Tetragonal crystal system


The tetragonal crystal system is one of the seven crystal systems in crystallography . It includes all point groups that have a fourfold axis of rotation or rotation inversion in exactly one direction .
Point groups
The tetragonal crystal system includes the point groups and . They form the tetragonal crystal family and can be described with the tetragonal grid system .
Grid system
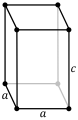
The tetragonal grid system has the holoedry . Analogous to the other whirling crystal systems , the fourfold axis is placed in the direction of the c-lattice axis. As in the monoclinic, the other two directions are perpendicular to the c-axis and - due to the fourfold nature of the c-axis - must also have the same length and be perpendicular to each other. Therefore there are only the two lattice constants a and c in this crystal system and the following conditions arise:
Bravais grid
In the tetragonal crystal system there are two Bravais lattices , the primitive and the body centered. The face-centered Bravais lattice does not correspond to the standard setup, since this lattice can always be described by an inner-centered lattice with half the size of the unit cell . The body-centered grid is obtained from the face-centered grid by rotating the a-axis by 45 ° around the c-axis and reducing it by the factor .
Point groups in the tetragonal crystal system and their physical properties
To describe the tetragonal crystal classes in Hermann-Mauguin symbology , the symmetry operations are given with respect to given directions (viewing directions) in the grid system. The viewing direction of the first symbol is the c-axis (<001>), of the second symbol the a-axis (<100>) and of the third symbol the diagonal of the c-surface (<110>).
Characteristic for the tetragonal room groups is a 4 ( 4 ) in the first position, but not a 3 ( 3 ) in the second position of the room group symbol.
| Point group (crystal class) | Physical Properties | Examples | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Crystal system | Surname | Schoenflies icon | International symbol ( Hermann-Mauguin ) |
Tepid class | Associated room groups ( no.) |
Enantiomorphism | Optical activity | Pyroelectricity | Piezoelectricity ; SHG effect | ||
| Full | Short | |||||||||||
| 9 | tetragonal | tetragonal-pyramidal | C 4 | 4th | 4th | 4 / m | 75-80 | + | + | + [001] | + |
Pinnoit Percleveit- (Ce) |
| 10 | tetragonal-disphenoidal | S 4 | 4th | 4th | 81-82 | - | + | - | + |
Clerk's seat Cahnit |
||
| 11 | tetragonal-dipyramidal | C 4 h | 4 / m | 4 / m | 83-88 | - | - | - | - |
Scheelite baotite |
||
| 12 | tetragonal-trapezoidal | D 4 | 422 | 422 | 4 / mmm | 89-98 | + | + | - | + |
Cristobalite maucherite |
|
| 13 | ditetragonal-pyramidal | C 4 v | 4 mm | 4 mm | 99-110 | - | - | + [001] | + |
Lenait Diaboleit |
||
| 14th | tetragonal-scalenohedral | D 2 d ( V d ) | 4 2 m or 4 m 2 | 4 2 m | 111-122 | - | + | - | + |
Chalcopyrite stannite |
||
| 15th | ditetragonal-dipyramidal | D 4 h | 4 / m 2 / m 2 / m | 4 / mmm | 123-142 | - | - | - | - |
Rutile zircon |
||
|
||||||||||||
For further tetragonal crystallizing chemical substances see category: Tetragonal crystal system
literature
- Hahn, Theo (Ed.): International Tables for Crystallography Vol. A D. Reidel publishing Company, Dordrecht 1983, ISBN 90-277-1445-2
- D. Schwarzenbach: Crystallography. Springer Verlag, Berlin 2001, ISBN 3-540-67114-5
- Will Kleber , Hans-Joachim Bautsch , Joachim Bohm , Detlef Klimm: Introduction to crystallography . 19th edition. Oldenbourg Wissenschaftsverlag, 2010, ISBN 978-3-486-59075-3 .
- Walter Borchard-Ott: Crystallography. 7th edition. Springer Verlag, Berlin 2009, ISBN 978-3-540-78270-4