Detroit
| Detroit | |
|---|---|
| Nickname : The Motor City, Motown, Hockeytown , Rock City, The D | |
 Skyline |
|
 seal |
 flag |
| Map of Wayne County and Michigan, Detroit highlighted in red | |
| Basic data | |
| Foundation : | July 24, 1701 |
| State : | United States |
| State : | Michigan |
| County : | Wayne County |
| Coordinates : | 42 ° 20 ′ N , 83 ° 3 ′ W |
| Time zone : | Eastern ( UTC − 5 / −4 ) |
|
Inhabitants : - Metropolitan Area : |
670,031 (as of 2019) 4,317,179 (as of 2018) |
| Population density : | 1,864.3 inhabitants per km 2 |
| Area : | 370.2 km 2 (approx. 143 mi 2 ) of which 359.4 km 2 (approx. 139 mi 2 ) is land |
| Height : | 183 m |
| Postcodes : | 48201-48288 |
| Area code : | +1 313 |
| FIPS : | 26-22000 |
| GNIS ID : | 1617959 |
| Website : | www.detroitmi.gov |
| Mayor : | Mike Duggan ( D ) |
 Satellite image of the Detroit area, Lake Erie below, Lake St. Clair above right |
|
Detroit on the map of the United States |
Detroit [ dɪˈtɹɔɪt ] is a city in the southeast of the US state Michigan . It is located directly on the Canadian border, on the Detroit River between Lake St. Clair and Lake Erie . Detroit is 370.02 km² in size and, according to an estimate by the US Census Bureau, had around 680,000 inhabitants in 2016; making it the largest city in Michigan. In 2010, 82.7% of residents were African American ; this makes Detroit one of the largest black communities in the United States. Detroit is the seat of Wayne County and the economic, political and cultural center of the metropolitan area of Detroit , the third largest metropolitan area in the Great Lakes area after Chicago and Toronto with (2010) around 5.2 million inhabitants.
overview
Originally a French-Canadian foundation, the city developed into an important trading center that was repeatedly contested between Canada and the United States in the 18th century due to its convenient location. Due to the high concentration of the activities of numerous American car pioneers, the city rose to become the leading location for the US automotive industry in the first half of the 20th century. “Detroit” became a metonym for the entirety of the economically and politically very influential automobile companies.
As a result of the economic structural change in the auto industry , a continuous decline and loss of importance set in in the second half of the 20th century, exacerbated by ethnic conflicts, the emigration of wealthy sections of the population, a poorly functioning administration and a poor education system. As a result, the city is still experiencing an enormous concentration of unemployment, poverty and crime. This development found further lows with the bankruptcy of General Motors in June 2009 and the city's financial bankruptcy in July 2013. It is estimated that Detroit amassed $ 18 billion in debt in 2013, while the municipality only earns a good $ 2 billion a year. As a result of emigration, fewer and fewer citizens are paying taxes. 78,000 houses stand empty and rot. The widely visible decay is offset by a wide range of culture and entertainment as well as significant examples of American architecture.
Detroit is home to a number of large national corporations (including General Motors), a Catholic archbishop , three major casinos and several professional league sports teams. There are one state and two Catholic universities , a Catholic seminary and several large car factories. The city is also home to numerous major events, including the Detroit Auto Show , the largest automobile show in the United States. The record label Motown founded here became internationally known.
geography
Position and extent
Detroit is located on the southeastern edge of Michigan and on the right bank of the Detroit River . Together with the St. Clair River and the nearby Lake St. Clair, this forms the outflow from the northern Huron Lake into the Erie Lake further south and also marks the border to the northern neighbor Canada in this area . Because the river at this point flows from the east in a south-westerly direction, Detroit is the only major city in the USA from which the view to Canada goes south.
Opposite, on the other side of the river and thus the border, is the city of Windsor . With 211,000 inhabitants (2011), it is considerably smaller than Detroit and belongs to the Canadian province of Ontario .
The urban area is 370.2 km 2 in size (of which 359.4 km 2 land area) and extends over some 17 kilometers along the river bank and between 10 kilometers on the eastern edge and 23 kilometers on the western edge to the interior. Furthermore, one of the Detroit around 4.6 km long and 3.9 km 2 large Belle Isle , an island in the Detroit River, which lies on the eastern outskirts.
Detroit is located in the northeast of the associated county, Wayne County . In particular, the northern city boundary is identical to the county boundary over its entire length. This extends over 28.5 kilometers precisely in a west-east direction and is marked by the 8-mile road. A little north of the geographic center of the urban area is an enclave of a few square kilometers, the two cities of Hamtramck and Highland Park with a total of around 34,000 inhabitants (as of 2010).
From an economic geographical point of view, Detroit lies in the northwestern part of the Rust Belt and formerly the Manufacturing Belt, the first densely populated industrial area in the USA, whose former centers are today often marked by the decline of heavy industry .
topography
Detroit lies in the middle of the Great Lakes Plain on the eastern edge of a flat ground moraine from the Wisconsin Ice Age . This extends from the west bank of the Huron Lake in the north in a south-westerly direction down to Lake Erie, is 25 to 40 kilometers wide and slopes gently and evenly to the south-east towards the waters with a gradient of significantly less than 1%. Accordingly, the city lies on a flat surface that rises slightly and evenly from the Detroit River to the northeast from 175 to around 206 meters above sea level . Due to the low gradient, the area remained almost without surface drainage and was therefore very boggy for a long time. On the other hand, there were practically no obstacles in the way of settlement activity after drainage.
At the same height as the two city centers of Detroit and Windsor is the Detroit terminal moraine of the former St. Clair glacier tongue , which was broken through by the Detroit River between the two cities . Therefore, the inner cities are a few meters higher on both sides than large parts of the hinterland. This fact determined the exact location of the first settlement at the time.
City structure
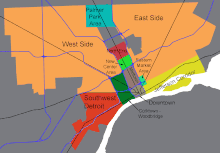
There is no fixed structure of the city in the actual sense. Administrative boundaries such as police and school districts or redevelopment areas exist side by side and have already been changed several times as a result of demographic developments. On the other hand, in addition to the city center (Downtown) directly on the Detroit River, Woodward Avenue plays a role in the public perception , a historically important and, until the 1960s, sometimes very splendid arterial road that runs from the city center in a north-northwest direction and the city extensively divides into a western and eastern part, the West Side and the East Side. Along this street, like a chain, there are several districts with very different profiles, starting with Downtown, Midtown, New Center and North End, which in turn is bounded by Hamtramck and Highland Park, and again north of it the area around Palmer Park. Also noteworthy are the southwestern tip on the Detroit River, southwest Detroit and the corridor along Jefferson Avenue east of downtown. In addition, contiguous residential areas often form informal boundaries in the form of so-called neighborhoods.
Development
The closed development has expanded very far outwards and extends on the American side over a radius of 40 to 60 kilometers around the city center. The vast majority of settlement activity took place in the period after the Second World War . The original practice, on the other hand, of gradually incorporating newly developed building areas on the edge of the settlement , came to an end as early as the mid-1920s, because the new suburbs appeared increasingly self-confident and have permanently prevented their incorporation into Detroit by means of legal maneuvers. Therefore, the cohesive development now extends especially to the north and west, far beyond the urban area of Detroit. As a result, there are only a few residential areas in the city with young buildings and modern living comfort.
The city center is marked by the densely built-up city center on the riverside with its ensemble of high-rise office buildings typical of North America. In addition, with the exception of a corridor along Woodward Avenue, there is predominantly small-scale development on small plots. Due to the decade-long migration, vacant houses and fallow land dominate the scene. Especially in the areas immediately to the west, east and north-east of the city center, the development is very thin over several kilometers; In many streets there are only single houses for long stretches. In contrast, some limited, traditionally affluent neighborhoods have survived the city's decline almost unscathed.
The industrial facilities are relatively evenly distributed across the entire Detroit area. They extend along the main railway lines and often form distinctive corridors that are kilometers long. In addition to Detroit itself, the suburbs Dearborn and River Rouge directly (south) west, Livonia further west, the corridor along Mound Road to the north with the cities of Warren and Sterling Heights as well as the cities of Pontiac and Auburn Hills in the far north-west are important industrial locations . However, the local industry are by the decline especially in the area of Detroit, many older establishments broke or are ruins expire.
Suburbs
Detroit's suburbs are partly residential communities and partly large cities with significant economic activities. Land area and population numbers vary widely and range from around 0.5 to 96 square kilometers and between 150 and 134,000 inhabitants. The majority of the suburbs are spread across Wayne Counties and its two northern neighbors Oakland and Macomb . Together with Detroit, the three counties have a total of 3.86 million inhabitants and thus make up the largest proportion of the population in the Detroit – Warren – Livonia Metropolitan Statistical Area , which together with three other counties has a population of around 4.3 million. The three counties mentioned make up 39.1% of Michigan's population.
Some communities are considered particularly wealthy. These are Dearborn, the area around Grosse Pointe (the northeastern part of Wayne County that does not belong to Detroit and lies on Lake St. Clair), and Rochester Hills and Bloomfield in the northwest just before Pontiac.
climate
Detroit is located in the cool temperate climate zone that spans large parts of the USA and the southern edge of Canada ( effective climate classification Dfa). As is typical for the continents, the seasons are pronounced with hot, humid summers and cold, relatively snowy winters. The annual average temperature is 9.3 degrees Celsius; 188 days are frost-free.
The winter months of December, January and February are the coldest; their monthly lowest temperatures are on average between −4.4 and −7.2 ° C; Severe frosts down to below −15 ° C are not uncommon at this time of year. Often the temperatures feel considerably colder in strong winds due to the wind chill effect. However, during this time of the year, thermal drops can temporarily increase temperatures well over 15 ° C. The lowest temperature to date was measured on January 21, 1984 at −29.4 ° C. On the other hand, the warmest summer months are June, July and August, with average highs of 26.1 to 28.5 ° C. During this time the temperature can temporarily rise to over 30 ° C. The highest temperature was measured on July 24, 1934 at 40.6 ° C.
The precipitation is distributed over the whole year, in the summer as rain and in the winter months as snow. The lowest rainfall is recorded in January and February. The average annual rainfall is a moderate 828.5 mm.
Lake effect snow , which is notorious for the Great Lakes region, does not usually occur in Detroit because the nearest large bodies of water are further east and thus on the leeward side of the main wind direction. Lake Michigan to the west is also far too far away for the snowfalls it caused to play a role in Detroit. However, in summer it can happen that air masses on the back of a low pressure area above Lake St. Clair absorb a lot of moisture, which then rains down over the city with heavy rainfall.
| Detroit, Michigan | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate diagram | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Monthly average temperatures and rainfall for Detroit, Michigan
Source: National Weather Service, US Dept of Commerce , Sun Hours: The International Climate Index
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
history
| Population development | |
|---|---|
| Census year |
Residents |
|
|
|
| 1840 | 9.102 |
| 1850 | 21,019 |
| 1860 | 45,619 |
| 1870 | 79,577 |
| 1880 | 116,340 |
| 1890 | 205,876 |
| 1900 | 285,704 |
| 1910 | 465.766 |
| 1920 | 993.078 |
| 1930 | 1,568,662 |
| 1940 | 1,623,452 |
| 1950 | 1,849,568 |
| 1960 | 1,670,144 |
| 1970 | 1,511,482 |
| 1980 | 1,203,339 |
| 1990 | 1,027,974 |
| 2000 | 951.270 |
| 2010 | 713.777 |
| 2013 | 681.090 |
| 2016 | 677.116 |
| 2017 | 673.104 |
Detroit was founded on July 24, 1701 by the French captain Antoine de la Mothe Cadillac at the outflow of Lake Erie, the Detroit River ( le détroit du Lac Érié ), as Ville d'Etroit ("City on the Strait"). 30 years earlier, Louis Hennepin had stopped by here as part of his expedition on the Le Griffon. In his works (including Description de la Louisiane, nouvellement découverte au Sud'Oüest de la Nouvelle France ) he called the north bank of the Detroit River the ideal settlement area where Detroit later emerged. During the wars with the British for supremacy in North America, the Fort Ponchartrain du Détroit , which was built there and named after the Comte de Pontchartrain, Minister of the Navy under Louis XIV , was an important base of the French armed forces. During the French and Indian War (1754–1763), it was one of the last fortifications to be occupied by the British.
On September 29, 1760, the French garrison surrendered the fort to British troops under Major Robert Rogers without a fight . After that, the name was reduced to Detroit. The French roots are still reflected in the city's official flag to this day. During the Pontiac uprising (1763–1764) of the Indians of the Ohiotals against British colonial rule, Detroit was a focal point of the fighting and was besieged by the Indians in vain. With 2144 inhabitants, Detroit was the largest city west of the Appalachians in 1778 , between Montreal and New Orleans and the third largest city in the province of Quebec , to which the British had defeated with the Quebec Act 1774 - after Quebec and Montreal.
During the American Revolutionary War , control of Detroit, which was increasingly popular with Anglo-American settlers, was a military goal of the US Army. In the Peace of Paris , the city was nominally placed under the rule of the United States, but it remained de facto under the control of the British and their allied Indian peoples. The British recognized the area around Detroit as part of the United States in the Jay Treaty in 1795 , as did the Indians after several military defeats in the Treaty of Greenville , and left the area a year later. In the years that followed, the city began to develop, with the French priest Gabriel Richard playing a crucial role by founding schools and building roads.
In 1805 the city became the capital of the newly reached Michigan Territory , but burned down completely in the same year and was rebuilt on schedule. The incorporation as a city took place on December 13, 1806. In 1812 the city was conquered by the British with the help of the Indian chief Tecumseh in the British-American War , in 1813 US troops recaptured the city, which meant the final expulsion of the Indians from the region . Under Governor Lewis Cass , the city finally received democratically elected institutions again in 1815. In the next few years, the city grew steadily, as it was located at the hub of trading routes in the Great Lakes area, and on the eve of the American Civil War, it had more than 45,000 inhabitants. Because of its location on the Canadian border, the city was an important place on the Underground Railroad , a network of escape routes for slaves from the American southern states. Many residents fought in voluntary regiments for the Union cause during the Civil War, but violent unrest broke out in 1863 when Irish and German Catholic immigrants refused to join the army and subsequently attacked the homes and businesses of African Americans in the city.
In the decades that followed, industrialization began to take off, when companies in the pharmaceutical , tobacco and cast-iron stoves settled in the city. The latter was the most important industry in the city in the 1890s, which is why it became known as the Stove Capital of the World . During this time, magnificent villas and palaces were built, which should show the prosperity of the entrepreneurs who became rich in the Gilded Age . As in other industrial cities in Europe and North America at the time, the industrial boom also led to rapid population growth: In the last 40 years of the 19th century, the population increased sixfold. The booming industry attracted workers, especially immigrants such as Irish , Germans and Poles . Detroit also became a stronghold for the union movement and the progressive movement . The Republican mayor (1889–1897) and later governor of Michigan (1897–1901), Hazen S. Pingree , is considered one of its masterminds. a. for paved streets and reliable street lighting owned by the municipality.
In 1909 the mass production of automobiles began with the Ford Model T in Detroit / Highland Park. Other car makers settled there. Detroit came to be known as Motor City or Motown . With the automotive industry , Detroit experienced a rapid rise and another population explosion: Between 1900 and 1930 the population quintupled, this time due to the influx of African Americans from the south as part of the Great Migration . There were several riots in the city in the 20th century, for example in 1943, when the three-day riot could only be ended by federal troops and 34 people died. The riots in 1967 43 people were killed.
The automotive monostructure also led to continued decline when the models of the US Big Three ( General Motors , Ford and Chrysler ) were no longer in great demand. Since the late 1960s, the city has had to contend with population decline and high crime rates, as the white middle and upper classes migrated to the suburbs ( White Flight ). Many houses are empty and dilapidated, even if the city has been trying to tear down or renovate such houses since the late 1990s. General Motors has relocated numerous plants overseas in recent decades and has lost market share due to a failed corporate strategy: While there were six General Motors plants in the city in 1972, which until 2003 mostly worked in three-shift operation, there was only one left after the financial crisis in 2009. Layoffs mainly affected black workers and black members of the middle class. On June 1, 2009, GM declared itself insolvent.
Detroit has lost over 60% of its population since 1950, when the population peaked. 35% of the urban area is now uninhabited. The city became synonymous with the decline of former industrial cities. Renaissance is the key word associated not only with the Renaissance Center but also with the revitalization of the city center: trying to get young people back to living in Detroit. With the move of the Detroit Tigers to the newly built Comerica Park and the Detroit Lions to Ford Field , sporting events from the surrounding area are brought back to downtown , there are attractive performances in the Fisher Theater . Nevertheless, Detroit has been one of the most dangerous cities in the US for years; for example, it was number one on Forbes' 2009 list of the most dangerous cities in the United States.
In 2001, at the age of 31, Democrat Kwame Kilpatrick was elected as the youngest mayor in the city's history. In November 2005, Kilpatrick was re-elected, despite predictions to the contrary. After a scandal, however, he was sentenced to prison in September 2008 and immediately resigned from his position. On March 15, 2013, Detroit was placed under government administration by Michigan Governor Rick Snyder because of its high debt. He appointed Kevyn Orr, who previously served at Chrysler, as bankruptcy attorney. Detroit is thus the largest city in the United States to date that has been removed from financial control. On June 14, 2013, the city stopped making payments to its creditors. Administrator Kevyn Orr put together a plan to save the city in which the creditors should forego some of their claims. Otherwise Detroit threatens bankruptcy. On July 18, 2013, Detroit filed for bankruptcy . The city's debt is estimated at $ 18.5 billion. Approx. 30% of the residents live in poverty. The crime rate is the highest in the United States. Nearly 80,000 homes in Detroit were vacant at the end of 2013. 40 percent of the street lamps were no longer lit. There were only 27 jobs for every 100 inhabitants.
In September 2014, the city regained control of its finances under the newly elected Mayor Mike Duggan . In the following years, the city made an effort to invest and, like other former industrial cities that have mastered the structural change more successfully, it managed to bring about a new economic boom through culture, tourism and the settlement of start-ups . Detroit has become a tourist attraction because of its rich architectural and industrial heritage, and entrepreneur Dan Gilbert , who bought numerous vacant buildings, managed to attract billions in investments to downtown and the Detroit business district . However, this upswing is very unevenly distributed and observers criticize that gentrification and the building boom in the city center have not brought any improvements for the many poor in the city.
population
Structure according to population groups
| Composition of the Detroit population by ethnic group (2010) |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ethnicity | percent | |||
| African American | 82.7% | |||
| white | 10.6% | |||
| Asians | 1.1% | |||
| Indians | 0.4% | |||
| Mixed race | 2.2% | |||
| Other | 3.0% | |||
|
Furthermore, according to the 2010 census, ethnic groups were 6.8% Hispanics and 93.2% non-Hispanics |
||||
In the last 2010 census , which differentiates by ethnicity , Detroit had 713,777 residents. This makes it by far the largest city in Michigan and ranks 18th in the US .
The vast majority of the population, 590,226 people or 82.7%, were African American . Their share is thus much higher than in Michigan as a whole (14.2%) or the US average (12.6%). Although a far above-average proportion of Afro-American population groups is typical for the old industrial cities in the northeastern United States, Detroit is an extreme case here. No major American city has a higher percentage of blacks in the total population than Detroit. The city also has the fourth largest black community in the United States, behind New York , Chicago and Philadelphia .
The second largest population group are by far the whites . With 75,758 people, they make up 10.6% of the total population. There are also around 2,600 Indians and a good 7,500 Asians as well as around 21,600 members of other ethnic groups and 15,900 mixed race. As Hispanics is 6.8% of the population consider; almost three quarters of them come from Mexico .
Among the white population, families with Irish , German and Polish ancestry have the highest proportion. The English and Italians follow at a great distance . The proportion of people of German origin in particular is significantly below the comparative values in Michigan or the US average, while a comparatively large number of people stated Polish ancestors. In addition, almost 8,500 people are of Arab origin.
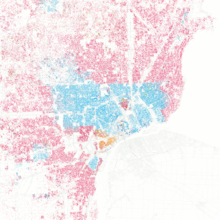
The Detroit metropolitan area is clearly divided between the different ethnic groups. While Detroit is almost exclusively inhabited by blacks and hardly any whites, it is the other way around in most suburbs, including most of the suburbs directly adjacent. The dividing line is so sharp that the city limits are clearly visible on the census maps over almost their entire length. In particular, the northern section along the 8-Mile-Road is seen as a psychological boundary and is used in the region as a winged word for the boundary line between the two subcultures mentioned and their different living conditions.
Detroit is also a stronghold of the Aramaeans / Assyrians (Chaldeans), who emigrated to the USA from their homeland, the Middle East, due to religious persecution. According to a study from 2008, 113,000 Arameans / Assyrians currently live in the Detroit area.
Population development
After Detroit was destroyed several times in the 18th century and lost its position as a trading center and administrative center in the first half of the 19th century, the population development shows a picture typical of industrial cities in the northeastern United States: a sharp increase in population from around 1850 to the height of the Population around 1950, then rapid growth in the suburbs until around 1970, then a decline in the population in the city itself and stagnation in the population in the metropolitan area as a whole.
Due to the initially less favorable conditions for industrial development, the population initially lagged behind other industrial cities in the region, such as Buffalo or especially Chicago. The rise of the automotive industry at the beginning of the 20th century caused the population to rise even faster afterwards. Detroit grew by more than 1.1 million people between 1910 and 1930, three times the size of 1910, overtaking many other industrial cities in the United States. The population peak was finally reached in 1950 with 1.85 million people.
The automobile boom of the post-war years again attracted large crowds to the region. However, most of the newcomers settled in the suburbs, so that the city could no longer benefit from this immigration. Detroit's population remained just over 1.6 million, while the suburbs of the Tri-County region grew from 750,000 to 2.7 million people between 1940 and 1970.
While the number of inhabitants in the region has remained more or less constant since then, it has now declined by over 60% in Detroit compared to 1950. Especially in the years after the uprising of 1967 and in the period after the turn of the millennium, sharp declines of more than 20% were recorded within a decade. At the last census in 2010 showed up for Detroit with a population of 713,777, about 237,000, or almost 25% less than the year 2000th
The following table shows the population development of the Metropolitan Statistical Area Detroit - Warren - Dearborn according to the definition of the US Census Bureau 2015:
| year | Residents¹ |
|---|---|
| 1990 | 4,248,699 |
| 2000 | 4,452,778 |
| 2010 | 4,293,313 |
| 2016 | 4,297,617 |
¹ 1990–2010: census results; 2016: US Census Bureau estimate
crime
According to statistics, Detroit is one of the most dangerous cities in the US. The city has now had extremely high crime rates for more than four decades and has held a top position among American cities for years, especially when it comes to violent crimes . Over the past few years, there has been an average of 350 murders per year. Measured by population, the homicide rate is roughly ten times the US average. Furthermore, with over 5,000 offenses, there are about six times as many robberies as the US average and over 10,000 cases of bodily harm offenses , which corresponds to about 5.5 times the average.
In addition, there are almost 50,000 property crimes , which is also a very high, if not so extreme, figure in comparison. Another phenomenon that has been widespread in Detroit for some time is arson , especially on old, vacant houses. Partly it was insurance fraud , partly blind destructive rage, which for some time became a cultural phenomenon, especially around Halloween as Devil's Night .
Most of the murder victims were young men of African American descent who died from gunfire . According to the police, the use of force is often related to family disputes or, to an even greater extent, drug-related crime . The threshold for violence is very low.
The reasons for the high propensity for violence are the lack of opportunities for social and economic advancement, an underfunded and sluggish judiciary, generally poor schooling and the easy availability of firearms in connection with the lure of illegally earned, quick money. There was also a considerable decline in morals . In addition, fear and apathy had spread among the population , which made the educational work visibly more difficult.
The most effective countermeasure is seen in increased youth work. This includes instruction in non-violent conflict resolution in schools as well as targeted action by the authorities against neglect in the home and truancy . The widespread “culture of secrecy” in Detroit must also be ended. An increase in the number of staff in the police service, on the other hand, is viewed as less effective, although the Detroit police force is considerably underfunded according to a study by the University of Berkeley.
In contrast to the slums all around, downtown Detroit has a crime rate that is slightly below average compared to the US average. If, in addition to the number of inhabitants, certain other social factors such as the number of tourists are taken into account, a study shows that the crime rate is very low even for large American inner cities. Most of the facts are burglary and car theft . The low crime rate in downtown is in complete contrast to the public perception, according to which the bad reputation of the city is visibly carried over to the main business district.
Culture and sights
education
Since the American education system depends heavily on the respective local economy, there are sometimes glaring shortcomings. Due to the severe population decline in the 1950s and 1960s, many schools were closed; Schoolchildren had to travel long distances to get to schools in other cities / towns.
There are a variety of public and private universities, some of which ( University of Detroit Mercy , Lawrence Tech, Eastern Michigan University , Wayne State University ) are among the most prestigious schools in the country.
music
The Motown label, which has had a significant influence on soul music and pop music , is known worldwide . This was done by producer Berry Gordy and Motown's own studio band The Funk Brothers , which can be heard on almost all of the label's albums. Detroit was also important for pre- punk rock: both MC5 and Iggy Pop had their first successes here in the 1960s. In the 1970s, Detroit's importance for American rock music found expression in songs by Ted Nugent ( Motor City Madhouse ) and the group Kiss ( Detroit Rock City ). Alice Cooper , who celebrated some successes with the band of the same name in the 1970s, is also based here.
Detroit's Cobo Hall , one of the largest rock concert halls, was of similar importance to American popular music as Madison Square Garden in New York City . The fact that Detroit continues to play a leading role in the music scene is due to the Detroit techno, which comes from the black neighborhoods of the city . The white rapper Eminem has also become known in hip-hop . The metal band Halloween and The White Stripes also come from Detroit .
In the 1920s (with McKinney's Cotton Pickers by Don Redman and the orchestra by Jean Goldkette , and the Casa Loma Orchestra also had its origins here) until the 1950s, the city was a jazz stronghold from which musicians like Milt Jackson , Yusef Lateef , Ron Carter , Howard McGhee , Donald Byrd , Kenny Burrell , Geri Allen and the Jones brothers ( Elvin Jones , Hank Jones , Thad Jones ) came. The Detroit International Jazz Festival has been held annually since 1980 .
Buildings
Detroit's shoreline features a number of different architectural styles . The postmodern neo-Gothic helmets of the Comerica Tower at Detroit Center (1993) were designed to blend in with the city's Art Deco skyscrapers. Art Deco structures include the Guardian Building and the Penobscot Building in the center, and the Fisher Building and Cadillac Place near Wayne State University . Well-known structures in the city include the largest Fox Theater in the United States, the Opera House, and the Detroit Institute of Arts .
While the center consists of high-rise buildings, the remaining parts of the city largely consist of low buildings and single-family houses. Outside the city center, high-rise residential buildings can be found in the areas from the East Riverfront to Grosse Pointe and Palmer Park , directly west of Woodward. The buildings that were built before the Second World War were built in the former working-class neighborhoods mainly in timber frame and brick construction, in the middle-class residential areas there are larger brick buildings, and ornate residences can be found in districts such as Brush Park, Woodbridge , Indian Village , Palmer Woods and Sherwood Forest. The oldest neighborhoods - such as Corktown , a workers' settlement of former Irish immigrants and Brush Park - are on the arterial road to Woodward and Jefferson , while the 1950s neighborhoods are further west and near 8 Mile Road .
Many of the city's significant structures are on the National Register of Historic Places . The city has one of the largest surviving collections of houses from the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Rosedale Park is the largest listed district in Michigan in terms of the number of contributing properties . There are also a number of important church buildings, such as St. Joseph Catholic Church and Saint Anne de Detroit Catholic Church .
In the city's heyday in the 1920s, many office buildings with elaborate decorations were built in the city center. The Renaissance Center in downtown Detroit is a group of high-rise buildings with a central tower and the four towers of General Motors headquarters. The Detroit People Mover provides an overview of the city center, which has some attractions to offer, for example Greektown and its casinos. The revival of downtown Detroit drew companies like Compuware to the center with newly built American football and baseball sports facilities .

The former Michigan Central Station was built in 1913; For a long time the building was the only port of call for trips to and from Detroit. The station experienced its heyday during the Second World War, when military material, weapons and ammunition were transported by rail and many Detroiters were sent to the front as soldiers from here. Due to the decline in passenger traffic due to competition from cars and aircraft, the station lost its importance from the 1950s, despite the establishment of the national railway company Amtrak in 1971, and was officially closed on January 5, 1988. The Ford company bought the building in mid-2018; they want to renovate the building in a completely contemporary way and accommodate a shopping center, apartments and part of the development department there.
To the east of Detroit lies Grosse Pointe on the shores of Lake St. Clair : One of the richest cities in the USA, in which some of the former “Autobarone” had their estates and the descendants of Henry Ford still live today. In Hamtramck you can experience the life of Polish immigrants in the style of the 1950s until today.
The Michigan Theater is part of a 13-story office building on Bagley and Cass Avenues and is a former movie theater. The Michigan interior, designed in the style of the French Renaissance, opened in August 1926 and had a capacity of 4035 seats. It was designed by the architects Cornelius W. and George L. Rapp and cost five million dollars. The theater was closed in 1976 and converted into a parking garage in 1977.
The historic Parke-Davis Research Laboratory (also known as Building 55-Detroit Research) is located on Joseph Campau Street on the Detroit River . The research laboratory building of today's pharmaceutical company Pfizer was listed on May 11, 1976 by the National Register of Historic Places as a historic monument with the number 76001039. It is also listed on the National Historic Landmark .
Museums and parks
The Detroit Institute of Arts is one of the most important US museums. In addition to the works of classical modernism (with works by Pablo Picasso and Vincent van Gogh, among others ), the frescoes of the Detroit industrial cycle by the Mexican artist Diego Rivera , who described the production processes at Ford based on photographic templates, are particularly worth mentioning. After Detroit's decline in the Great Depression, the frescoes were considered a symbol of economic renewal. The communist artist managed to take both the perspective of capitalist entrepreneurship and the Marxist perspective of the role of work in big industry. In contrast to the paintings by Rivera in New York's Rockefeller Center (1934), which were destroyed because of the communist content, this important cycle has been preserved to this day. The city's emergency services wanted to sell the valuable collection of the Detroit Institute of Art in 2014 to pay off the city's debts, but this was averted. The Christie auction house, commissioned with the appraisal of the collection, found it to be between $ 454 million and $ 867 million.
Other museums deal with the city history of Detroit (Detroit Historical Museum), Afro-American history ( Museum of African American History ) and the development of Motown music (Motown Historical Museum) . There is also a science museum (The new Science Center of Detroit) . NASA's Space Center is located outside of downtown Detroit itself . The laws of nature that are important for space travel are clearly presented through interesting exhibits, in which everyone and children can actively participate.
Between Detroit and the industrial suburb of Dearborn, the Henry Ford Museum is located on a huge site with a collection of automobiles, locomotives, airplanes and machines and Greenfield Village, where Henry Ford had historically important buildings transported from all over the USA, including z. B. the original laboratory of Thomas Edison and the bicycle workshop of the Wright brothers .
The most important parks are Belle Isle, an island in the Detroit River with a casino and a public indoor riding arena, and Palmer Park with two public golf courses, River Rouge Park, Chene Park and Campus Martius Park in downtown Detroit.
"Motor City" and other nicknames
Detroit is also called Motor City because of its importance to the automotive industry . This is also reflected in the further nickname Motown , a suitcase word from motor and town. This has meanwhile been distributed all over the world, primarily through the internationally known record label Motown, which was founded here . Another well-known nickname, Hockeytown , is derived from the world famous Detroit Red Wings ice hockey team from the NHL , but is also used for other cities with strong hockey traditions and famous teams.
Sports
The city's ice hockey team is called the Detroit Red Wings and is one of the most famous and successful ice hockey teams in the world. The team has won the Stanley Cup 11 times , most recently in 2008 . The Red Wings played at the Joe Louis Arena until 2016 . In 2017 they moved to the Little Caesars Arena, which was newly built for $ 628 million downtown .
In the Major League Baseball ( American League , Central Division) playing Detroit Tigers . Their home stadium is the modern Comerica Park . The Detroit Tigers are one of the most successful and high-class teams in Major League Baseball: For example, they were last in the MLB league finals, the World Series, in 2012 . There they had to admit defeat to the San Francisco Giants with a sweep in the best-of-seven series .
Both the ice hockey team and baseball team are owned by Mike Ilitch , whose Little Caesars company sponsors various sports clubs and events.
In basketball, Detroit is represented by the Detroit Pistons . The Pistons reside in the Little Caesars Arena and last won their 3rd NBA Championship in 2004. Recently, however, the results have been average at best.
The city's football team, which resides at Ford Field in downtown Detroit, is called the Detroit Lions . On February 5, 2006, the Super Bowl XL was held in Detroit.
Detroit applied six times without success to host the Summer Olympics.
flag
The city's flag was designed by David E. Heineman in 1907 and officially adopted in 1948. The flag consists of five parts. The lower left quarter contains lilies , representing the French who founded the city in 1701. The upper right quarter contains three lions and represents Britain, which ruled the city between 1760 and 1796. In the upper left quarter there are thirteen white stars on a dark blue background. These stand for the thirteen founding states of the USA. In the lower right quarter there are a total of 13 white and red stripes. These have the same symbolism.
In the center of the circle are two women, one next to a burning city and one next to a flourishing city. The women each stand for destruction and resurrection. The motto is Speramus Meliora and Resurget Cineribus ( We hope for better things and It will rise from the ashes ). In 1805 the city burned down on June 11th.
Economy and Infrastructure
economy

The metropolitan area of Detroit generated a gross domestic product of 252.7 billion US dollars in 2016, making it 13th among the metropolitan areas of the United States. The unemployment rate in the metropolitan area of Detroit was 4.5 percent and was still slightly above the national average of 3.8 percent (as of March 2018). In the city itself, it was 8.7% in March 2018 (in mid-2009 it was 28.5%). In recent years unemployment has fallen and the city has seen some economic recovery. In 2016, economic output grew by 2.1 percent.
As a formerly flourishing industrial city, Detroit is now struggling with vacancies after the crisis in the automotive industry . Despite all efforts to diversify , the automotive industry remains the main branch of industry . In addition, in the vicinity are cotton , rice , corn , vegetables and oats grown. Aerospace companies and oil and gas companies are also increasingly settling in Detroit.
Detroit is the headquarters of General Motors , which together with the other two companies in the Big Three - the Ford Motor Company from the neighboring town of Dearborn and Chrysler , based in nearby Auburn Hills - makes the metropolitan area of Detroit a symbol of the American automotive industry. The German Volkswagen group is also represented in the northern suburb of Auburn Hills. General Motors and Chrysler asked for government assistance in November 2008 to cope with the financial and sales crisis and shrank significantly over the next few years.
The largest automobile exhibition in the USA, the North American International Auto Show ( "NAIAS" for short ), takes place in Detroit every winter .
Mainly because of the sharp fall in property prices and the high number of vacancies, there has been a resettlement of businesses (e.g. bicycle construction) and creative industries since around 2013.
In a ranking of cities according to their quality of life, Detroit ranked 71st among 231 cities worldwide in 2018.
traffic
Street
Detroit is connected to its hinterland by numerous interstate highways. Major highways lead to Cincinnati ( I-75 ), Chicago ( I-94 ), Lansing ( I-96 ), Lake Superior (I-75), Lake Huron and Toronto (both I-94). In addition, cross-connections have been created within the agglomeration, which mostly run along the cardinal points. The motorway network is very dense, especially in the urban area of Detroit itself, and in the inner city area often runs well below ground level, similar to a canal bed. Historic residential areas were partially destroyed for the construction of these streets, an approach that is still controversial today.
With the Ambassador Bridge and the Detroit-Windsor Tunnel there are two toll road crossings to Canada. In that order they are the two most frequented border crossings to Canada. There is also a heavy-duty truck ferry for the transport of dangerous goods , which are not allowed to pass the other two crossings.
In addition, six dead straight, historic main streets radiate out from the city center into the hinterland. Together with a few other squares and cross streets in the downtown area, they form a systematic street network based on an absolutist pattern, which is very rare in the USA.
rail
Similarly, numerous railroad lines from the hinterland and other industrial cities converge in a star shape in Detroit. Once built and operated by numerous railway companies, the routes are now operated (often jointly) by CSX Transportation , Norfolk Southern , Canadian National and Canadian Pacific . Important branch lines within the city lead to the local port facilities and the two car factories. The former Ringbahn of the Detroit Terminal Railroad can no longer be used continuously.
With the Michigan Central Railway Tunnel , opened in 1910, there is also a continuous rail link to Canada for the railroad. The tunnel was built from 1906 to 1910 as an immersed tunnel with a slab track and thus embodies a technical pioneering achievement. It is only used by freight trains.
The once important local and long-distance passenger transport has no longer played a role since the 1960s. In long-distance traffic, Amtrak serves the Pontiac-Detroit-Chicago route with (2017) three train pairs a day and uses a small inconspicuous stop about 4.5 kilometers north of downtown in the New Center area. The original and much larger main train station from 1913, Michigan Central Station around three kilometers west of the city center, has only survived as a ruin that can be seen from afar.
Local transport
Urban public transport is currently almost exclusively carried out using regular buses . Only in the downtown area has there been a fully automatic people mover since 1987 , designed as a 4.7 kilometer long, single-track elevated railway ring. The system fell far short of its expectations and is continuously criticized due to its low capacity utilization and the associated poor cost-benefit ratio.
On May 12, 2017, the QLine, a 5.3-kilometer tram route along Woodward Avenue between downtown and New Center, went into operation. In addition, suburban trains are to run on a 64-kilometer section between Detroit and Ann Arbor from 2022. With these two projects, decades of Detroit as one of the largest metropolitan areas in the USA without (real) local rail transport came to an end.
air traffic
The main airport is the Detroit Metropolitan Wayne County Airport , which opened in 1929 . It is located 28 kilometers southwest of the city center in the area of the city of Romulus . It serves as a hub for Delta Air Lines , has six runways and, with 33.5 million passengers and 380,000 aircraft movements annually, is one of the 20 largest airports in the USA. In addition, there are five other landing sites in the greater Detroit area, most of which are used for general aviation and are of secondary importance. This includes the city's original airport, Coleman A. Young International Airport, located about nine kilometers northeast of downtown on Detroit's corridor.
shipping
The Port of Detroit is Michigan's largest port . Due to its location on the Detroit River, it is connected to the Atlantic Ocean by the Saint Lawrence Seaway . The operator is the Detroit / Wayne County Port Authority (DWCPA); it is the owner of part of the operating facilities and is also responsible as the supervisory authority for the private port facilities in the area. The most important goods handled are raw materials, including above all iron ore, as well as coal, building materials, crude oil and steel. The turnover of goods is 15 to 20 million tons annually. In addition, a passenger terminal was opened in 2011, which is intended to enable both ferry traffic to Canada and visits by cruise ships.
The lower reaches of the River Rouge have been dredged over a length of 4.5 kilometers. This allows cargo ships to go straight to Dearborn to AK Steel's steel mill and Ford's Rouge factory complex.
phone
313 is the phone code for Detroit and a few nearby suburbs. After 1993, the number of numbers became scarce due to explosive new registrations of fax and mobile phones, and the city of Flint , which could previously also be reached under 313, and the region of The Thumb were assigned their own area code, the 810. Through further reallocations, the "313 area" shrank to its present size and thus became an identification feature for the real Detroit resident , whose area code indicates that he lived in Detroit before 1993. In the hip-hop scene in Detroit in particular, 3-1-3 has become a popular saying, made famous, for example, by the film 8 Mile , in which Eminem plays the lead role. This is also satirized in the episode The Tale of the Two Springfields of the television series The Simpsons .
Water, gas and electricity
The municipal water works, the Detroit Water and Sewerage Department (DWSD), supply Detroit and 127 of its suburbs, and thus around four million people, with drinking water. According to the company, this makes it one of the largest water suppliers in the USA. The drinking water is obtained from Lake Huron and the upper reaches of the Detroit River and treated in five plants. At the same time, the DWSD collects and purifies the wastewater from Detroit and from 76 suburbs in a central sewage treatment plant , which is also one of the largest in the USA. In the course of the city's bankruptcy, the company was partially privatized; the networks outside the city limits have since been leased for $ 50 million annually to a joint venture in the suburbs in order to be able to subsidize the drinking water for the poorer sections of the population in Detroit.
The electricity and gas supply in the Detroit area, however, is in the hands of private companies. DTE Electric, a subsidiary of the listed DTE Energy based in Detroit, is responsible for the power supply in a wide area . The gas network in Detroit and most of its southwestern suburbs is also owned by DTE (DTE Gas), while the northern suburbs are connected to Consumers Energy's network.
In addition, numerous pipelines for crude oil, petroleum products and liquefied gas converge in Detroit . An overhead power line crossing spans the Detroit River near the mouth of the River Rouge .
The path to bankruptcy in 2013
Detroit gained global attention when it declared bankruptcy on July 18, 2013. Detroit was the first city of its size to take this step under Chapter 9 of the US Bankruptcy Code. The state of Michigan is one of the 27 states in the USA in which this option is at all possible under state law; even if it has never been used before. The history of the bankruptcy declaration began in December 2011 when the state government ordered an external budget analysis. Nevertheless, a further special situation under state law was required for this step. Because not the mayor himself declared the bankruptcy, but the emergency manager Kevin Orr appointed by the state government of Michigan . The legal basis required for this was only in force for a few months.
On May 13, 2013, after inspecting the city's finances, the Michigan state-appointed emergency manager Kevyn Orr declared that it was "clearly insolvent". In his report, Orr stated that the city's spending from 2008 to 2012 exceeded revenue by an average of $ 100 million annually. He also expressed the conviction " ... only a complete restructuring of the city's finances and operations will allow Detroit to regain its footing and return to a path of prosperity " (... only a complete restructuring of the city's finances and businesses will allow Detroit to regain its ground to gain underfoot and return to a path of prosperity.)
Several factors are named as the causes of the decline: the main one was the decline of the automotive industry, which Detroit increasingly abandoned as a production location from the 1970s. As a result, the city had an unemployment rate of around 18.2% at the time of bankruptcy (US average: around 7.6%) and a third of its residents were classified as “living in poverty”. Only around 53% of homeowners were able to pay property tax in 2011 and the number of run-down, vacant buildings is estimated at almost 80,000. Between 2000 and 2010 alone, 250,000 residents emigrated. The steady decline in population from a total population of approximately 1.9 million in the 1950s to about 713,000 in 2011 has resulted in a massive loss of urban revenue. From 2004 to 2013, revenue shrank by a nominal 27%. City expenses are significantly burdened by pension payments. In May 2013, there were two retirees with pension entitlements for every municipal employee.
The steadily worsening financial situation led to drastic savings measures many years before the bankruptcy declaration. Between 2004 and 2013, the city cut almost half of its workforce. Public services and infrastructure fell into disrepair. For example, in January 2011, for reasons of cost, emergency medical care (EMS) was outsourced from the fire brigade and privatized. On June 26, 2012, another 15 fire engines were disbanded (10 fire engines and four turntable ladders were shut down or sold).
The consequences of de-industrialization were promoted by an unfavorable system of communal finances and communal collective agreements for the city. Furthermore, it is undisputed that political omissions, incompetence and corruption also contributed to the city's decline. In March 2013, former Detroit Mayor Kwame Kilpatrick was convicted of corruption and bribery. Kilpatrick has been found guilty of 24 criminal transactions, fraud and taking bribes in exchange for city contracting.
Various pension funds filed a lawsuit against the city's bankruptcy petition because they feared a serious devaluation of their pension entitlements, which amount to around US $ 9 billion, against the city (initial plans included a debt devaluation in the ratio of US $ 1 to 10 cents).
On November 7, 2014, the bankruptcy judge approved the city's bankruptcy plan. That included bondholders' write-downs of around 80% and a cut in the pension scheme for urban workers. The accounting reduction in liabilities is approximately $ 7 billion. Furthermore, the insolvency plan promises investments in the city and places them under the supervision of the state. The ultimately relatively quick and constructive agreement can largely be explained by the debate about the Detroit Institute of Arts . The liquidator planned to auction works of art in order to increase the bankruptcy estate. To prevent this, a broad alliance (Grand Bargain) was formed from citizens, foundations and companies, which together with the state and federal government collected alternative funds.
politics
The city of Detroit is a city council (City Council) and a mayor (Mayor) out.
The city council consists of nine members who are elected for a four-year term. The city council decides in particular on the city budget and city statutes. The members of the city council receive an annual allowance of $ 73,181 for their work and the chairman of the city council receives $ 76,911.
The Mayor of Detroit heads the city's government. The mayor's salary is $ 176,176 per year.
sons and daughters of the town
Twin cities
Detroit has partnerships with the following cities:
-
 Basra , Iraq
Basra , Iraq
-
 Chongqing , People's Republic of China
Chongqing , People's Republic of China
-
 Dubai , United Arab Emirates
Dubai , United Arab Emirates
-
 Kitwe , Zambia
Kitwe , Zambia
-
 Minsk , Belarus
Minsk , Belarus
-
 Nassau , Bahamas
Nassau , Bahamas
-
 Toyota , Japan
Toyota , Japan
-
 Turin , Italy
Turin , Italy
literature
- Yves Marchand, Romain Meffre: The Ruins of Detroit. Steidl-Verlag, Göttingen 2010, ISBN 978-3-86930-042-9 .
- Katja Kullmann: Furious ruins: How Detroit is reinventing itself. Suhrkamp, Berlin 2012, ISBN 978-3-518-06218-0 .
- Scott Martelle: Detroit: a biography. Chicago Review Press, Chicago 2012.
- Thomas J. Sugrue: The Origins of the Urban Crisis Race and Inequality in Postwar Detroit. Updated reissue of 1996 first edition. Princeton University Press, Princeton 2014, ISBN 978-1-4008-5121-8 .
- Mark Jay: A People's History of Detroit. Duke University Press, Durham 2020, ISBN 978-1-4780-0935-1 .
Web links
- Official website (English)
- Shrinking Cities about the phenomenon of the shrinking city and the attempt to revive it
Individual evidence
- ↑ Frank Herrmann: Resurrection from the ruins . In: Die Rheinpfalz from July 22, 2013.
- ^ A b Parkins, Almon Ernest: The historical geography of Detroit . Michigan Historical Commission, Lansing 1918, p. 151 ff . ( umich.edu ).
- ^ Detroit High Point, Michigan. Peakbagger.com, 2013, accessed July 20, 2013 .
- ↑ Neighborhoods in Detroit in the English language Wikipedia
- ↑ a b National Weather Service, US Dept of Commerce
- ^ A b NWS Detroit / Pontiac - Climate Information. National Weather Service Forecast Office (NWS), accessed July 20, 2013 .
- ↑ http://www.census.gov/popest/cities/tables/SUB-EST2009-01.csv ( Memento from January 2, 2011 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ - ( Memento of the original from September 26, 2013 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ https://www.census.gov/quickfacts/table/PST045215/2622000
- ↑ factfinder.census.gov: Annual Estimates of the Resident Population
- ↑ Udo Sautter : Lexicon of American History. CH Beck, 1997, ISBN 3-406-39294-6 , p. 311 f.
- ^ Solveig Grothe: The wreck city. on: one day January 17th, 2011.
- ↑ Allan Popelard, Paul Vannier: Detroit, Detroit. In: Le Monde diplomatique January 15, 2010.
- ^ Zack O'Malley Greenburg : In Pictures: America's Most Dangerous Cities. In: Forbes.com , April 23, 2009 (English)
- ^ State takes over financial control in Detroit. In: Die Zeit , March 15, 2013
- ↑ Detroit "practically bankrupt" In: n-tv , June 14, 2013.
- ↑ Detroit, the auto metropolis, files for bankruptcy. In: Spiegel Online , July 19, 2013.
- ↑ Detroit files for bankruptcy. In: SRF , July 19, 2013.
- ↑ Chris Christoff, Hasan Dudar: Detroit, the most dangerous city in the United States, tries to get up in: Die Welt , July 20, 2012.
- ↑ Damir Fras: Motor City is dying. In: Berliner Zeitung , January 14, 2014.
- ↑ https://detroit.curbed.com/maps/detroit-construction-development-map
- ↑ https://www.theguardian.com/commentisfree/2017/jul/09/detroit-economic-recovery-poverty-mike-duggan
- ↑ https://www.bridgemi.com/detroit-journalism-cooperative/what-gentrification-much-detroit-getting-worse
- ↑ a b c American FactFinder - Community Facts. US Department of Commerce, US Census Bureau, 2011, accessed July 29, 2013 (United States Census 2010).
- ^ Eight Mile Road. Detroit Historical Society, 2013, accessed July 29, 2013 .
- ↑ Source: United States Census Bureau (census)
- ↑ a b c d Damron, Gina: Detroit's homicide rate nears highest in 2 decades. Detroit Free Press - freep.com, December 28, 2012, accessed August 28, 2013 .
- ↑ a b Crime in the United States by Metropolitan Statistical Area, 2010. US Department of Justice, Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI), 2011, accessed August 28, 2013 .
- ↑ a b United States cities by crime rate
- ↑ a b Damron, Gina: 2012 was Detroit's most violent in nearly 20 years; shootings, bloodshed have 'become the norm'. Detroit Free Press - freep.com, January 4, 2013, accessed August 28, 2013 .
- ↑ Shelton, Steven Malik: Top cop urges vigilance against crime. (No longer available online.) Michigan Chronicle, Jan. 29, 2008, formerly original ; Retrieved August 28, 2013 . ( Page no longer available , search in web archives ) Info: The link was automatically marked as defective. Please check the link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ Chalfin, Aaron and McCrary, Justin: The Effect of Police on Crime: New Evidence from US Cities, 1960-2010. (PDF; 7.8 MB) UC Berkeley, November 11, 2012, accessed August 28, 2013 .
- ↑ Jason C. Booza, Demographer: Reality v. Perceptions: Analysis of 2007 Crime and Safety in Downtown Detroit. (PDF; 720 kB) (No longer available online.) July 23, 2008, archived from the original on January 7, 2013 ; Retrieved August 27, 2013 . Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ^ Robert Sharoff: American City: Detroit Architecture. Wayne State University Press, Detroit (Michigan) 2005, ISBN 0-8143-3270-6 .
- ↑ Ford is converting Detroit's historic train station. June 20, 2018, accessed June 30, 2018 .
- ↑ NRIS
- ↑ National Historic Landmarks Program (Parke-Davis Research Laboratory) ( Memento of the original from June 7, 2008 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was automatically inserted and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ Red Wings Kick off final Joe Louis Season , Crains Detroit , October 17, 2016
- ↑ Peter Gavrilovich, Bill McGraw (Ed.): The Detroit Almanac: 300 Years of Life in the Motor City . Detroit Free Press, 2000, ISBN 0-937247-34-0 , p. 619.
- ↑ Detroit's Official Symbols . Detroit Historical Society. Retrieved May 9, 2011.
- ^ US Department of Commerce, BEA, Bureau of Economic Analysis: Bureau of Economic Analysis. Retrieved July 4, 2018 (American English).
- ↑ detroit unemployment rate - Google search. Retrieved August 22, 2018 (de-US).
- ↑ Detroit-Livonia-Dearborn, MI Economy at a Glance. Retrieved July 4, 2018 .
- ↑ Nicolai Kwasniewski: Resurrection as Bike City. Spiegel online , July 26, 2013.
- ↑ Mercer's 2018 Quality of Living Rankings. Retrieved July 30, 2018 .
- ^ When Detroit paved over paradise: The story of I-375. Detroit Free Press, December 15, 2013, accessed March 13, 2017 .
- ↑ DETROIT, MICHIGAN 511 CASE STUDY - FHWA Office of Operations. United States Department of Transportation - Federal Highway Administration, February 1, 2017, accessed March 13, 2017 .
- ^ Detroit-Windsor Truck Ferry. Detroit-Windsor Truck Ferry, Inc., CMT Canadian Maritime Transport, Ltd., November 6, 2011, accessed March 13, 2017 .
- ↑ National Hazardous Materials Route Registry [Docket No. FMCSA – 2014–0022] . In: Federal Register . tape 80 , no. 82 , April 29, 2015, p. 23862 and 23935 ( dot.gov [PDF; accessed March 13, 2017]). National Hazardous Materials Route Registry [Docket No. FMCSA – 2014–0022] ( Memento of the original dated February 18, 2017 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ cf. Graßnick, Martin (ed.): City building history from antiquity to modern times . Vieweg, Braunschweig 1982, ISBN 978-3-528-08684-8 , pp. 80 .
- ↑ AMTRAK SERVICE IN MICHIGAN (Revised) . (PDF) National Railroad Passenger Corporation, October 31, 2016, accessed March 13, 2017 .
- ↑ James Risen: People Mover in Detroit Seen as Transit Disaster (English) , Los Angeles Times. December 8, 1985. Retrieved March 13, 2017.
- ↑ Ken Brown: The Detroit People Mover Still Serves as "a Rich Folks' Roller Coaster" ( English ) Michigan Capitol Confidential. December 11, 2007. Retrieved March 13, 2017.
- ↑ Michael A. Fletcher: Grand plans by presidents, both Democrats and Republicans, fail in Detroit (English) , The Washington Post. August 8, 2013. Retrieved March 13, 2017.
- ↑ QLINE Streetcar Grand Opening Celebration. M-1 RAIL, accessed March 13, 2017 .
- ^ Leonard N. Fleming: RTA wants Detroit-Ann Arbor commuter rail service (English) , The Detroit News. May 19, 2016. Retrieved March 10, 2017.
- ↑ Facts. Wayne County Airport Authority (WCAA), accessed March 13, 2017 .
- ^ National Plan of Integrated Airport Systems (NPIAS) 2017-2021. (PDF) United States Department of Transportation, Federal Aviation Administration, October 2016, pp. A-44, A-46, and B-30 , accessed March 13, 2017 .
- ^ Welcome to The Detroit / Wayne County Port Authority (DWCPA). Port Detroit, 2015, accessed March 13, 2017 .
- ↑ About The Port of Detroit. Port Detroit, 2015, accessed March 13, 2017 .
- ^ Detroit's New Public Dock Open For Business. CBS Broadcasting, CBSLOCAL, July 18, 2011, accessed March 13, 2017 .
- ↑ DETROIT WATER AND SEWERAGE DEPARTMENT :: facts. (PDF) (No longer available online.) Detroit Water and Sewerage Department, June 10, 2014, archived from the original on October 10, 2015 ; accessed on March 13, 2017 . Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ^ Joe Guillen: Detroit council approves new water authority, Syncora deal. Detroit Free Press, September 19, 2014, accessed March 13, 2017 .
- ^ Lambert, Lisa: Detroit council approves regional water authority deal. Reuters, September 19, 2014, accessed March 13, 2017 .
- ^ Gas Utility Service Areas. (No longer available online.) State of Michigan, Department of Licensing and Regulatory Affairs, Public Service Commission, January 2011, archived from the original March 14, 2017 ; accessed on March 13, 2017 . Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ^ Petroleum Product Pipelines. (No longer available online.) State of Michigan, Department of Licensing and Regulatory Affairs, Public Service Commission, May 2014, archived from the original on June 15, 2016 ; accessed on March 13, 2017 . Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ MICHIGAN OIL PIPE LINE MAP. (PDF) (No longer available online.) State of Michigan, Department of Licensing and Regulatory Affairs, Public Service Commission, archived from the original August 13, 2015 ; accessed on March 13, 2017 . Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ Detroit. The story of a historical bankruptcy ( Memento of the original from May 5, 2016 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. Bertelsmann Foundation website. Retrieved May 5, 2016.
- ^ René Geissler: Detroit. Background of a historical bankruptcy Analysis & Concepts. No. 2/2015.
- ↑ Detroit 'clearly insolvent', says emergency manager. BBC News, May 13, 2013, accessed July 19, 2013 .
- ^ Financial and Operating Plan May 12, 2013. (No longer available online.) May 13, 2013, archived from the original on June 25, 2013 ; accessed on July 19, 2013 (English). Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ a b Detroit becomes largest US city to file for bankruptcy. BBC News, July 18, 2013, accessed July 19, 2013 .
- ^ Detroit in Pictures. BBC News, February 23, 2013, accessed July 19, 2013 .
- ↑ City of Detroit. Financial and Operating Plan. Office of the Emergency Manager. Detroit 2013, pp. 194f.
- ↑ City of Detroit. Financial and Operating Plan. Office of the Emergency Manager. Detroit 2013, p. 219.
- ^ Detroit legal battle over bankruptcy petition. BBC News, July 20, 2013, accessed July 2, 2013 .
- ↑ Rick Cohen, "Detroit's Grand Bargain. Looking back and looking Forward" In: Nonprofit Quarterly. May 2015.
- ↑ - ( Memento of the original from July 28, 2014 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and not yet checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ http://www.freep.com/interactive/article/20130512/NEWS01/130512005/Detroit-city-council-compensation-comparison
- ↑ http://ballotpedia.org/Detroit_employee_salaries