Telomerization (dimerization)
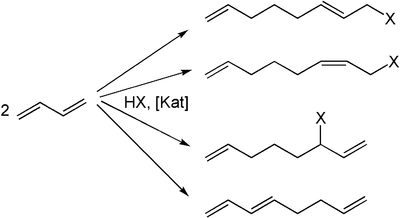
In the telomerization is the linear dimerization of 1,3-dienes with simultaneous addition of a nucleophile .
history
The reaction was independently discovered by EJ Smutny at Shell and Takahashi at Osaka University in the late 1960s. The general reaction equation is:
the formation of several isomers is possible.
reaction
In addition to 1,3-butadiene , it is also possible to use substituted dienes such as isoprene or cyclic dienes such as cyclopentadiene . A large number of substances, such as water, ammonia , alcohols or also CH-acidic compounds can also be used as nucleophiles . If water is used, for example, diunsaturated alcohols are obtained.
In particular, organometallic palladium and nickel compounds are used as catalysts .
The reaction has not yet found any industrial use.
Web links
literature
- T. Fischer: Process concepts for transition metal-catalyzed telomerization of isoprene with water or methanol. Shaker Verlag , 2002, 176 pages, ISBN 3832204148 , ISBN 978-3832204143 .
- EJ Smutny: J. Am. Chem. Soc. 89 ( 1967 ) 6793.
- S. Takahashi, Tetrahedron Lett. 1967 , 2451.