Failure Process Matrix
The Failure Process Matrix (FPM) is a method for preventive error avoidance and was at the Fraunhofer Institute for Manufacturing Engineering and Automation developed around at typical conditions of assembly processes, such as high proportion of manual activities or simple assembly operations, a noticeable overhead in FMEA to reduce.
application
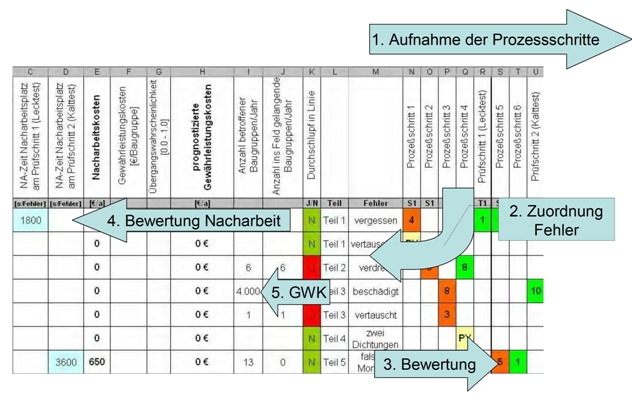
In the basic principle of FPM, the process steps in one axis and the possible errors in the other axis are linked in the spanned matrix with a value for the probability of occurrence of the error or the probability of detection of an error.
As in the FMEA, the probabilities of the occurrence or detection of an error are identified with numerical values from 1 to 10, the allocation of the numerical values of the probability of occurrence is based on time terms ("daily", "weekly" etc.). Due to the time base of one year, this evaluation can easily draw on the experience of the workers. By linking to the planned number of items, a precise estimate of the number of errors to be expected can be made during the planning phase; by evaluating the errors according to the error costs (reworking, scrap costs, warranty costs, process disruptions), the economic viability of changes to the process or additional tests can be determined.
The FPM has proven itself in various large planning projects since 2004 and has been increasingly used in a wide variety of industrial areas in recent years.
Rules for a successful FPM
first rules of the FMEA:
- the team composition must not change between different meetings
- the team must be composed heterogeneously (production, production planning, QM, engineering, ...)
- keep the team in a good mood (drinks, fruit, possibly biscuits)
Furthermore:
- Workers with production experience (preferably from similar production steps) must be there
Experience has shown that FPMs that are "only" created with planners and test planners are not very meaningful.
literature
- A. Schloske: Using the Error Process Matrix (FPM) to optimize complex assembly processes in terms of costs, quality and productivity. Association of German Engineers -VDI-, Training Center, Stuttgart. Assembly design seminar, May 24th and 25th, Stuttgart 2007
Web links
- Download the FPM tool
- Failure Process Matrix (FPM) Fraunhofer IPA