Indapamide
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Structural formula without stereochemistry | |||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Indapamide | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 16 H 16 ClN 3 O 3 S | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
White, slightly bitter powder |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | |||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | |||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 365.83 g · mol -1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
160-162 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| pK s value |
8.3 |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
soluble in ethanol |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Indapamide ( INN ) is a benzamide derivative that is used as a diuretic . This is a diuretic that is used to regulate high blood pressure and heart rate .
General
The prescribed daily doses ( DDD ) for indapamide were 12.1 million in 2016. That is an increase of 4.2% compared to the previous year.
Type and duration of the effect
The calcium flow in the muscle cells is reduced and a redistribution of the calcium stored in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) takes place. This achieves a blood pressure lowering effect from 1.5 mg, more pronounced at 2.5 mg daily.
The drug also reduces sodium reabsorption in the distal tubule of the kidneys. This leads to a reduction in water recovery, which creates a flushing effect. The flushing effect only occurs from 5 mg. Thus, the drug is one of the diuretics .
Indapamide reduces the risk of arteriosclerosis .
The half-life is 15 to 18 hours.
Distribution in the body
Over 90% of indapamide is chemically converted in the liver . 60 to 70% of the resulting products are passed through the kidneys into the urine . 16 to 20% of the metabolites end up in the stool. 7% of the original substance can be found in the urine.
Side effects
Allergic reactions, rashes, exacerbation of pre-existing lupus erythematosus , nausea, dry mouth , constipation, dizziness, headache, paresthesia , pancreatitis .
Stereochemistry
Indapamide contains a stereocenter and consists of two enantiomers . This is a racemate , i.e. a 1: 1 mixture of ( R ) and ( S ) form:
| Enantiomers of indapamide | |
|---|---|
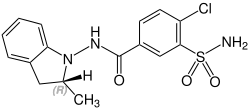 CAS number 77083-52-4 |
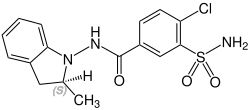 CAS number 77083-53-5 |
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j F. v. Bruchhausen, G. Dannhardt, S. Ebel, AW Frahm, E. Hackenthal, U. Holzgrabe (Eds.): Hager's Handbook of Pharmaceutical Practice: Volume 8: Substances E – O , Springer Verlag, Berlin, Edition 5, 1993, Pp. 534-536, ISBN 978-3-642-63428-4 , doi : 10.1007 / 978-3-642-57994-3 .
- ↑ S. Gayathri, TS Renuga, S. Gunasekaran (Ed.): Qualitative and quantitative analysis on some cardiovascular drugs . In: Asian Journal of Chemistry, Volume 22, No. 8, pp. 5824-5834, 2010.
- ↑ ATM Serajuddin, M. Rosoff, D. Mufson (ed.): Effect of thermal history on the glassy state of indapamide . In: Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology, Vol. 38, No. 3, pp. 219-220, 1986.
- ↑ There is not yet a harmonized classification for this substance . A labeling of indapamide in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), which was retrieved on December 9, 2017, is reproduced from a self-classification by the distributor .
- ↑ a b c d Rote Liste Service GmbH (Ed.): Rote Liste 2017 - drug directory for Germany (including EU approvals and certain medical devices) . Rote Liste Service GmbH, Frankfurt / Main, 2017, edition 57, ISBN 978-3-946057-10-9 , p. 190.
- ↑ U. Schwabe, D. Paffrath, W.-D. Ludwig, J. Klauber (Ed.): Drug Ordinance Report 2017 . Springer Verlag, Germany, 2017, ISBN 978-3-662-54629-1 , p. 479.
- ↑ a b c d F. Block (Ed.): Compendium of neurological pharmacotherapy . Springer Medizin Verlag, Heidelberg, 2008, ISBN 978-3-540-31348-9 , p. 300.