Resonance absorption
Resonance absorption , including resonant absorption , refers to the acquisition of the vibration energy of a signal source by a with its natural frequency oscillating resonator where the vibration energy usually in heat is converted. The less the natural frequency of the resonator deviates from the frequency of the transmitter, the greater the energy transmitted (and thus taken from the original signal) .
In gases

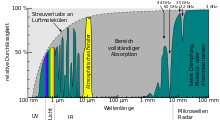
Electromagnetic waves are more and more attenuated in the atmosphere with increasing frequency. Free-flying molecules absorb particularly strongly at certain frequencies. In particular, water vapor in the atmosphere is responsible for the fact that frequencies in the K-band are hardly used for signal transmission in rainy areas. The absorption lines of oxygen and water are at 22.235 GHz (H 2 O), 60 GHz (O 2 ), 118.75 GHz (O 2 ), 183.31 GHz (H 2 O), 325.153 GHz (H 2 O).
If light, which contains all spectral colors, is sent through a cloud of sodium vapor, the two yellow sodium D spectral lines of sodium are missing in the light shining through . One speaks here of the inversion of the sodium D lines. Something similar can be observed on the way from the sun to the earth: Here you can analyze which gases occur in the space ( Fraunhofer lines ). In the vicinity of such resonance points, abnormal dispersion occurs.
In nuclear physics
In the field of nuclear physics , too , wave or particle radiation is absorbed by microphysical systems as a result of resonance phenomena. This mainly happens at frequencies that they can also emit. The "recoil-free resonance absorption" is used, for example, in Mössbauer spectroscopy .
In astrophysics
In astrophysics, the Lyman break technique is used to search for red-shifted absorption lines of the shortest-wave hydrogen line . The “ Lyman Alpha Forest ” that is often observed during this process facilitates the search for highly redshifted galaxies .
With mechanical vibrations
The aim is to convert kinetic energy with specific, precisely defined frequencies into thermal energy , as with vibration absorbers in high-rise buildings. If the frequency of the unwanted movement is not precisely defined or occur at many different frequencies, without friction -prone vibration used, which are not as effective.
The roll tank reduces the rolling of ships when the waves hit the side.
In room acoustics , Helmholtz resonators and membrane absorbers can be specifically used to absorb narrow-band, low-frequency room modes .
High-voltage lines are excited by the wind to vibrate, which can lead to short circuits or breaks. For this reason, Stockbridge vibration absorbers are installed, especially in the case of long spans , with a fixed resonance frequency .
In chemistry
The electrons in chlorophyll molecules of plants can only resonantly absorb light in the wavelength ranges around 450 nm and 650 nm. This is why they emit green light around 550 nm, because the electrons can only perform low-loss, forced oscillations at these wavelengths.
In electrical engineering
A suction circuit absorbs energy in the range of the resonance frequency, the majority of which is converted into heat in the loss resistance of the coil. This is often used in communications and measurement technology as a selective short circuit for undesired signals ( notch filter ). Frequency mixtures can be analyzed with an absorption frequency meter and resonance points of oscillating circuits and antennas can be determined with a dipmeter .
With harmonic filters unwanted harmonics in the current or voltage of electric power supply systems can be suppressed by selective absorption. Harmonics arise u. a. in systems for high-voltage direct current transmission , in thyristor controllers and in frequency converters .
In an atomic clock , resonance ensures that the frequency of a quartz oscillator exactly matches the energy differences in the atomic shell of certain atoms. With RFIDs and Indusi , energy and data are transmitted through resonance absorption over distances of up to a few meters. To secure goods in department stores, resonance methods are used, which can be "defused" by changing the resonance frequency. Sensitive high-frequency receivers always receive their signals from tuned dipole antennas because they absorb a lot of energy from the electromagnetic field due to resonance absorption. With frequency deviations of a few percent, the signal strength drops considerably. For this reason, the receiving antennas for the extremely weak NMR signals in magnetic resonance tomographs are tuned to a narrow frequency band in the range of the expected Larmor frequency. This suppresses the detection of interfering signals and noise from other frequency ranges.
In a bandpass filter , a particularly large amount of energy is transmitted between the resonant circuits when the resonance frequencies match. The more different the resonance frequencies of the two oscillating circuits, the lower the energy transfer. With the Tesla transformer , this resonance effect generates high voltage .
The cyclotron resonance of free electrons is the basis of the function of the gyrotron and magnetron . Both are powerful microwave generators.