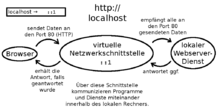
localhost
In network technology, the domain name localhost names the local computer ('local host'). With its help, network-compatible computer programs can communicate with one another on a name-based basis within a computer.
Domain name
The Internet standards RFC 2606 and RFC 6761 reserve localhost as a top-level domain for the Domain Name System (DNS). It should contain a static AAAA Resource Record or A Resource Record on IP addresses of the loopback interface. Specifically, these are the IPv6 address ::1 and the IPv4 address 127.0.0.1 . However, this recommendation is not implemented by every DNS server .
Operating systems translate localhost into the above addresses independently of the DNS server using the hosts file.
use
If computer programs are to communicate with each other within a computer (coll .: locally), the Internet protocol is often used as the universal standard. The possibility of always addressing the local computer as localhost means that a connection can be established without knowledge of the individual host name or exact IP addresses or protocols.
Specifications
- D. Eastlake, A. Panitz: RFC 2606 . - Reserved Top Level DNS Names . June 1999. (Updated by RFC 6761 - English).
- R. Hinden, S. Deering: RFC 4291 . - IP version 6 addressing architecture . [Errata: RFC 4291 ]. February 2006. Standard: [Draft]. (Replaces RFC 3513 - updated by RFC 5952 - English).
- M. Cotton, L. Vegoda, R. Bonica, B. Haberman: RFC 6890 . - Special Use IPv4 Address . [Errata: RFC 6890 ]. April 2013. Standard: [BCP 153]. (Replaces RFC 5736 - Updated by RFC 8190 - English).