Dwarf signal
A dwarf signal is a railway signal that is installed in a low design next to the track. It stands on a small mast, or it is placed on the ground without a mast. In Switzerland , the term dwarf signal is included in the national driving regulations and is used with precisely defined signal terms.
In Germany it is a slang term for various types of railway signals. The term dwarf signal is not included in the German railway signal regulations and in the signal book of Deutsche Bahn AG ; also not in the signal regulation DV V2 of the ÖBB . In the guidelines of the Deutsche Bahn AG for structural engineering, control, signaling and telecommunications technology, the term dwarf signal is used.
Switzerland
The dwarf signal is a light signal that primarily regulates maneuvering movements. At the same time, it also secures the routes within a train station and offers side protection. It thus fulfills functions for both shunting and train operations. It is also used to secure level crossings within the maneuvering area of a train station and when changing lanes.
As a rule, dwarf signals are always placed to the left of the track. However, if the local conditions require it, it can exceptionally be on the right. In this case, a reflective or luminous arrow on the front points to the associated track. Dwarf signals are located directly on the ground next to the track, only in special individual cases are they raised for better visibility.
Signal aspects
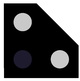
A dwarf signal has three white lamps arranged in an L. Three different signal aspects can be displayed:
| Signal aspect | meaning | Relationship to other signals |
|---|---|---|
|
Trip |
The next dwarf signal shows driving or driving with caution . |
|
|
Drive with caution |
The next dwarf signal shows stop , drive with caution or nothing else follows. A blocking signal or another signal indicating a stop can also follow. |
|
|
Stop |
A preceding dwarf signal indicates driving with caution. |
|
|
On the back of the dwarf signals, the white, oblique light strip lights up when driving or driving with caution . |
Functionality in operation
Dependencies
Not every train station in Switzerland is equipped with dwarf signals. However, wherever dwarf signals are set up, they are taken into account when shunting; the approval for a maneuvering run is given by the dwarf signal. When the train is running, they apply in addition to the main signals, which correspond to either the signal system L or the signal system N. Should a dwarf signal stop or be disturbed during a train journey, it must be stopped beforehand.
One dwarf signal is always dependent on the next. If, for example, a maneuvering run is to be carried out over two track sections, which are secured by a dwarf signal at the beginning and the end, the first shows a journey , the second warns by driving with caution and the last shows a stop .
The illustration shows the signal image of a shunting route from track 4 via track 44 to track 34.
- The dwarf signal at the destination of the journey (at switch 13) shows stop .
- The penultimate dwarf signal in the route at turnout 14 shows driving with caution .
- The dwarf signal at the starting point of the journey at switch 17 shows that the vehicle is moving .
With the signal aspect drive , maneuvering drives may be driven at the locally determined maximum permissible speed. With the driving term " drive with caution" , the speed must be selected so that you can stop at any time in front of an obstacle.
Check for free travel
The interlocking technology used also plays a role. An electronic interlocking checks the set route of the shunting route for occupancy. If track 44 were (partially) occupied in the illustrated example, then the dwarf signal at point 17 would also show travel with caution - and not travel .
In the case of relay interlockings, on the other hand, this check does not take place, so the first dwarf signal would show "moving" even if track 44 is occupied. This is referred to as a "false dwarf" in railway jargon and is forbidden for safety reasons according to Swiss driving regulations or only allowed after consultation between the dispatcher and the shunter.
Shunting trips against set train routes
In principle, no shunting routes may be set against a set train route. Exceptional case:
- It is driven against braked vehicles that are in front of the set train route.
In stations with dwarf signals, it is also permitted to set a shunting route against a set train route if
- the destination of the shunting run named by the shunting manager is on the track in front of the set train route and shows a dwarf signal HALT
OR
- the shunting run is used to set up trains directly on the platform.
Dependency of the main signal on the dwarf signal
Due to the interlocking technology in relay interlockings (domino interlocking), train routes are unilaterally dependent on the dwarf signals. A train route can only be set here if a shunting route has first been successfully set in the same route; all dwarf signals lying in the route must therefore show that they are driving or driving with caution . There must be at least one lamp on in each dwarf signal. It is thus possible to set a train route even if a dwarf signal lamp is defective; with two defective lamps in a dwarf signal, depending on the case, no train route can be set, with three defective lamps generally not.
In the case of electronic interlockings (Simis, Elektra), however, this dependency does not exist. A train route can also be set here when the dwarf signals are not illuminated.
If a main signal signals halt , the associated dwarf signal can also indicate halt; does not have to, however, if, for example, a shunting route is set from this track, for example to remove or weaken the train composition.
In the case of an occupied entrance, i.e. a train route into a track that is partially occupied, the last dwarf signal always indicates driving with caution . The occupied entrance is indicated on the main signal with driving aspect 2 or 6 in combination with the occupied signal. Put simply, both mean that you have to drive at a reduced speed.
However, not all stations are equipped with appropriate signals for the occupied entrance. Where this is not the case, an occupied entrance can only be set as a train route using an emergency operator.
The last dwarf signal at a set Zugfahrstraße against the route always shows drive . This is never the case with a shunting route that is set up to the limit of the station. Here the last dwarf signal always shows you are driving with caution .
If a driver of a passing train detects a dwarf signal in his route indicating a stop , he has to stop the train immediately and contact the dispatcher.
Dwarf signals are also used for flank protection. If a necessary flank protection switch cannot reach an end position when setting up a shunting route or if it is occupied in a position that does not offer protection, this is considered a flank protection violation. The dwarf signal responsible for edge protection then remains on hold .
In the event of malfunctions
An unlit dwarf signal is to be interpreted as a stop signal. In the case of an unclear signal with a burning lamp, the safe variant should be assumed. That means:
- If only the upper lamp is on, drive with caution .
- If only one of the lower lamps works, stop is to be assumed.
Only signals with the white triangular attachment may be driven over in the dark. Otherwise the process for disturbed signals must be followed.
The lamps are not connected in series but in parallel . This means that if a lamp is defective, only this one will fail.
Germany
Low- profile blocking signals are colloquially referred to as dwarf signals. In special cases there are also low standing main signals.
Individual evidence
- Swiss Driving Regulations (FDV) A2016 Federal Office of Transport (FOT), July 1, 2016 (PDF; 3 MB). R 300.2, section 2.4 dwarf signals
- www.lokifahrer.ch
- ↑ https://www.gesetze-im-internet.de/bundesrecht/eso_1959/ overall.pdf
- ↑ Signals of the German Railways , Pocket Lexicon, GeraMond
- ↑ Guideline 885.1101 Structural Engineering, Control, Signaling and Telecommunication Technology - Deutsche Bahn AG
- ↑ Archive link ( Memento from October 15, 2008 in the Internet Archive )