Wilhelm Dilich
Wilhelm Dilich , also Dilich-Schäffer , actually Wilhelm Scheffer , Schöffer (* 1571 in Wabern or Nieder-Wildungen in Hesse ; † April 4, 1650 in Dresden ) was a German builder , engineer , wood cutter , engraver , draftsman , topographer and military writer. He described himself as "Geographus and Historicus".
Life

Dilich was the son of pastor Heinrich Scheffer (also Schaeffer, called Dilich or Diichius; † 1615) from Wabern near Kassel. He attended the school of scholars in Kassel and studied from 1589 to 1590 at the University of Wittenberg and until 1591 at the Philipps University of Marburg . There he got to know the later Landgrave Moritz von Hessen-Kassel , for whom he worked as a tear- away artist (draftsman) from 1592 .
At different places
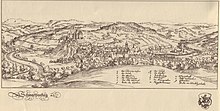
From 1594 to 1596 he made various trips on behalf of the landgrave. In 1594 he stayed in Leipzig , as evidenced by five pen drawings. From 1596 to 1597 he lived in Hamburg and visited Bremen in 1596 , where he made a drawing of the Bremen market square and negotiated with the council about the creation of a chronicle of Bremen , which he presented in 1602 as a small-format Topographia inclytae urbis Bremae . The inadequate texts and etchings led to complaints from Bremen's Mayor Heinrich Krefting , who provided him with new texts. The work in Latin Urbis Bremae et praefecturarum, quas habet, Typus et Chronicon was published improved in 1603/04 and finally contained 22 etched maps and views, some based on drawings by Christian von Apen . Dilich worked with the Bremen-based publisher Wilhelm Wessels in Kassel, who also published other of his illustrated works.
Back in Kassel
From 1597 to 1622 Dilich was again in the service of the Hessian landgrave. Most recently he was employed as the head of fortifications in Wanfried near Eschwege . At the court of Landgrave Moritz in Kassel , his outline of the knight's game was printed in 1601 from a pen drawing by Dilich.
He married in Leipzig in the same year. The fortress builder Johann Wilhelm Dilich, born in Kassel in 1600, came from the marriage .
1603–1605 he worked on an illustrated Bremen chronicle , which today is an important source for the conditions in the Hanseatic city at the beginning of the 17th century.
His main work is the Synopsis totius Hassiae from 1605. In this book he depicts all the cities of Hesse in the 16th century. His cityscapes are often the oldest demonstrable historical pictorial images.
Between 1607 and 1622 he worked on the country tables of Hessian offices between the Rhine and Weser (today in the Kassel University Library), which, however, remained unfinished. The scale of the photos ranges from maps to the construction of individual castles such as the Ziegenhain water fortress , the Marksburg or Rheinfels over St. Goar.
In Saxony
From 1622 to 1625 he was imprisoned for exceeding his authority. With the help of the governor Wilhelm von Hessen he managed to escape to Electoral Saxony . From March 1625 Wilhelm Dilich worked as a war engineer, cartographer, master builder and vedute draftsman in the service of the Saxon Elector Johann Georg I in Dresden . He eventually rose to head the entire fortress and master builder in Saxony.
After receiving the travel letter issued on June 28, 1627 by Elector Johann Georg I of Saxony, he traveled through Electoral Saxony in order to make a total of 17 city views for the decoration of the giant hall in Dresden Castle . This hall was raised and vaulted by Dilich from 1627 to 1630. 1633 vault was Kilian Fabritius according Dilichs templates painted with Saxon town views and completed. In the window reveal is his self-portrait as Germanus . The twelve signs of the zodiac on the ceiling based on his designs were destroyed after a fire in 1701.
Dilich was later appointed head of the expansion measures for the fortifications in Dresden. In 1650 he resigned from the Electoral Saxon service at a very old age and wrote several theoretical treatises on fortress construction. His pen drawings were often the basis for works by Matthias Merian . He had a good library of geographical, historical, and technical works.
Honors
Monuments in Wittenberg and Weimar remind us of his work.
Works
- De Electoribus Saxonicis . 1590
- Synopsis descriptionis totius Hassiae tribus libris comprehensae . 1591
- Brevis Lipsiae descriptio . 1594
- Description and outline of the knight's game, according to the translucent Mr. Moritz. Landgrave of Hesse ... on the princely christening of children Frewlein Elisabethen ... arranged at the princely court in Cassel, celebrated in August 1596 in Cassel . 1601
- Biblia , 1601
- Hungarian Chronicle , 1601
- Bremen Dilich Chronicle :
- Preliminary specification: Urbis Bremae typus et chronicon , 1602.
- Edition authorized by the city: Urbis Bremae et Praefectuarũ quas habet typus et chronicon , 1603 ff. In several editions.
- Hessian Chronica . 1605 Digital copy of the ULB Saxony-Anhalt
- Own, short description and outline of the so far famous Keyserlichen city of Constantinobel . 1606
- Brief description and actual demolitions of the countries and fortresses, according to the Türcke, therefore in Europe, but especially in Hungary, Slavonia, Dacia, Dalmatia and Greece, partly contested with war, partly brought under its yoke, sanpt the Hungarian Chronica . 1609
- Hessian Chronica . 1617
- Land tables of Hessian offices between the Rhine and Weser . 1607/1622 (Kassel University Library 2 ° Ms. Hass. 679)
- Urbs et Academia Marpurgensis succincte descripta. 1627 (unfinished); Reprint: N [oa] G [ottfried] Elwert, Marburg 1867.
- Peribologia or Wilhelm Dilichii Hist. of Vestungsgebewen. Many places multiplied ... and publicirett by Wilhelm Dilichium . 1640
- Kurtzer Underricht to build bulwarks . 1645
- Wilhelmi Dilichii… Highly sensible founded and established, divided into certain classes, previously closed, but now opened war school . 1647
- War book Wilhelmi Dilichii, in it the old and new militia of all places increased, actually describes
- Vitae professorum thelogiae qui in… Academia Marburgensi… docuerunt… Accedit Wilhelm Dilichii manuscript
Works in art collections
- State library of the city of Kassel (drawings, including Moritzburg Castle , Malsfeld, etc.)
literature
- Johannes Kurzwelly : Dilich, Wilhelm . In: Ulrich Thieme (Hrsg.): General Lexicon of Fine Artists from Antiquity to the Present . Founded by Ulrich Thieme and Felix Becker . tape 9 : Delaulne-Dubois . EA Seemann, Leipzig 1913, p. 288–290 ( Text Archive - Internet Archive ).
- Günter Klos: Dilich, Wilhelm . In: General Artist Lexicon . The visual artists of all times and peoples (AKL). Volume 27, Saur, Munich a. a. 2000, ISBN 3-598-22767-1 , pp. 390 f.
- [After Caesar]: Dilich, Wilhelm . In: Allgemeine Deutsche Biographie (ADB). Volume 5, Duncker & Humblot, Leipzig 1877, p. 225 f.
- Franz Lerner: Dilich, Wilhelm. In: New German Biography (NDB). Volume 3, Duncker & Humblot, Berlin 1957, ISBN 3-428-00184-2 , p. 718 ( digitized version ).
- Bettina Schleier: Wilhelm Dilich's Bremen Chronicle . In: Bremisches Jahrbuch 73, 1994, pp. 12–47. [Also on Dilich's complete works].
- Walther Killy : Literature Lexicon: Authors and works in the German language . Bertelsmann-Lexikon-Verlag, Gütersloh / Munich 1988–1991 (CD-ROM: Berlin 1998, ISBN 3-932544-13-7 ) Volume 3, p. 53
- Carl Michaëlis (ed.): Rhenish castles based on hand drawings by Dilich (1607) . With contributions by C. Krollmann and Bodo Ebhardt. Berlin 1900. Online edition dilibri Rhineland-Palatinate
- Wilhelm Dilich: jousting games anno 1596 . Reprint of the Cassel edition. Wessel. 1598. Edited as a reprint and provided with an afterword by Hartmut Broszinski and Gunter Scheikhart. Kassel 1986.
- Ingrid Baumgärtner , Martina Stercken, Axel Halle (eds.): Wilhelm Dilich. Land tables of Hessian offices between the Rhine and Weser 1607–1625 . kassel university press, Kassel 2011. ISBN 978-3-89958-450-9
- Horst Nieder: Wilhelm Dilich (around 1571–1650). Draftsman, writer and cartographer in court service . Lemgo 2002.
- Dilich or Dillich, Wilhelm Scheffer. In: Johann Heinrich Zedler : Large complete universal lexicon of all sciences and arts . Volume 7, Leipzig 1734, column 925.
- Johann Samuelersch , Johann Gottfried Gruber : General Encyclopedia of Sciences and Arts Vol. 25 p. 204
Web links
- Literature by and about Wilhelm Dilich in the catalog of the German National Library
- Literature on Wilhelm Dilich in the Hessian Bibliography
Individual evidence
- ^ Herbert Black Forest : The Great Bremen Lexicon . 2nd, updated, revised and expanded edition. Edition Temmen, Bremen 2003, ISBN 3-86108-693-X .
| personal data | |
|---|---|
| SURNAME | Dilich, Wilhelm |
| ALTERNATIVE NAMES | Dillich, Wilhelm; Dilich-Schäffer, Wilhelm; Scheffer, Wilhelm; Schöffer, Wilhelm |
| BRIEF DESCRIPTION | German engraver, topographer, fortress construction engineer, chronicler, war writer |
| DATE OF BIRTH | 1571 |
| PLACE OF BIRTH | Wabern or Bad Wildungen , Hesse |
| DATE OF DEATH | April 4, 1650 |
| Place of death | Dresden |