Sanaga
| Sanaga | ||
|
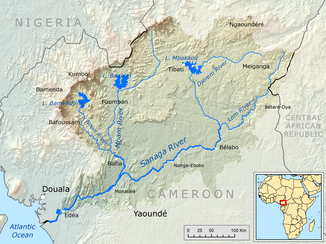
Catchment area of the Sanaga |
||
| Data | ||
| location |
|
|
| River system | Sanaga | |
| origin | Confluence of Djérem and Lom 5 ° 19 ′ 26 ″ N , 13 ° 23 ′ 52 ″ E |
|
| Source height | 628 m | |
| muzzle | in the Bay of Bonny ( Gulf of Guinea ) Coordinates: 3 ° 34 ′ N , 9 ° 39 ′ E 3 ° 34 ′ N , 9 ° 39 ′ E |
|
| Mouth height | 0 m | |
| Height difference | 628 m | |
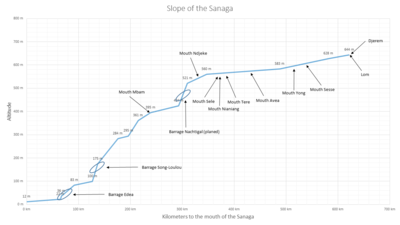
| Bottom slope | 1.1 ‰ | |
| length | 582 km | |
| Catchment area | 132,990 km² | |
| Discharge at the Edea gauge (1338050) A Eo : 131,520 km² Location: 67 km above the mouth |
NNQ (min. Month Ø) MNQ 1943–1980 MQ 1943–1980 Mq 1943–1980 MHQ 1943–1980 HHQ (max. Month Ø) |
234 m³ / s 517 m³ / s 1985 m³ / s 15.1 l / (s km²) 5431 m³ / s 6950 m³ / s |
| Left tributaries | Long , Tete , Sele , Mfam , Ngoba | |
| Right tributaries | Mbam , Mbuku , Ligene , Djam , Dorong , Jape , Uem | |
| Reservoirs flowed through | Edéa , Song Loulou | |
| Big cities | Edéa | |
| Residents in the catchment area | 4,262,270 | |
|
The Sanaga in Edea |
||
The Sanaga with a length of 582 kilometers (with Djerem 976) of the longest flow in the Central African Cameroon . Its catchment area is also the largest in Cameroon with 28.6% of the country's area.
course
It has two source rivers, the Djérem and the Lom . The Djérem rises in the highlands of Adamaua at 1150 m, the Lom in the highlands of Jadé at 1200 m. In most sources, the Sanaga takes its name after the confluence of the Lom and Djérem rivers. The rough direction of flow of the Sanaga is oriented from east-northeast to west-southwest. Most of the vegetation along the upper reaches is tree savannah , but changes to the middle and lower reaches of the tropical rainforest . In the lower reaches of the river it forms the boundary between the two vegetation areas.
Navigability begins below Edéa up to the coast, where the Sanaga flows into the Atlantic Ocean .
The largest tributary of the Sanaga is the Mbam .
Hydrometry
The flow rate of the river was measured for 37 years (1943–1980) in Edéa, about 70 km above the mouth in m³ / s.

Drainage management
Due to the strong seasonal fluctuations in the flow of the Sanaga (factor 10), a combination of reservoirs was created in the system of Cameroon's largest river. The Mbakaou Lake , the Bamendjing and the Mapé Reservoir , as well as other smaller reservoirs, are not used directly to generate electricity. The national energy producer Eneo (formerly AES Sonel) uses these reservoirs to regulate the amount of water in the Sanaga. This compensates for the fluctuations in the flow of the Sanaga and optimizes the power generation of the Edéa and Song Loulou power plants on the lower reaches of the Sanaga, which supply the electricity required for aluminum production in the region. In addition, the Lom Pangar power plant was built on the Lom , the reservoir of which can store 6 billion m³ of water, but which, in addition to the storage factor , is also used to generate energy.
Web links
Individual evidence
- ^ Soviet General Staff Map , accessed on August 20, 2012 from http://www.topomapper.com
- ↑ a b c PDF on the hydrology of Cameroon (French) Accessed July 25, 2018
- ↑ a b Homepage UNH / GRDC - The Sanaga in Edéa. Retrieved January 3, 2016
- ↑ Entry "Sanaga" in the colonial dictionary
- ^ Plan d'Action national de Gestion intégrée des Ressources en Eau (Pangire) Accessed September 12, 2018
- ↑ a b PDF on the catchment area of the Sanaga (French)
- ↑ Hydropower in Cameroon, p 23; Sebastien Tchuidjang Tchouaha, Bachelor's Thesis.