Lindane
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
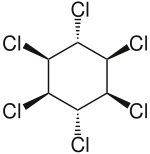
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Lindane | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 6 H 6 Cl 6 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless and odorless solid |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 290.83 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.85 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
112.9 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
323 ° C (decomposition) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
approx. 0.04 Pa (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| MAK |
DFG / Switzerland: 0.1 mg m −3 (measured as inhalable dust ) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Lindane or γ-hexachlorocyclohexane is a halogenated hydrocarbon that is mainly used as an insecticide . In 2009 it was included in Appendix A of the Stockholm Convention .
history
Lindane was first made by Michael Faraday in 1825 . It is named after the Dutch chemist Teunis van der Linden (1884–1965), who in 1912 isolated and described γ-hexachlorocyclohexane for the first time. The insecticidal effect of hexachlorocyclohexane was discovered in 1935, apparently at the same time by the British Imperial Chemical Industries and by the French chemist André Dupire, and Marc Raucourt from the Agricultural Research Center in Versailles is also mentioned as a co-discoverer. Lindane has been used as an insecticide since 1942. From 1946 onwards, a mixture of hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH) isomers was used in Switzerland . It soon turned out that the application of HCH gave beets , potatoes and cabbage a musty taste that made them inedible. Since the impairment of taste did not originate from γ-HCH but from other HCH isomers , processes were developed to isolate pure lindane. In 1950, the production of lindane started in Switzerland. In 1952, the federal research institutes responsible at the time withdrew the approvals for pesticides based on HCH. After a peak around 1969, lindane production declined worldwide. In Germany, since 1980, lindane may only be used in the form of isomerically pure gamma-hexachlorocyclohexane as a food and contact poison. The alpha and beta isomers (CAS numbers: 319-84-6, 319-85-7) that were brought out earlier were found to be more toxic and even more difficult to break down than the equally problematic gamma structure. Lindane has been manufactured in the FRG since 1984 and in the former GDR since 1989, but is still used abroad. No plant protection products containing this active ingredient are permitted in the EU or Switzerland .
synthesis
Hexachlorocyclohexane is produced by the additive photochlorination of benzene . An excess of chlorine is dissolved in benzene and irradiated with high-energy UV light. The reaction product is a mixture of different isomers , of which only gamma-hexachlorocyclohexane has insecticidal properties. The proportion of this isomer is only 15%. For isolation, the isomer mixture is extracted with methanol , whereupon γ-hexachlorocyclohexane in particular goes into solution. A purity of 99.5% is finally achieved through several crystallization processes. The undesired isomers have been converted to trichlorobenzene in a pyrolytic process since the early 1970s .
Responsiveness
When exposed to heat, lindane decomposes to form a toxic, corrosive vapor mixture of hydrogen chloride and phosgene . When it comes into contact with metal powder ( aluminum , iron , zinc ), lindane decomposes with the formation of trichlorobenzene.
use
Lindane was previously used as an insecticide in agriculture and forestry, for example to control white grubs and pests on rape and cabbage. Wood preservatives were another important field of application , for example lindane and PCP were contained in the wood preservatives Xylamon BV and Xyladecor. In addition, it is used in medicine in about one percent dilution as an external medicine against skin parasites , primarily for scabies , pubic lice and pediculoses . According to Regulation (EC) No. 850/2004 , lindane was only allowed to be used as an insecticide in the European Union until the end of 2007.
Hazard potential
The WHO International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) classified lindane in 2015 as " carcinogenic in humans" (Group 1).
Lindane tends to be strongly adsorbed, e.g. B. on algae, and is toxic to aquatic organisms . Since it is only slowly broken down and is relatively highly lipophilic , it accumulates in the human food chain , especially via fish . Lindane must therefore under no circumstances enter the environment in an unbound form. Together with other insecticides based on chlorinated hydrocarbons, lindane is also discussed as a contributing factor in Parkinson's disease .
Lindane is also suspected of causing serious illnesses if the normal values are exceeded: changes in the internal organs, blood formation, multiple sclerosis, nerve damage. Not only farmers, craftsmen and chemical workers are affected, but also house residents who are exposed to lindane, which is used as a wood preservative, through the air they breathe. According to a judgment of the Nuremberg Higher Regional Court, lindane poses a health hazard that cannot be neglected if the lindane concentration in the blood exceeds 0.08-0.10 pg / l.
Contaminated sites
It is estimated that the production of lindane has generated between four and seven million tons of waste worldwide over sixty years. This consists of around 80% of α-HCH and a smaller proportion of β-HCH. Some of this waste is stored in open landfills.
In Barsbüttel , Schleswig-Holstein , a former landfill was contaminated. In the former GDR, large parts of the Mulde and Elbe meadows in the Bitterfeld / Dessau area are heavily contaminated with lindane residues.
In the border area in Basel , Alsace ( Haut-Rhin ) and Weil / Loerrach (known Dreyeckland ) was an unknown amount of 100,000 tons of lindane production residues of the firm Ugine-Kuhlmann ( Huningue ) among others in dust form as concrete - aggregate "disposed of". Because of the unpleasant smell, the affected population did not accept it as a road surface . B. given to local agriculture for paving dirt roads; Samples have an HCH content of up to 75%. The HCH can now be detected locally in groundwater and surface water ; Despite the 40-year time spent outdoors, it can still be smelled.
Today, woods treated with lindane are a serious building pollutant in many buildings , which often requires extensive renovation.
Analytical evidence
The chemical-analytical detection in environmental samples, food and animal feed is carried out after suitable sample preparation to separate the matrix and gas chromatographic separation of minor components by high-resolution mass spectrometry techniques such as flight mass spectrometry (Time-Of-Flight mass spectrometry).
Wood preservative process
Due to the toxicity, especially when inhaling wood preservatives (including Xylamon BV, Xyladecor) in connection with pentachlorophenol , serious illnesses occurred in humans. This was dealt with in the Frankfurt wood preservative trial from 1991 to 1993, the largest environmental criminal trial in the Federal Republic. Erich Schöndorf was the responsible public prosecutor; Wolfgang Huber works as an expert. In his report, he explains the relationship between the biocidal ingredients of various wood preservatives and the resulting immune disorders .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g Entry on lindane in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 1, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c Entry on lindane. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on June 20, 2014.
- ↑ Entry on γ-HCH or γ-BHC in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on February 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ Swiss Accident Insurance Fund (Suva): Limit values - current MAK and BAT values (search for 58-89-9 or lindane ), accessed on November 2, 2015.
- ↑ a b CliniTox poisonous substance: Chlorinated cyclic hydrocarbons - ruminants. Retrieved June 14, 2019 .
- ↑ Press Release - COP4 - Geneva, 8 May 2009: Governments unite to step-up reduction on global DDT reliance and add nine new chemicals under international treaty , 2009.
- ↑ a b c Lukas Straumann: Useful pests . Chronos Verlag, Zurich, 2005, pp. 272-277, ISBN 3-0340-0695-0 .
- ↑ General Directorate Health and Food Safety of the European Commission: Entry on Lindane in the EU pesticide database; Entry in the national registers of plant protection products in Switzerland , Austria and Germany ; accessed on March 26, 2016.
- ↑ DER SPIEGEL: Bathing in Xylamon , 22/1993.
- ↑ IARC Monographs evaluate DDT, lindane, and 2,4-D , June 23, 2015.
- ↑ A. Trautmann, B. Streit: Sorption of lindane (gamma-hexachlorocyclohexane) on Nitzschia actinastroides (LEMM.) V. GOOR (Diatomeae) under different growing conditions . Arch. Hydrobiol./ Suppl. 55: 349-372 (1979).
- ↑ Bruno Streit: Uptake, accumulation and release of organic pesticides by benthic invertebrates. 3. Distribution of 14 C-atrazine and 14 C-lindane in an experimental 3-step food chain microcosm . Arch. Hydrobiol./ Suppl. 55: 374-400 (1979).
- ↑ Parkinson's disease of a farmer due to pesticides recognized as an occupational disease ( Memento from June 7, 2012 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ John Vijgen, PC Abhilash, Yi Fan Li, Rup Lal, Martin Forter, Joao Torres, Nandita Singh, Mohammad Yunus, Chongguo Tian, Andreas Schäffer, Roland Weber: Hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH) as new Stockholm Convention POPs — a global perspective on the management of Lindane and its waste isomers. In: Environmental Science and Pollution Research . 18, 2011, pp. 152-162, doi : 10.1007 / s11356-010-0417-9 .
- ↑ Badische Zeitung , Annette Mahro, badische-zeitung.de: chemical waste in Alsace makes for discomfort in the triangle , February 9th, 2015.
- ↑ Eric J. Reiner, Adrienne R. Boden, Tony Chen, Karen A. MacPherson and Alina M. Muscalu: Advances in the Analysis of Persistent Halogenated Organic Compounds . In: LC GC Europe . 23 (2010) 60-70.
- ↑ SWR-concerns: The wood preservative victims - legally poisoned, then forgotten .
- ^ Coalition against BAYER Dangers .
- ↑ Long-lasting poison in wood preservatives , article in the Lausitzer Rundschau
- ^ The judgment in the Frankfurt wood preservative trial