Hammer bushes
| Hammer bushes | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

Night jasmine ( Cestrum nocturnum ) |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Cestrum | ||||||||||||
| L. |
The hammer bushes ( cestrum ) are a genus with around 150 to 200 species from the nightshade family . They come from the tropical areas of America. Some species are cultivated as ornamental plants. The botanical name is derived from the Greek késtra = hammer.
Occurrence
Hammer shrubs are found mainly in the tropical areas of America ( Neotropic ), although they are not found in the central Amazon basin . The total distribution area extends from Mexico to Argentina . A center of species diversity (diversity center) is Brazil with nearly 50 species represented; another is located in the Andes region from Venezuela to northern Argentina, where about 100 species are found. The number of species to be found decreases significantly towards the south, of the 18 species to be found in Bolivia, only eleven occur in Argentina and only Cestrum parqui can be found in Chile .

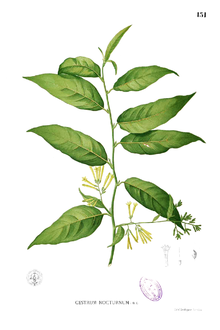

description
Hammer shrubs usually grow as a shrub , only rarely as a tree 4 to 12 m high, occasionally also as a climbing plant , they are usually evergreen. The plants can be hairy or smooth. The alternate, simple leaves are petiolate.
The often multi-flowered, axillary or terminal inflorescences are particularly striking, but the flowers can also stand individually. Many species bloom at night. The flowers are five-fold. The sepals are tubular, inverted cone-shaped, bell-shaped or cup-shaped fused, (rarely 1) 2.5 to 8 (rarely up to 14) mm long and five-toothed or five-fold incised. The petals can be tightly inverted cone-shaped, cylindrical, funnel-shaped or slightly fused urn-shaped, 9 to 56 mm long, appear in many colors and are often enlarged above the petals and constricted below the tips.
The fruits of the hammer bushes are black, red or white, juicy, egg-shaped to almost round berries , have a size of (5) 8 to 13 × (3) 6 to 8 mm and contain (rarely one) two to 18 seeds.
use
Some species and varieties are ornamental plants in tropical to subtropical parks and gardens. In cooler climates, some species and their varieties are used as container plants.
The leaves of Cestrum laurifolium L'Herit. are very poisonous and are therefore used by the natives to poison arrows. From the juice of the black-blue berries of Cestrum tinctorium Jacq. a blue, almost indestructible ink was obtained, which was used in Caracas when issuing official letters (source: Meyers Konversationslexikon).

Systematics
There are around 175 species of cestrum in total , which are divided into three sections within the genus. Molecular biological studies have shown, however, that this subdivision is not monophyletic .
Selection of types according to sections:
- Cestrum section
- Cestrum fragile Francey
- Cestrum fulvescens Fernald
- Cestrum glanduliferum Kerber ex Francey
- Cestrum laxum Benth.
- Cestrum luteovirescens Francey
- Cestrum mortonianum J.L.Gentry
- Night jasmine ( Cestrum nocturnum L. )
- Chilean hammer bush ( Cestrum parqui (Lam.) L'Hérit. )
- Cestrum poasanum Donn.Sm.
- Cestrum thyrsoideum Kunth
- Section Habrothamnus (Endl.) Schltdl.
- Cestrum aurantiacum Lindl.
- Cestrum chiriquianum Francey
- Cestrum dasyanthum Donn.Sm.
- Mexican hammer bush ( Cestrum elegans (Brongn.) Schltdl. )
- Cestrum endlicheri (Schltdl.) Miers
- Cestrum fasciculatum (Schltdl.) Miers : It occurs in the Mexican states of Puebla and Veracruz.
- Cestrum guatemalense Francey
- Cestrum irazuense Kuntze
- Cestrum milciomejiae T. Zanoni
- Cestrum miradorense Francey
- Cestrum oblongifolium Schltdl.
- Cestrum Pacayense Francey
- Cestrum Regelii Planch.
- Cestrum roseum Kunth
- Cestrum sphaerocarpum O.E. Schulz
- Cestrum violaceum Urb.
- Cestrum virgaurea Urb. & Ekman
- Section Pseudocestrum Urb.
- Cestrum acutifolium Alain
- Cestrum inclusum Urb.
- Cestrum tomentosum L.f.
- Cestrum tuerckheimii O.E. Schulz
Other types without assignment to a section:
- Cestrum alternifolium (Jacq.) OESchulz
- Cestrum auriculatum L'Hér.
- Cestrum diurnum L.
- Dama da Noite ( Cestrum laevigatum Schltdl. ), Rarely called "Lady of the Night" in literal translation
- Cestrum laurifolium L'Hér.
- Willow-leaved hammer bush ( Cestrum salicifolium Jacq. )
proof
literature
- Armando T. Hunziker: The Genera of Solanaceae . ARG Gantner Verlag KG, Ruggell, Liechtenstein 2001. ISBN 3-904144-77-4
Individual evidence
- ^ A b Juan Carlos Montero-Castro, Alfonso Delgado-Salinas, Efrain De Luna and Luis E. Eguiarte: Phylogenetic Analysis of Cestrum Section Habrothamnus (Solanaceae) Based on Plastid and Nuclear DNA Sequences . In: Systematic Botany , Volume 31, Number 4, 2006. pp. 843-850.
- ↑ Christine Berg and J. Greilhuber: Cold-sensitive chromosome regions and heterochromatin in Cestrum (Solanaceae): C. strigillatum, C. fasciculatum, and C. elegans . In: Plant Systematics and Evolution , Volume 185, Numbers 1-2, 1993. pp. 133-151. doi : 10.1007 / BF00937725
- ^ Cestrum in the Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN), USDA , ARS , National Genetic Resources Program. National Germplasm Resources Laboratory, Beltsville, Maryland. Retrieved November 28, 2017.

