Opening phase
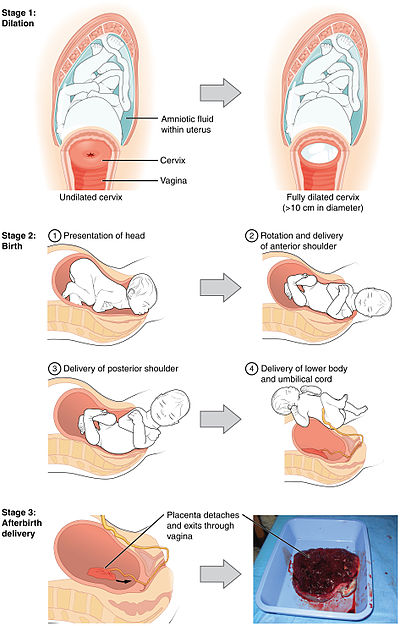
Under the first stage is defined as the time from the start of regular nut mouth effective labor until full dilation of the cervix to ten centimeters. The opening phase is divided into a latency phase and an active opening phase .
procedure
The latency phase begins with the onset of Braxton Hicks contractions . Contractions of the uterus are contractions that are irregular in frequency, duration and strength. They cause the preceding part of the child to go deeper into the maternal pelvis, the cervix shortens, the cervix becomes softer and opens up to two to three centimeters. It is typical of pre-contractions that they are position-dependent and tend to subside or even stop when lying down or during a relaxing bath.
The active opening phase begins when the cervix is two to three centimeters open and the contractions become increasingly stronger and longer. The pauses between labor become shorter and the contractions take place in a regular rhythm with an interval of 3 to 5 minutes. The contractions last about 60 to 90 seconds. The opening labor pushes the child deeper and the pressure of the preceding part expands the cervix. At ten centimeters, the cervix is fully opened.
The opening phase is the longest phase of childbirth and lasts on average 10 to 12 hours for a primiparous woman and 2 to 6 hours for multiparous women. The differences, however, are considerable.
literature
- Christine Mändle, Sonja Opitz-Kreuter: The midwife book: textbook of practical obstetrics. 5th edition. Stuttgart 2007, Schattauer GmbH ISBN 978-3-7945-2402-0
Individual evidence
- ^ Gerhard Martius: Textbook of obstetrics, including obstetric operations. Georg Thieme, Stuttgart / New York 1985, ISBN 3-13-375311-8 , p. 320 f