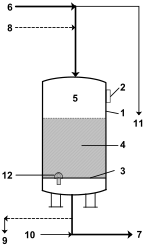
DC exchanger
Direct current exchangers (also direct current filters ) have been a frequently used container design for ion exchange in water treatment since the beginning of large-scale plant construction. This is used when the content of dissolved salts in the water is to be changed (e.g. with softening) or reduced (e.g. with partial or full desalination). Further detailed information can be found in the article on ion exchangers . Below is a sketch with the main features for a DC exchanger :
Typical direct current exchangers are e.g. B. Softening ° , H-decarbonizing and mixed-bed exchangers .
- ° Note : With larger softening filters, it is sometimes also economical to use a countercurrent exchanger , a further development of the cocurrent exchanger .
Such filters are cylindrical pressure vessels with a nozzle base on which the ion exchange resin is poured. According to the name, the flow direction is the same for loading and regeneration through the resin bed, it is from top to bottom. Both normal and compound or progressive regeneration (required for sulfuric acid as the regeneration acid) are used as regeneration techniques.
In spite of the simple construction and handling, the disadvantage of this type of container for demineralization is the high demand for chemicals and washing water, while the pure water quality is not optimal at the same time. Furthermore, the ion exchange resins must be backwashed before regeneration.
literature
- P.Pracht; Babcock manual water ; Edition 1962, chap. 4.3, pp. 63-107
- CHDallmann, AA Askew; Selection Demineralization Equipment; in: Power Engineering , Nov. 1971, pp. 44-47