Hangang
|
Hangang Han-gang |
||
|
View over the Hangang in Seoul |
||
| Data | ||
| location | South Korea , North Korea | |
| River system | Hangang | |
| confluence | of Bukhangang and Namhangang 37 ° 31 ′ 36 " N , 127 ° 18 ′ 38" E |
|
| muzzle | in the Yellow Sea Coordinates: 37 ° 45 ′ 0 ″ N , 126 ° 11 ′ 0 ″ E 37 ° 45 ′ 0 ″ N , 126 ° 11 ′ 0 ″ E |
|
| Mouth height |
0 m
|
|
| length | 497 km total length with source river | |
| Drain at the Hangang Bridge level |
NNQ (December 15, 1998) MQ 2004/2013 HHQ (July 16, 2006) |
16.78 m³ / s 670 m³ / s 22,899.82 m³ / s |
| Right tributaries | Imjin | |
| Big cities | Seoul | |
|
Lower course of the Hangang |
||
| Korean spelling | |
|---|---|
| Korean alphabet : | 한강 |
| Hanja : | 漢江 |
| Revised Romanization : | Hangang |
| McCune-Reischauer : | Han'gang |
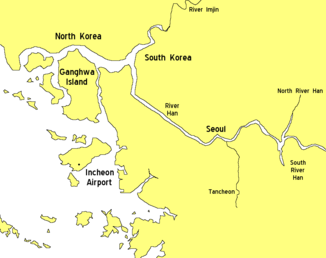
The Hangang (= Han River ) is 497.5 km, the fourth longest river on the Korean Peninsula and the second longest in South Korea .
The northern arm ( Bukhangang ), which is 325.5 km long, has its source in North Korea near the Kŭmgangsan , the southern arm ( Namhangang ) (394.25 km long) in the Geumdaesan Mountains in Gangwon Province , South Korea . After merging at Yangsuri (35 km from Seoul ), the Hangang flows in a W-shape through the South Korean capital, then to the northwest, where it forms the border with North Korea, and flows into the Yellow Sea in front of Ganghwado Island .
An old inscription from the time of King Gwanggaeto (ruled 391-413) names the river Arisu ( 아리수 ; 阿利 水 ).
Web links
- The Han - the lifeline of the Korean Peninsula ( Memento from October 8, 2006 in the Internet Archive ), Korea Today, May 2003
- Andrei Lankov: [The Dawn of Modern Korea] (284) Han River ( Memento from March 10, 2007 in the Internet Archive ) (English)