List of quantum gates
This is a listing of different quantum gates and their function.
Quantum gate with one input
| Symbol and function 1 | designation | function | description |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
identity | Identity of the hyper-complex entrance and therefore no change in the quantum state | |
 |
Pauli-X-gate non-gate |
Mirroring the hyper-complex entrance on the X-axis
Example: |
|
 |
Pauli Y gate | Mirroring the hyper-complex entrance on the Y-axis
Example: |
|
 |
Pauli-Z-gate | Mirroring the hyper-complex entrance on the Z-axis | |
 |
Hadamard Gate | Reflection of the hypercomplex input on the X + Z axis | |
 |
X rotation gate | Rotates the complex input 90 ° (π / 2) around the X axis. Also known as a gate. |
|
 |
Y rotation gate | Rotates the hypercomplex input 90 ° (π / 2) around the Y axis | |
 |
(−X) rotation gate | Rotates the complex input −90 ° (−π / 2) around the X axis | |
 |
(−Y) rotation gate | Rotates the hypercomplex input −90 ° (−π / 2) around the Y axis | |
 |
S-gate, phase gate | Rotates the phase 90 ° (π / 2) around the Z axis. Also known as a gate. |
|
 |
T-gate, π / 8-gate phase (shifter) gate |
Rotates the phase 45 ° (π / 4) around the Z axis. Also known as a gate. |
|
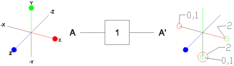 |
General phase (shifter) gate 2,3 . |
k is set arbitrarily Rotates the phase π / 2 k around the Z axis. |
|
 |
Arbitrary unitary gate 3 |
With |
All properties are set arbitrarily |
|
1 Using the example of three different input signals with different spins and their position after crossing the gate. The Z-axis (at the blue input) shows the real value, the X- (at the red input) and Y-axis (at the green input) the phase position. The input is marked with A, the output with A '. see also: Bloch sphere 2 output shown for the values k = 0, k = 1 and k = 2 |
|||
Quantum gate with two inputs
| symbol | designation | function | description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
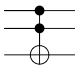
Controlled-not gate (CNOT, XOR operation ) |
|
The real value of the second qubit (B) is either retained (A = 0) or negated (A = 1) depending on the real value of the first qubit (A).
The value of the first qubit is retained. |
|
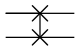
Exchange node ("Swap") |
|
The two input qubits are swapped |

|
Root swap | Universal gate that half swaps the input qubits | |

|
Controlled Z-flip (CZ) | Also known as controlled Z-gate, controlled phase flip (CPF) or controlled-SIGN (CSIGN) | |

|
Controlled phase (C phase) | can be chosen arbitrarily. | |

|
Controlled |
Matrix representation: Dirac representation:
|
The second qubit is transformed according to the unitary mapping if the first qubit has the value "1" and remains otherwise unchanged. (C-NOT and C-phase are special cases of CU) |

|
Any unitary transformation | The independent variables of the complex unitary 4x4 matrix (16 real parameters) can be chosen as desired. In this way one can describe all interactions between the two qubits. |
Quantum gate with three inputs