Gulf of Bothnia
| Gulf of Bothnia | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Partly frozen Gulf of Bothnia, satellite image (2002) |
||
| Waters | Baltic Sea | |
| Land mass | Europe | |
| Geographical location | 62 ° N , 20 ° E | |
|
|
||
| width | 240 km | |
| depth | 725 km | |
| surface | 117,000 km² | |
| Greatest water depth | 301 m | |
| Medium water depth | 60 m | |
| Islands | Hailuoto , Stora Fjäderägg , Öja , Norrbyskären , Replot , Trysunda , Örskär , Gräsö | |
| Tributaries | Torne älv , Kemijoki , Lule älv , Ume älv | |
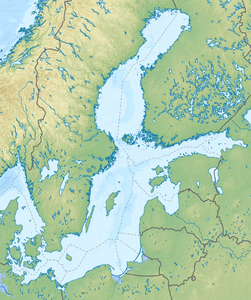
The Gulf of Bothnia ( Swedish Bottniska viken ; Finnish Pohjanlahti ) is the northern branch of the Baltic Sea between Sweden and Finland .
The name is related to the Swedish name for this part of the Baltic Sea, Botten [-] havet ( bottom sea ). It is uncertain whether this is the original meaning of the name or a folk etymological reinterpretation. In him the landscapes bordering Norr botten , Väster botten and Oester botten .
Since the Gulf of Bothnia is frozen over for several months a year, it is of minor importance for shipping . However, there are some port cities such as B. Luleå and Oulu .

According to the definition of the International Hydrographic Organization , the Gulf of Bothnia is bounded in the south by a line that extends from the Simpnäsklubb lighthouse (59 ° 54'N) in Sweden over the southernmost Åland Islands to Hanko (59 ° 49'N) in Finland . This definition, are the Åland Islands, which lie between the Swedish mainland and Åland Sea of Åland and the lying off the southwest coast of Finland Archipelago Sea parts of the Gulf of Bothnia. According to other definitions, the bay begins north of Åland.
The Gulf of Bothnia consists of two basins that are separated by the Kvarken strait : the Bottensee in the south and the Bottenwiek in the north. The salinity decreases from south to north. In the Bottensee the salt content is low enough to be called brackish water , the water of the Bottenwiek is practically fresh water . Therefore, freshwater fish such as pike and perch also occur there .
Overall, the gulf has a north-south extension of 725 km, the greatest width is 240 km. At the narrowest point in Kvarken, the Swedish and Finnish mainland are about 80 km apart. The area is 117,000 km², which roughly corresponds to the area of the two largest German federal states Bavaria and Lower Saxony combined. The amount of water is about 7,000 km³, which is a third of the entire Baltic Sea or about twice as much as the Huron Sea in North America.
The average depth is 60 m, the greatest depth is reached at 301 m in the Åland Sea , which is the second deepest point in the Baltic Sea after the Landsorttief . If the Åland Sea is not included in the Gulf of Bothnia, the deepest point at 295 m off the coast is at Härnösand in the Bottensee. The deepest point of the Bottenwiek is 146 m deep and is halfway between Lohtaja and the Swedish coast.
Web links
Individual evidence
- ^ Limits of Oceans and Seas , 3rd edition, 1953, International Hydrographic Organization, accessed November 30, 2017