Rubidium chloride
| Crystal structure | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| __ Rb + __ Cl - | |||||||||||||||||||
| Crystal system |
cubic |
||||||||||||||||||
| Space group |
Fm 3 m (No. 225) |
||||||||||||||||||
| Coordination numbers |
Rb [6], Cl [6] |
||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Rubidium chloride | ||||||||||||||||||
| Ratio formula | RbCl | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless and odorless solid |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 120.92 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
2.76 g cm −3 |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
715 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
1390 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
good in water (910 g l −1 at 20 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.493 |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | |||||||||||||||||||
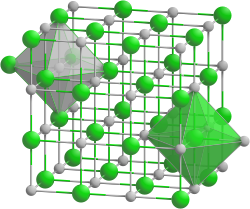
Rubidium chloride is a white, crystalline compound made up of the elements rubidium and chlorine with the formula RbCl. It is also commercially available as a fine powder. Rubidium chloride crystallizes in the cubic sodium chloride structure type .
Extraction and presentation
Rubidium chloride can be obtained by neutralizing aqueous rubidium hydroxide solution with hydrochloric acid :
properties
|
Solubility of RbCl in various alcohols (given in g / l at 25 ° C) |
|
| Methanol | 14.1 |
| Ethanol | 0.78 |
| n-propanol | 0.15 |
| Amyl alcohol | 0.025 |
Rubidium chloride is hygroscopic . The melting point is 718 ° C. The water solubility increases with increasing temperature. The refractive index of the crystals is n D = 1.4936, the lattice parameter a = 658.1 pm, there are four formula units in the unit cell .
The solubility in acetone is 0.0021 g / kg at 18 ° C and 0.0024 g / kg at 37 ° C. The solubility in various alcohols is given in the table.
The standard enthalpy of formation of rubidium chloride is Δ f H 0 298 = −430.86 kJ mol −1 , the standard free enthalpy of formation ΔG 0 298 = −405.3 kJ mol −1 .
Rubidium chloride forms well-crystallizing double salts with various metal chlorides .
use
Rubidium halides such as rubidium chloride, rubidium bromide and rubidium iodide are used therapeutically as pain relievers and sedatives as well as antidepressants . 82 Rb rubidium chloride is used as a tracer for myocardial scintigraphy .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h data sheet rubidium chloride (PDF) from Merck , accessed on January 19, 2011.
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Index of Refraction of Inorganic Crystals, pp. 10-247.
- ^ A b R. Abegg, F. Auerbach, I. Koppel: "Handbuch der inorganic Chemie", Verlag S. Hirzel, 1908, 2nd volume, 1st part, p. 426ff. Full text
- ↑ a b Aterton Seidell: "Solubilities Of Organic Compounds Vol - I", S. 1429. Full text
- ^ Jean D'Ans, Ellen Lax: Pocket book for chemists and physicists. 3. Elements, inorganic compounds and materials, minerals, Volume 3. 4. Edition, Springer, 1997, ISBN 978-3-5406-0035-0 , p. 686 ( limited preview in the Google book search).
- ^ A b R. E. Dickerson, HB Gray, H.-W. Sighting, MY Darensbourg: "Principles of Chemistry", Verlag Walter de Gruyter 1988, ISBN 9783110099690 , p. 976. ( limited preview in Google book search)
- ^ R. Godeffroy: "Some new salts and reactions of cesium and rubidium" in reports of the German chemical society 1875 , 8 (1), pp. 9-11. doi : 10.1002 / cber.18750080104 full text
- ^ H. Erdmann: Textbook of inorganic chemistry , p. 300, 1900, Verlag F. Vieweg and son
- ↑ Manfred Georg Krukemeyer, Wolfgang Wagner: Radiation Medicine: A Guide for the Practitioner. Walter de Gruyter, 2004, ISBN 3-11-018090-1 , p. 133; limited preview in Google Book search.

