Pharyngeal cancer
Throat cancer , also called pharyngeal carcinoma , is a malignant tumor of the throat . The throat tumors belong to the group of head and neck tumors . There are very different variants of throat cancer.
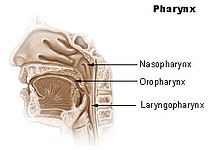
Anatomically, the human throat is divided into three areas, which in turn are assigned to different types of cancer. Most throat tumors are derived from the lining of the throat. Cancer of the nasopharynx ( nasopharynx or epipharynx ) is known as nasopharyngeal carcinoma or epipharyngeal carcinoma . A malignant disease in the oropharynx is called oropharyngeal carcinoma and in the case of tumors in the lower pharynx (Greek hypo = "under") it is called hypopharyngeal carcinoma .
Typical of all throat tumors is the early ingrowth into neighboring tissue and metastasis on the lymphatic pathway into the cervical lymph nodes .
etiology
The frequency of the different throat tumors varies greatly. What can be observed in common is that they tend to occur in older men. However, in the last few years there has been a significant increase in the number of illnesses among women, which is generally explained by the changed smoking and drinking habits.
Epidemiology
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma
0.5 new cases per 100,000 inhabitants per year, with men mostly falling ill from the age of 60. Asians are more often affected than Western Europeans. The EBV antigen is often found .
Oropharyngeal cancer
0.5 to 2 new cases per 100,000 inhabitants per year. Men get sick three to four times more often than women - preferably in their sixth and seventh decades of life.
Hypopharyngeal carcinoma
Hypopharyngeal carcinoma is the most common type of cancer of the throat, with 3.5 new cases per 100,000 inhabitants per year. Here, too, men become significantly more likely than women.