Grief
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Grief | |||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 11 H 14 N 2 | |||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 174.25 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
138-139 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
practically insoluble in water |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Gramin (also Donaxin is called) a naturally occurring in various plant species indole - alkaloids . Gramin could play a role in the self defense of plants because it is toxic to various organisms.
Occurrence and characteristics
Gramin has been found in cereals , cauliflower , silver poplar and glossy grass . On grazing livestock such as B. Sheep , gramin is deleterious, while it is low in toxicity to mice and rats.
use
Gramin is mostly used in organic chemistry as a starting material for tryptophan synthesis.
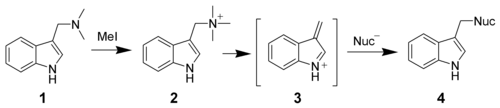
All of Gramin's reactions follow the same general reaction scheme:
- Gramin is treated with a strongly electrophilic substance such as B. methyl iodide added to form a quaternary ammonium salt
- The ammonium salt undergoes Hofmann elimination or Michael addition to give the very active intermediate 3
- which can combine with a wide variety of nucleophilic particles to give the desired product 4
synthesis
Although found in many different plants, gramin is much easier to synthesize directly from indole via the Mannich reaction with dimethylamine and formaldehyde .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c Entry for CAS no. 87-52-5 in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on July 14, 2011 (JavaScript required)
- ↑ a b c d Entry on Gramin in the ChemIDplus database of the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM) .
- ↑ GL Marten, RM Jordan, AW Hovin: Biological significance of reed canarygrass alkaloids and association with palatability variation to grazing in sheep and cattle , Agronomy Journal 68 (1976), pp. 909-914.
literature
- LJ Corcuera: "Biochemical basis of the resistance of the barley to aphids", Phytochemistry 1993 , 33 , 741-747.
- Orechoff; Norkina: Chemical reports 1935 , 68 , 670.
- Pachter et al .: J. Org. Chem. 1959 , 24 , 1285.