Propiolactone
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
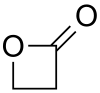
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Propiolactone | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 3 H 4 O 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless liquid with a pungent odor |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 72.06 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.15 g cm −3 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
−33 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
155 ° C (decomposition) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
soluble in water, ethanol, acetone and chloroform |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.4105 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| MAK |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermodynamic properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ΔH f 0 |
−329.9 kJ / mol |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Propiolactone (according to IUPAC oxetan-2-one ) is an organic chemical compound and belongs to the group of β- lactones , intramolecular , cyclic esters .
Extraction and presentation
Propiolactone is produced industrially by reacting formaldehyde with ketene in the presence of aluminum chloride , zinc chloride or boron trifluoride as a catalyst .
The selectivity to propiolactone is 90%. The reaction can be carried out in a solvent or in the gas phase .
In 2010, the synthesis of propiolactone by reacting ethylene oxide with carbon monoxide in the presence of a complex-stabilized carbonyl cobaltate in a higher-boiling dipolar aprotic solvent with conversion and selectivity of up to 99% was described.
properties
Physical Properties
Propiolactone is readily soluble in water and also dissolves in ethanol . At room temperature, propiolactone is a flammable, colorless liquid with a slightly sweet odor. The substance irritates eyes and skin and is considered to be carcinogenic. Propiolactone has a disinfecting effect.
Chemical properties
The highly reactive compound is stable for a few hours when dissolved in water; Only when strongly diluted or left to stand for several hours does the lactone hydrolyze to β-hydroxypropionic acid :
- Propiolactone hydrolyzes to β-hydroxypropionic acid
The compound can react analogously with amines , thiols and other nucleophiles with ring opening, in which case the corresponding amides, thiol carboxylic acids or other carboxylic acid derivatives of 3-hydroxypropionic acid are formed.
Propiolactone reacts quantitatively at 140–180 ° C and 25–250 bar with orthophosphoric acid and copper powder as a catalyst to form acrylic acid and, in the presence of an alcohol, the corresponding acrylic acid esters .
use
Propiolactone is among other things to virus inactivation and sterilization of vaccines used. 0.2 to 0.4% aqueous solutions are virucidal over a wide pH range . Since the substance disintegrates in an aqueous medium within a few hours, no residue of the toxic lactone remains.
literature
- W. Stephan: Inactivation of hepatitis viruses and HIV in plasma and plasma derivatives by treatment with beta-propiolactone / UV irradiation. In: Current studies in hematology and blood transfusion. Number 56, 1989, pp. 122-127, PMID 2642784 (review).
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j Entry on propiolactone in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on July 2, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Hans-Dieter Jakubke, Ruth Karcher (coordinators): Lexicon of Chemistry in three volumes, Spektrum Verlag, Heidelberg, Volume 3, 1999, ISBN 3-8274-0381-2 , p. 105.
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Physical Constants of Organic Compounds, pp. 3-408.
- ↑ Entry on Propiolactone in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on August 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ Schweizerische Unfallversicherungsanstalt (Suva): Limits - Current MAK and BAT values (search for 57-57-8 or propiolactone ), accessed on November 2, 2015.
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Standard Thermodynamic Properties of Chemical Substances, pp. 5-23.
- ↑ a b c Hans-Jürgen Arpe: Industrial organic chemistry - important preliminary and intermediate products . 6th edition. WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim 2007, ISBN 978-3-527-31540-6 , p. 322 .
- ↑ Patent application WO 2010/118128: Process for beta-lactone production. Scott D. Allen et al., Novomer Inc., published 14 October 2010.
- ↑ a b F. v. Rheinbaben, MH Wolff: Manual of virus-effective disinfection. Springer, 2002, ISBN 978-3-540-67532-7 .
- ↑ HP Latscha, U. Kazmaier, HA Klein: Organische Chemie: Chemie-Basiswissen II , 6th Edition, Springer, 2008, ISBN 978-3-540-77106-7 , p. 281.



