Chemical furnace
|
Chemical furnace constellation |
|
|---|---|
| Latin name | Fornax |
| Latin genitive | Fornacis |
| Abbreviation | For |
| Right ascension | 01 h 45 m 24 s to 03 h 50 m 21 s |
| declination | −39 ° 30 ′ 46 ″ to −23 ° 45 ′ 23 ″ |
| surface | 397.502 deg² rank 41 |
| Completely visible | 50.5 ° N to 90 ° S |
| Observation time for Central Europe | September - January |
| Number of stars brighter than 3 mag | 0 |
| Brightest star (size) | α Fornacis (3.87) |
| Meteor streams |
no |
|
Neighboring constellations ( clockwise from north ) |
|
| swell | IAU , |
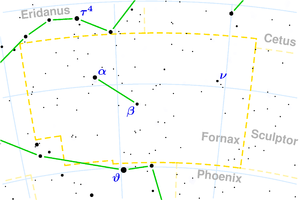
The chemical furnace , in today's technical language Fornax (from Latin ) is a constellation of the southern sky.
description
Fornax is an inconspicuous constellation made up of faint stars . Only one star reaches the 3rd magnitude . The constellation is largely surrounded by the extensive Eridanus .
Fornax can only be seen completely from southern Germany, Austria or Switzerland (there it is low above the horizon in late autumn) and more southern latitudes.
In the constellation is the Fornax galaxy cluster , which contains 58 galaxies . At a distance of about 60 million light years, it is the second closest galaxy cluster after the Virgo galaxy cluster .
The Fornax dwarf galaxy is found in Fornax . However, it does not belong to the Fornax galaxy cluster, but is a member of the Local Group , to which our Milky Way also belongs , with a distance of only 450,000 light years .
history
The constellation was introduced in 1756 under the name le Fourneau ( Fornax Chimiae in 1763 ) by Nicolas Louis de Lacaille . Johann Elert Bode took it over as Apparatus Chemicus in his star atlas Uranographia .
Between 2003 and 2004 the Hubble Space Telescope recorded the Hubble Ultra Deep Field in a relatively star-poor area in Fornax . The images show about 9,500 galaxies , with the most distant ones having a redshift of about 7.
Celestial objects
Stars
| B. | Names or other designations | Size (mag) | Lj | Spectral class |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| α | Dalim, Fornacis | 3.80 | 40 | F7 + G7 |
| β | 4.45 | 200 | G7 III | |
| ν | 4.45 | 370 | B9.5 III | |
| ω | 4.96 | 465 | B9 V | |
| δ | 4.99 | 785 | B5 III | |
| φ | 5.13 | 154 | A2.5V | |
| κ | 5.19 | 74 | G0 V | |
| μ | 5.27 | 315 | A0 V | |
| π | 5.34 | |||
| γ 2 | 5.13 | 515 | A1 V | |
| η 3 | 5.48 | |||
| ρ | 5.52 | |||
| ζ | 5.69 | |||
| χ 2 | 5.71 | |||
| ι 1 | 5.74 | |||
| λ 2 | 5.78 | |||
| ι 2 | 5.13 | 115 | F6 V | |
| ε | 5.85 | 104 | G9 V | |
| λ 1 | 5.91 | |||
| σ | 5.91 | |||
| η 2 | 5.92 | |||
| ψ | 5.93 |
Beta Fornacis is about 200 light years away. It is a yellowish shining star belonging to the spectral class G7.
Double stars
| object | Apparent brightness (mag) | distance |
|---|---|---|
| α | 3.9 / 5.8 | 5.2 " |
| ω | 4.9 / 7.9 | 10.8 " |
Alpha Fornacis , the brightest star in Fornax, is a binary star system 40 light years away. The two components belong to the spectral classes F7 and G7 and can be observed with a small telescope.
NGC objects
| NGC | other | size | Type | Surname |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MCG -06-07-001 | 9.3 | Galaxy | Fornax dwarf galaxy | |
| 1097 | 9.3 | Galaxy | ||
| 1316 | 8.2 | Galaxy | ||
| 1344 | Galaxy | |||
| 1350 | Galaxy | |||
| 1360 | 9.4 | Planetary nebula | ||
| 1365 | 9.3 | Galaxy | ||
| 1374 | Galaxy | |||
| 1381 | Galaxy | |||
| 1380 | Galaxy | |||
| 1387 | Galaxy | |||
| 1398 | Galaxy | |||
| 1399 | 8.8 | Galaxy | ||
| 1404 | Galaxy | |||
| 1425 | Galaxy |
In Fornax there is NGC 1360 , one of the largest planetary nebulae with a diameter of 390 arc seconds . It can already be seen well in prism binoculars . To make the 11 bright central star visible, however, you need a medium-sized telescope.
The Fornax dwarf galaxy has a very low surface brightness and was therefore only discovered on photographic plates by Harlow Shapley in 1938 . Although it is twice the diameter of the full moon in the night sky , it cannot be visually observed with a telescope. It only becomes visible in long-exposure photographs .
14 members of the Fornax galaxy cluster are brighter than 11.5 and therefore clearly visible even in an amateur telescope.
See also
Web links
- Is Fornax moving? from the alpha-Centauri television series (approx. 15 minutes). First broadcast on Dec 21, 2005.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Ludewig Ideler: Investigations into the origin and meaning of star names: A contribution to the history of the starry sky. Berlin 1809. p. 363.