Inuinnaqtun
| Inuinnaqtun (ᐃᓄᐃᓐᓇᖅᑐᓐ) | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Spoken in |
|
|
| speaker | 2,700 (ict) or 1,000 | |
| Linguistic classification |
|
|
| Official status | ||
| Official language in |
|
|
| Language codes | ||
| ISO 639 -1 |
iu (macro language Inuktitut) |
|
| ISO 639 -2 |
iku (macro language Inuktitut) |
|
| ISO 639-3 |
ikt, iku (macro language, Inuktitut) |
|
Inuinnaqtun (sometimes, but not officially, Inniunaqtun ) refers to one or more Inuit dialects in Canada .
The Eskimo languages form a dialect continuum from Alaska in the west to Greenland in the east .
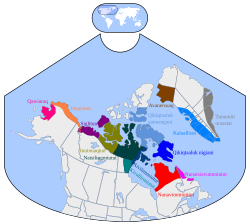
To some extent, under Inuinnaqtun - equivalent to Western Canada Inuktun or with Inuvialuktun understood the entire western region of the Canadian Inuit dialects (as for example in. - (in the broad sense) ISO 639-3 ict). This corresponds to Siglitun, Inuinnaqtun and Natsilingmiutut on the map on the right or approx. 2,700 speakers.
For the most part, however - as also on the map on the right - Inuinnaqtun only refers to the dialect in western Kitikmeot ( Cambridge Bay , Kugluktuk , Umingmaktuk , Bathurst Inlet ) in Nunavut and around Ulukhaktok in the Northwest Territories (also called Kangiryuarmiutun in Ulukhaktok ); together approx. 1,000 speakers.
Inuinnaqtun is recognized as an official language in Nunavut alongside Inuktitut , as well as in the Northwest Territories alongside Inuktitut and Inuvialuktun (in the narrower sense; corresponds to Siglitun on the map).
Unlike Inuktitut, Inuinnaqtun is not written in syllabary , but in Latin letters.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c UNESCO Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger
- ↑ https://www.ethnologue.com/language/ikt
- ↑ so also Inuit Language Protection Act, S.Nu. 2008, c. 17 , p. 1 (2)
- ^ Official Languages of the Northwest Territories
- ↑ Official Languages Act, S.Nu. 2008, c. 10 , p. 3
- ↑ Official Languages Act, RSNWT 1988, c. O-1 , p. 4th