84 | 4th | 10.06 | 4th | 10.13 | 1 | 3.03 | 0 | 0.72 | - | - | 0 | 2.09 | 0 | 3.63 | 0 | 2.29 |
| Green | 2 | 5.88 | 2 | 5.42 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Independent | 0 | 0.3 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Others | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | n / a | 8.18 |
| Total 1 | 38 | 100 | 38 | 100 | 38 | 100 | 38 | 100 | 39 | 100 | 39 | 100 | 39 | 100 | 39 | 100 | n / a | 100 |
| voter turnout | 51.45% | 58.21% | 57.66% | 59.37% | 83.77% | 69.20% | 70.79% | 76.68% | 90.59% | |||||||||
1 without taking into account rounding differences
- Result of the local elections on May 25, 2014
mayor
- 1946–1948 Waldemar Boedts
- 1948–1952 Hermann Finkeldei (CDU)
- 1952–1974 Adolf Evers (CDU)
- 1975–1989 Theo Böhle (CDU)
- 1989–1999 Friedhelm Kaup (CDU)
- 1999-2009 Wolfgang Runge (CDU)
- 2009 – today Burkhard Schwuchow (CDU)
Burkhard Schwuchow ( CDU ) has been mayor since October 21, 2009 ; he was elected on August 30, 2009 with 66.47% of the valid votes. On May 25, 2014, he was re-elected with 69.9%. Deputy mayors are Christian Bambeck (CDU) and Heinz Kirse (SPD).
badges and flags
The city of Büren has a city coat of arms that is based on the city's oldest seal from 1299. The coat of arms was approved on January 16, 1976 by the Detmold district president. It corresponds to the coat of arms of the city of Büren before the municipal reorganization, which was approved by the Prussian king on September 2, 1908, following a proposal by the Reichsheroldsamt. Previously, the city of Büren had only used the red diamond chevron in the white shield as a coat of arms.
- Blazon :
- In red on a green three-mountain, a silver (white) castle with three tin towers, the middle of which is wider and has an open archway, in which there is a silver (white) triangular shield with a red diamond rafter.
The diamond rafter represents the coat of arms of the Büren house, which ruled over Büren and Bürener Land until the 17th century . It can be found in the coat of arms of the old district of Büren, the district of Paderborn and the city of Bad Wünnenberg. The coat of arms of the House of Büren can also be seen in the coat of arms of the former Büren office next to the Wewelsburg.
Also on January 16, 1976, the city of Büren received the right to its own city flag.
- Flag description
- Banner: Red and white striped lengthways with the city's coat of arms in the rectangular head of the banner.
- Hoisted flag: From red and white, longitudinally striped with the coat of arms of the city in the rectangular, continuous flag head.
Town twinning
- Kortemark (Belgium) - Partnership signed in 1981
- Charenton-le-Pont (France) - Partnership signed in 1989
- Mittersill (Austria) - Partnership signed in 1995
- Ignalina (Lithuania) - partnership signed in 2003
- Baruth / Mark (Teltow-Fläming district) - since 1990 within the framework of the municipal administration aid East
At the local level of the city of Büren, the locality of Wewelsburg has maintained a partnership with the municipality of Précigné / Sarthe in France since 1965 , which was officially sealed in 1991 by the signing of the partnership document.
The people of Büren live out their town twinning in various forms at club and church level. For example, a group from Ignalina attended World Youth Day and spent the first week in Büren.
But also clubs like the volunteer fire brigade, music or shooting clubs regularly go to the Büren partner cities to exchange experiences.
Culture and sights
theatre
In the theater of the Büren town hall, plays by professional artists and amateurs are performed at irregular intervals.
Museums
In the Wewelsburg is the district museum of the Paderborn district with an exhibition on the medieval castle history, the time as an SS terror and cult site and an exhibition on the subject of expulsion.
The popular Bernhard-Wolf school museum of the city of Büren can be found in the core city, known as the "school town". The middle mill and the drill mill have been converted into a " hands- on museum" and prepared. In addition, two other privately owned museums are waiting to be discovered in an exclusive tour: the Büren Hospital Museum and a museum for radio history.
music
In Büren there are a total of 33 choirs, music associations, drum corps and a district music school. The Prince Regent fanfare procession is the only one in the Bürener Land. The choirs and music associations usually invite you to a concert once a year and sing or play at the local shooting festivals and church services.
Buildings
- Catholic Church of St. Nicholas
- The cruciform basilica with west tower was first mentioned in 1220. The building was changed in the 19th century. The furnishings include a late-Gothic tabernacle from the end of the 15th century, a pulpit from around 1600 and the baroque organ from 1744, which was originally created for the Böddeken monastery .
- Jesuit College
- The building now houses the Mauritius high school , it was built by the Jesuits between 1719 and 1728 in the Baroque style.
- town hall
- The multi-wing building previously served as the widow's seat of the noblemen of Büren. After the death of Moritz von Büren in 1661 it became the property of the Jesuit order, which initially settled here. The building then appears to have been extensively renovated; the archway leading to the inner courtyard is dated 1664. In 1802/03 it fell to the Prussian state, which leased it to the pharmacist Quicken in 1806. In 1933 the Büren district acquired the complex, which had a new district building built here using older parts. Until 1975 it was the seat of the Büren district administration. Today it serves as the town hall; The employment office, a police station and a branch of the Paderborn district administration are also located here.
- Former tithe barn
- The core of the plastered quarry stone building with a mansard roof probably dates back to the 16th century, but was largely rebuilt around 1720. For a long time it served as a rent and forest office. Together with the Niedermühle, the Jesuit College and the adjoining 18th century farm building (now Café Stilbruch), it forms an impressive urban ensemble.
- With a steep pitched roof provided quarry stone was built in 1532 and is the oldest secular building in the downtown area. The mill was restored together with the neighboring drilling mill and operated as a museum by the Büren eV Heimatverein
- Former Niedermühle
- The oldest parts of the two-storey quarry stone building with a gable roof date from 1537. Today it is part of the Niedermühle u. a. used for concerts.
- Only a few older residential buildings have survived in the town center because of the numerous demolitions that took place in the 1960s and 1970s . The house at Markt 14 is particularly noteworthy . The half-timbered hall house with a crooked hip roof is marked on the gate beam in 1608. It is the oldest surviving residential building in the city. However, the ground floor was drastically changed for use as a shop. The house Südmauer 20 , a single-storey half-timbered building above a high basement, was built in the 19th century. The building at Bahnhofstrasse 2 is a large two-story half-timbered building with a hipped roof, which was probably built around 1840/50. The left half of the first floor was broken open in 1901 by installing a shop. The type of building at Kapellenstrasse 8 , which was designed as a semi-detached house in 1873 , is particularly interesting . It is a Querdeelenhaus , whose left gate was added later.
- Two towers and remnants of the wall have been preserved from the city fortifications .
- The Wewelsburg is the landmark of the Paderborn region .
- Ringelstein castle ruins with witch cellar
- The Ringelstein castle ruins are located above the valley on a ridge and are now part of the Harth area. The remains of the castle built by the nobles von Büren around 1400 can be viewed here.
- Accommodation facility for those obliged to leave the country , largest deportation center in Europe
- The facility went into operation in 1994 on the site of an abandoned NATO barracks.
- The former Böddeken monastery near Wewelsburg was founded by Saint Meinolf and is now home to a boarding school. In the vicinity of Gut Böddeken there is also the Friedenstal with a military cemetery.
- The former Cistercian convent Holthausen was founded in 1243 by the noblemen von Büren. The monastery church and the former monastery buildings were built around 1700 in the Baroque style using parts of the original medieval structure. Today they are privately owned. The noblemen of Büren are buried in the chapel of the monastery.
- With the Hünenburg on the Hahnenberg above the Alme valley between Büren and Brenken , the remains of an early medieval hill fort, which was rebuilt in the 14th century, have been preserved.
Natural monuments
Eleven nature reserves are designated in the urban area of Büren . The two largest are the forests near Büren (PB-066) with 1515.7931 hectares and the Leiberger Forest (PB-060) with 1232.6710 hectares. ( see also : List of nature reserves in the Paderborn district )
sport and freetime
The city of Büren has two outdoor pools, one between Harth and Weiberg and one in Büren itself. There is also an indoor pool. Almost every district has a football club and a sports field, with the exception of Barkhausen and Eickhoff. In the core town of Büren, the SV 21 Büren football club also runs athletics. The TV 13 Büren offers gymnastics, volleyball, table tennis, basketball, rope skipping and kickboxing. In the sports of kickboxing and ropeskipping, he is currently German champions and European champions. The sports and gymnasiums in the schools can also be used by clubs. One of the oldest tennis clubs in the East Westphalia district is also located in the city center. The TC Blau-Weiß Büren, founded in 1948, maintains an eight-place facility on Bennenberg.
There is a shooting range for the Bürener Bürgererschützenverein (BSV) near the Bruchs stadium in Büren. The shooting sports department of the BSV regularly provides world champions or vice world champions in various shooting categories. In the industrial area Büren-West there is a go-kart track and a Gotcha -Areal. Since the beginning of 2007, the Niedermühle cultural initiative has been providing a colorful entertainment and cultural program.
Regular events
In addition to the rifle festivals in the individual districts, the Moritzmarkt, the largest festival in Büren, takes place every year in the last week in September. The Nikolausmarkt is held on the weekend around December 6th. Another highlight is the Büren Hiking Day, for which hikers from all over Germany and the neighboring EU countries come to Büren every year in May . At the beginning of the summer holidays, the three-day open-air cinema "BOA Kino" takes place in the Bürener Almeauen every year. In 2018, BürenOpenAir was added to an event series for the first time with the rock concert BOArocks. Wingenfelder and The Hooters played on stage.
Culinary specialties
There are two regionally known schnapps in Büren , the Bürener Ratstropfen , which can be described as herbal schnapps, and the Bürener Moritzbrand , a fruit schnapps with caraway, which is dedicated to the last Bürener nobleman.
societies
The Büren Heimatverein was founded in 1987. The association has set itself the goal of researching the history of the city and making it better known, maintaining monuments and preserving Büren customs. The Heimatverein also runs the museum of the middle mill and the drill mill in the Bürener Almeauen.
Archery:
The St. Sebastian Brotherhood is probably the oldest association in Büren. It was founded in 1490, but its roots go back to the 12th century. The brotherhood accepted all of Bürener's Christian faith who had lived in the city for ten years. In the Middle Ages, the "Sebastiöner" took over the city guard, which is why, since 2007, some riflemen in the costumes of the old guards have marched at the rifle festival.
When more and more Protestants who could not join the brotherhood settled in Büren with the founding of the Büren district in 1816, they founded the Bürener Bürgerschützen in 1828. Since then there have been two rifle clubs in Büren, with the brotherhood having around 400 members and the civil rifle around 2000.
In 1958, on the initiative of the Haaren shooting club, the Büren District Rifle Club was founded, to which all clubs in the old Büren district are eligible and are allowed to shoot the district shooting bird. The place that provides the king also hosts the next district rifle festival.
Economy and Infrastructure
traffic
Bus transport
The city belongs to the area of the Paderborn-Höxter local transport network , which was replaced by the Westphalian tariff in August 2017 . The entire urban area is regularly connected to the city center via a city bus system. The express bus lines S60 and S61 connect Büren with the Paderborn regional center. After Geseke and Salzkotten regularly more bus routes. Brilon can be reached via the school buses with a change in Brilon-Alme by public transport.
Rail transport

There used to be connections with the Almetalbahn to Paderborn and Brilon and to Geseke .
Street
The A 44 motorway (Dortmund-Kassel) crosses the city in a west-east direction. From the Wünnenberg-Haaren motorway junction , the A 33 leads to the A 30 in Osnabrück .
air traffic
The international airport Paderborn / Lippstadt is located in the Büren-Ahden district . There is also the glider airfield in the city , which is operated by Aero Club Lippstadt e. V. and the Aero Club Büren is used.
media
The local radio for the Paderborn and Höxter districts, Radio Hochstift , can be received on the frequencies 88.1 MHz or 104.8 MHz. The daily newspapers in Büren are the Neue Westfälische and the Westfalen-Blatt , each with a local section for the Bürener Land. In addition, the weekly newspaper Neue Regionale from Geseke appears every Sunday with local news for Büren. In addition, the quarterly magazine Die Warte for the Paderborn and Höxter districts appears in the Hochstift Paderborn with articles on regional history, literature and art.
Since 2011 the magazine "Facette" has had its editorial office at Paderborn-Lippstadt Airport as a magazine for medium-sized businesses. It appears monthly and has a circulation of around 30,000 copies.
Public facilities
Next to the Bürener town hall in the former district administration there is a branch of the Paderborn district, in which, among other things, the Paderborn district culture office, the ARGE , the Paderborner Land tourism center e. V. and a police station are housed. In addition, the district archive and the archive of the city of Büren are located in Büren.
Germany's largest deportation detention center, UfA Büren , is operated in a former NATO barracks near the city of Büren .
The city of Büren is responsible for the municipal indoor pool and the two outdoor pools in Büren and Harth / Weiberg.
Education - School City Büren
The following schools are located in the city center of Büren: The Moritz von Büren School (special needs focus on hearing and communication) and the Almeschule (special needs focus on learning, language and emotional and social development) as special schools, and the Josef School as primary schools with the main location at the Wegwarte school network and the Lindenhofschule, the Mühlenkampschule and the Niederntudorf / Wewelsburg secondary school, the Heinz-Nixdorf-Realschule Büren as the secondary school . As grammar schools, the Mauritius grammar school and the Liebfrauengymnasium, as well as vocational colleges, the Ludwig-Erhard vocational college and the Richard-von-Weizsäcker vocational college. In 2016, a comprehensive school was founded in the school center.
In the Büren districts there are Catholic primary schools in Steinhausen and Siddinghausen , Harth (part of the Wegwarte school association), as well as Wewelsburg (as the main location) and Brenken (as a part of the school association Almetal Ahden / Brenken / Wewelsburg).
In 2007, the city's schools with 270 teachers taught a total of 4,197 pupils, of which 26.6% in elementary schools, 10% in secondary schools, 16.3% in secondary schools and 40.1% in grammar schools, as well as 6 , 1% at special schools.
Forest school
The city of Büren maintains a forest school. For this purpose, a former hunting lodge near the city was converted into a forest school. The aim is to bring the natural relationships in the forest closer to the children and adolescents in general education schools. For this purpose, suitable teaching material, which takes regional characteristics into account, is used. The facility is used by around 800 pupils per year. Twelve schools in the city are currently taking advantage of this special school offer.
Community College
The city of Büren is a member of the Adult Education Association Bad Wünnenberg, Büren, Delbrück, Hövelhof and Salzkotten.
childcare
There are 15 childcare facilities in the Büren urban area. The Christopherus kindergartens in the Steinhausen and Emmaus districts of Büren stand out as family centers. The facilities in Brenken, Harth, Steinhausen, Wewelsburg and four kindergartens in Büren are run by the church. The city of Büren is responsible for the facilities in Ahden, Hegensdorf, Siddinghausen, Steinhausen, Weiberg, Weine, and one in Büren.
Open youth facilities
In addition to Büren, the districts of Steinhausen and Wewelsburg also have their own youth club, all of which are sponsored by the municipal youth care organization in Büren. In the remaining parts of the city, youth work usually takes place through clubs or parishes. The youth club in Büren was reorganized in 2011, in which two facilities were merged. The current “Treffpunkt 34” has a usable area of approx. 300 m².
Book bus
The Paderborn District's mobile library was launched in 1971 by the Büren District and since then has served as a mobile library in small parts of the towns and communities in the Paderborn District. A total of 46 locations with 77 stops are controlled every three weeks. You can borrow magazines, material videos, CDs, MCs, CD-ROMs and floppy disks with a wide range of EDP software.
Children and young people who are to be introduced to the library at an early age make up around 60% of the visitors to the book bus, but due to the multiple use of book bus cards, which are a prerequisite for their use, this data cannot be precisely determined in families.
Established businesses
- BHK Kottmann, manufacturer of laminate floors and ceiling coverings
- Bürener Maschinenfabrik GmbH, manufacturer of conveyor and filter systems as well as injection molded parts
- CP autosport GmbH, developer and producer of racing components
- EMG - Engineering & Maschinenbau GmbH, manufacturer of devices, machines and systems for various industrial sectors, NC joining technology - servo presses with force-displacement monitoring, special systems for the battery industry (dry fill levels for industrial batteries).
- Heggemann AG, developer and producer of metal components for the automotive, aerospace and aerospace industries
- Guntram Heinelt GmbH & Co. KG, manufacture of office supplies and packaging
- Pauli GmbH, manufacturer of precast concrete parts for residential, agricultural and industrial construction.
- Freight forwarder Friedrich Biermann
- Unity AG, technology-oriented management consultancy for strategies, processes, technologies and systems
- Duex HandelsGmbH, hot air ovens, hot air steamers and snack devices
- Heinrichs GmbH, market for wallpaper, curtains, paints, floor coverings, painting company
- BVH Busverkehr Hornschuh, bus company for scheduled, school and occasional transports (until 2017)
Healthcare
There are nine general practitioners in Büren and the surrounding area, two of whom work together in a group practice.
There is also a doctor for ophthalmology , ear , nose and throat diseases , for internal diseases , pediatrics , skin diseases , a psychiatrist and a doctor for orthopedics . Two doctors specializing in gynecology and obstetrics have also established themselves. There are also ten dentists, six of whom work together in three group practices.
In addition to the surgeries there were to October 2010 in Buren nor the St. Nicholas - Hospital which diseases around the heart and circulation , lungs , gastrointestinal tract , kidney , metabolism , blood and blood-forming organs , hormone-forming systems and rheumatic diseases could handle.
The Büren hospital was most recently part of the Marseille-Kliniken AG , based in Hamburg . The hospital employed 70 people and had a capacity of 60 beds . Every year 4450 were approximately patient hospitalized. On October 14, 2010, the last patients were discharged and the hospital closed.
Since February 1, 2011 there has been an emergency service practice in Büren, which is open on weekends and on public holidays.
Aid organizations
In Büren there is a local association of the German Life Saving Society that has existed since 1936. The Büren branch of the Technical Relief Organization was founded in 1964 and is based in Harth- Ringelstein . Furthermore, the DRK and the Malteser Aid Service have accommodation in Büren. The volunteer fire brigade is represented in all parts of the city of Büren. The district fire brigade headquarters of the Paderborn district is located at Paderborn / Lippstadt Airport in the urban area of Büren.
Büren Community Foundation
The Bürgerstiftung Büren was founded in autumn 2000 and aims to promote and bundle the voluntary commitment of the Büren citizens.
Projects carried out
- Büren flourishes
- To improve the appearance of the city, the community foundation has planted more than 30,000 daffodil bulbs. Further measures are to follow soon, but they are not yet known.
- Heinrich Steinbrecher Fund
- The fund has assets of 50,000 euros and is run by the community foundation. The aim of the founder and the fund is to specifically promote projects to beautify the cityscape. This is accompanied by a competition in which the most beautiful garden in the city is to be determined. The Bürens Beste campaign is also supported by the Heinrich Steinbrecher Fund. Here young people who prove themselves through great commitment are awarded.
- Cultural initiative Niedermühle
- The Niedermühle in Büren was also transformed into a cultural center through voluntary work. Cabaret and theater performances are now taking place here. Music groups also perform frequently. There is a cinema program for children and young people during the summer holidays.
- Redesign of the Almeauen
- Under the motto Büren you can feel , the redesign of the Almeauen began in 2007. A mountain bike route was built, a Tibet bridge built, a barefoot path laid out and a volleyball and basketball field laid out. This project won a national competition and was awarded 15,000 euros as a flagship project.
advancement
The community foundation supports non-profit projects in the areas of education, upbringing, international understanding, art, culture, science, research, youth welfare, elderly care, environmental and nature protection as well as home care exclusively with the interest income from their share capital, which each foundation member brings in when they join or through further donations. The prerequisites for funding are a high proportion of voluntary work and civic self-government, the coexistence of generations and a connection to the city of Büren.
Personalities
Honorary citizen
Adolf von Oeynhausen (1877–1953) was made an honorary citizen in 1933 . He was born on Gut Holthausen in the urban area of Büren and worked as the regional president of the Prussian administrative district of Minden (1933 to 1945) as well as a member first of the paramilitary organization Stahlhelm and later of the NSDAP as well as an SS leader in the region.
sons and daughters of the town
- Saint Meinolf (around 795–857), founder of the Böddeken monastery
- Adelheid II von Büren († 1220), abbess
- Moritz von Büren (1604–1661), President of the Imperial Court of Justice and Jesuit, founder of the Jesuit College
- Ernst von Hartmann (1817–1883), Prussian infantry general
- Reinhard Franz von und zu Brenken (1818–1870), landowner, district administrator and member of the Reichstag of the North German Confederation, the Customs Parliament and the Prussian mansion
- Rosa Bodenheimer (1876–1938), women's rights activist
- Hermann Finkeldey (1894–1970), member of the State Parliament of North Rhine-Westphalia 1946–1947
- Jo Glahé (1925–2018), painter, graphic artist and entrepreneur
- Berna Kirchner (1927–2018), Germanist, pedagogue, entrepreneur and art collector
- Hildegard Sennlaub (* 1934), educator and writer
- Bert Brune (* 1943), writer
- Michael Henke (* 1957), soccer player and coach
- Ludger Egidius Schulte (* 1963), Catholic theologian
literature
- Adolf Hüttemann: Contributions to the history of the city and rule of Büren. PN Esser, 1908.
- J. Körner: District of Büren . In: The architectural and art monuments of Westphalia . Aschendorff, Münster 1926.
- Martin Moser: The city of Büren and its coat of arms . 1973.
- Achim Walder: Sights in Paderborn and the surrounding area: With description of the places: Paderborn, Altenbeken, Bad Lippspringe, Borchen, Büren, Delbrück, Hövelhof, Lichtenau, Salzkotten and Wünnenberg . Walder-Verlag, 2006, ISBN 3-936575-21-5 .
Web links
- Website of the city of Büren
- Documents from the Büren City Archives / Digital Westphalian Document Database (DWUD)
- Website of the Heimatverein Büren
- Website of the town hall Büren Publisher Stadt Büren - announcement of the cultural events
- Büren in the Westphalia Culture Atlas
Individual evidence
- ↑ Population of the municipalities of North Rhine-Westphalia on December 31, 2019 - update of the population based on the census of May 9, 2011. State Office for Information and Technology North Rhine-Westphalia (IT.NRW), accessed on June 17, 2020 . ( Help on this )
- ↑ Geological Service NRW: Geoscientific community descriptions NRW. Büren ( Memento from July 30, 2012 in the web archive archive.today )
- ↑ Geological Service NRW: Using geothermal energy - Geothermal study provides planning basis ( Memento from September 14, 2005 in the Internet Archive ) (PDF; 369 kB)
- ↑ a b State Office for Data Processing and Statistics North Rhine-Westphalia: Municipal profile Büren ( Memento of the original from May 5, 2008 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was automatically inserted and not yet checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ^ Geographical Commission for Westphalia (ed.): Geographisch-Landeskundlicher Atlas von Westfalen, Topic X Administration and Management, double sheet state and municipal administrative structure , Münster 1990.
- ↑ Main statute of the city of Büren ( Memento of the original from January 24, 2016 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was automatically inserted and not yet checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. dated September 8, 2014.
- ↑ Population development 2019 . In: Stadt Büren (Hrsg.): City mirror of the city of Büren . Issue No. 178 , March 7, 2020, p. 4 .
- ↑ Hermann Gottfried Gengler: Regesta and documents on the constitutional and legal history of German cities in the Middle Ages. Erlangen 1836, pp. 439-442.
- ^ Matthias Becher: Between imperial politics and regional orientation: Paderborn in the High Middle Ages (1050–1200) . In: Frank Göttmann, Karl Hüser, Jörg Janut (eds.): Paderborn. History of the city in its region . tape 1 . Ferdinand Schönigh, Paderborn, Munich, Vienna, Zurich 1999, ISBN 3-506-73120-3 , pp. 144 .
- ↑ State Office for Data Processing and Statistics: Students at general education schools in North Rhine-Westphalia according to religious affiliation
- ^ Federal Statistical Office (ed.): Historical municipality directory for the Federal Republic of Germany. Name, border and key number changes in municipalities, counties and administrative districts from May 27, 1970 to December 31, 1982 . W. Kohlhammer, Stuttgart / Mainz 1983, ISBN 3-17-003263-1 , p. 320 .
- ↑ IT NRW: Population in the administrative district of Detmold ( Memento of the original from December 12, 2012 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. , accessed January 18, 2013.
- ↑ Population development 2019 . In: Stadt Büren (Hrsg.): City mirror of the city of Büren . Issue No. 178 , March 7, 2020, p. 4 .
- ↑ State database NRW; Election results for the municipality code 05774016
- ^ State Office for Information and Technology in North Rhine-Westphalia: Local elections
- ^ Veddeler: coat of arms, seal flags. The municipal emblems of the regional association, the districts, cities and municipalities in Westphalia-Lippe. Münster 2003, p. 109 f.
- ↑ Current information from Bad Wünnenberg, Büren, Delbrück, Geseke and Salzkotten. Retrieved September 27, 2018 .
- ↑ Article in the Neue Westfälische: Gesamtschule is picking up speed ( Memento of the original from October 6, 2016 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was automatically inserted and not yet checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. Article dated September 3, 2016, accessed October 5, 2016
- ↑ finding aid of the archive Grevenburg the fiber optic Archives Office, no. 1177A, accessed 13 July 2010