Catalase
| Catalase | ||
|---|---|---|
|
||
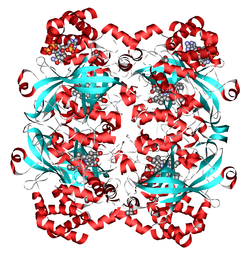
| Ribbon model of human catalase according to PDB 1DGF | ||
| Properties of human protein | ||
| Mass / length primary structure | 526 amino acids | |
| Secondary to quaternary structure | Homotetramer | |
| Cofactor | Hamm | |
| Identifier | ||
| Gene name | CAT | |
| External IDs | ||
| Enzyme classification | ||
| EC, category | 1.11.1.6 , oxidoreductase | |
| Substrate | 2 H 2 O 2 | |
| Products | O 2 + 2 H 2 O | |
| Occurrence | ||
| Homology family | Catalase | |
| Parent taxon | Creature | |
Catalase ( gene name: CAT ) is an enzyme that converts hydrogen peroxide (H 2 O 2 ) into oxygen (O 2 ) and water (H 2 O). Hydrogen peroxide results from the breakdown of hyperoxides by superoxide dismutase . It is a by-product of the breakdown of purines and the oxidation of fatty acids and can damage the genome and proteins . Catalases are therefore found in almost all aerobic living organisms, in humans especially in the peroxisomes of the liver and kidneys , and in the erythrocytes . Mutations in the CAT gene can lead to hereditary catalase deficiency ( akatalasia ), which is common in Japan .
Systematics
Catalases are divided into three classes based on sequence and structure .
- monofunctional heme- containing enzymes
- bifunctional heme-containing catalase peroxidases
- manganese-containing enzymes (without heme group)
The human catalase ( PDB 1DGF ) consists of four identical subunits of 60 kDa each . Each of these contains a heme group and a NADPH binding site.
Catalyzed reaction
The reaction takes place in two steps. In the first step, hydrogen peroxide is reduced and the enzyme is oxidized , creating the product water.
In the second step, both hydrogen peroxide and the enzyme are reduced and oxygen is oxidized and thus released as a product in addition to another water molecule.
The sum equation is:
Both the turnover number and the catalytic efficiency of the enzyme are among the highest values ever found for enzymes ( table ).
At low hydrogen peroxide concentrations, the oxidized catalase can oxidize methanol and ethanol via the aldehyde to form acid .
Use in the laboratory
In microbiology, the catalase test is used to differentiate between bacteria. The differentiation of catalase-positive staphylococci from catalase-negative streptococci is of particular clinical importance. A drop of catalase reagent (3 percent hydrogen peroxide solution) is placed on a microscope slide and a loop of bacterial material is briefly held in it. Positive reaction: direct bubbling, blistering; Negative reaction: no or delayed effervescence. Alternatively, diluted hydrogen peroxide can be dripped directly onto a bacterial colony on an agar plate.
Most aerobic and facultative anaerobic bacteria as well as fungi have the enzyme catalase, which is able to break down the H 2 O 2 , which is toxic to the cells .
Hydrogen peroxide is used experimentally in biology to induce programmed cell death in isolated eukaryotic cells.
use
For neutralizing hydrogen peroxide in 2-component contact lens cleaners.
Individual evidence
- ↑ catalase. In: Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man . (English).
- ↑ P. Chelikani et al., CMLS, Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences . 61 (2004), pp. 192-208; doi : 10.1007 / s00018-003-3206-5 (English)
- ↑ CD Putnam et al., Journal of Molecular Biology . 296 (2000), pp. 295-309; doi : 10.1006 / jmbi.1999.3458 (English)
- ↑ Information on the type or individual evidence is missing.
- ↑ Oliver Auferkamp: Investigation of the reaction mechanism of beef liver catalase . Duisburg / Essen 2007, p. 18 , urn : nbn: de: hbz: 465-20080305-090734-6 (dissertation, University of Duisburg-Essen).
Web links
- Jennifer McDowall / Interpro: Protein Of The Month: Catalase. (engl.)


