Telmatosaurus
| Telmatosaurus | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
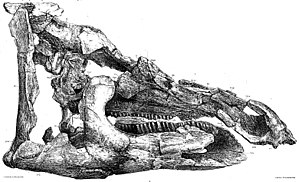
Original drawing of the type specimen of Telmatosaurus transsylvanicus from 1900. |
||||||||||||
| Temporal occurrence | ||||||||||||
| Upper Cretaceous ( Maastrichtian ) | ||||||||||||
| 72 to 66 million years | ||||||||||||
| Locations | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Telmatosaurus | ||||||||||||
| Nopcsa , 1903 | ||||||||||||
| Art | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
Telmatosaurus ("swamp lizard") is a genus of bird's pelvis dinosaurs (Ornithischia) from the group of Hadrosauridae ("duck bill dinosaurs"). Fossil finds come from the late Upper Cretaceous ( Maastrichtian ) of Romania , France and possibly Spain . The onlyspeciesscientifically described so faris T. transsylvanicus . The Telmatosaurus specimensknown todate are among the few hadrosaurid fossils discovered in Europe.
features
Telmatosaurus is known from five to ten fragmentarily preserved skulls, as well as from some elements of the postcranial skeleton ( vertebrae , elements of the shoulder girdle, extremity bones) found together with these .
At around five meters in length, Telmatosaurus is a relatively small hadrosaur. It has a tall skull, similar to Gryposaurus , but in contrast to it does not have a broad premaxillary formed as a “duck's bill”, but a rather narrow front snout, similar to Iguanodon or Camptosaurus .
Based on egg finds, Telmatosaurus could have laid 14 round eggs with a diameter of about 150 mm in four linear clusters of two to four eggs each, with the individual depositing points each about 0.5 m apart.
Taxonomic history
The type species Telmatosaurus transsylvanicus was described in 1900 by Franz Nopcsa as " Limnosaurus transsylvanicus ". However, since the generic name " Limnosaurus " had already been assigned by Othniel Marsh in 1871 for a fossil crocodile , Nopcsa changed the generic name in 1903 to the name Telmatosaurus, which is still valid today .
References
This first find came from the locality Sânpetru in the Hunedoara district in western Romania (" Transylvania "). In the area that during the Late Cretaceous was an island, a number of other dinosaur fossils have been discovered in numerous excavations, including the sauropod Magyarosaurus which Ankylosaurier struthiosaurus transsylvanicus , probably in the Iguanodontia classify Rhabdodon priscus and not clearly identifiable remains of theropods ( " Megalosaurus hungaricus ").
Two other sites of fossil Telmatosaurus remains are in France. In the Grès de Saint-Chinian in the Hérault department , Telmatosaurus was found together with Hypselosaurus priscus (Sauropoda), Rhabdodon priscus and unidentifiable theropod remains (" Megalosaurus pannoniensis "). The same taxa as well as the sauropod Titanosaurus indicus occur together with Telmatosaurus in the Grès à Reptiles in the Var department . It is unclear whether the hadrosaur found in the province of Lleida in northern Spain are also Telmatosaurus . The accompanying fauna also consisted of the above-mentioned taxa (minus the theropods) and another hadrosaur, which has now been placed in the genus Orthomerus .
Systematics
Telmatosaurus is considered the most original genus of hadrosaurs and accordingly has no characteristics derived from other hadrosaur groups in addition to the features that apply to all hadrosaurs (synapomorphies). Compared to Gilmoreosaurus , which is only a little more derived than Telmatosaurus , it still has relatively wide "molar teeth", for example, which resemble those of more original ornithopods.
Within the genus, only the type species Telmatosaurus transsylvanicus (Nopcsa, 1900) is currently considered valid. Telmatosaurus cantabrigiensis (Lydekker, 1888), originally described as " Trachodon cantabrigiensis ", is considered a noun dubium . The same applies to Telmatosaurus dolloi (Seeley, 1883), originally " Orthomerus dolloi ".
literature
- David B. Weishampel , Peter Dodson , Halszka Osmólska (eds.): The Dinosauria . 1st paperback edition. University of California Press, Berkeley CA et al. 1992, ISBN 0-520-06726-6 .
- David B. Weishampel, David B. Norman , Dan Grigorescu: Telmatosaurus transsylvanicus from the Late Cretaceous of Romania: The most basal hadrosaurid dinosaur. In: Palaeontology. Vol. 36, No. 2, 1993, ISSN 0031-0239 , pp. 361-385, PDF; 2 MB
Individual evidence
- ^ Gregory S. Paul : The Princeton Field Guide To Dinosaurs. Princeton University Press, Princeton NJ et al. 2010, ISBN 978-0-691-13720-9 , p. 295, online . Note: Paul only mentions Romania as a distribution area and does not mention the locations in France and Spain listed by Weishampel (1992). Accordingly, he narrowed the stratigraphic range of the genus to the upper Maastricht.
- ^ A b Franz Nopcsa : Telmatosaurus, new name for the dinosaur Limnosaurus. In: The Geological Magazine. NS, Decade 4, Vol. 10, 1903, ZDB -ID 206323-2 , pp. 94-95, digitized .
- ↑ a b Franz Nopcsa: Dinosaur remains from Transylvania (skull of Limnosaurus transsylvanicus nov. Gen. Et spec.). In: Memoranda of the Imperial Academy of Sciences, Vienna. Vol. 68, 1900, ZDB -ID 961131-9 , pp. 555-591, PDF; 4.4 MB .
- ^ A b David B. Weishampel, John R. Horner , Catherine A. Forster: Hadrosauridae. In: Weishampel et al. (Ed.): The Dinosauria . 1992, p. 555 f.
- ↑ a b c d e Telmatosaurus ( Memento from October 4, 2007 in the Internet Archive ), data sheet on Dinoruss.org
- ^ Weishampel et al .: Telmatosaurus transsylvanicus from the Late Cretaceous of Romania. 1993.
- ^ A b c David B. Weishampel: Dinosaur Distribution. In: Weishampel et al. (Ed.): The Dinosauria . 1992, p. 126 ff.
