Slicer software
As Slicer software , short slicer , or slicing software is a software called, which in most 3D printing processes is a 3D object model in specific instructions used to convert for the printer. In particular, the conversion of a model in STL format into printer commands in G-code format in fused deposition modeling and other similar processes.
functionality
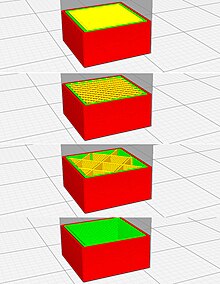
The slicer first converts the object model into a stack of flat layers and describes these as linear movements of the 3D printing extruder, fixing laser or other tools. The slicer software creates a three-dimensional grid model from the STL data (or other formats), which is provided with horizontal sections. All of these movements, along with some specific printer commands, such as those to control the extruder temperature or the bed temperature, are eventually written into the machine-readable G-code file that can be transmitted to the printer. The G-Code is a programming language for numerical controls that gives the 3D printer instructions for printing, moving the axes, infeed and other process steps.
Almost all slicers have a few additional features including:
- Infill : solid print objects require a large amount of material and printing time. The slicer can convert solid solids into hollow ones, which saves material and time when printing. The hollow object can be partially formed by internal structures, such as e.g. B. inner walls are filled to ensure additional stability. The amount of these structures is called the infill density, as this parameter is one of the adjustments that must be made available to the slicer.
- Support : In most 3D printing processes, the object is created layer by layer from bottom to top, with the layer under construction being placed on top of the previous one. This has the consequence that all object parts have to be placed at least partially on top of others. In the case of a floating object plane (e.g. the flat roof of a house or a horizontally outstretched arm in a figure) the slicer can automatically add supports for that object. The supports touch the object in a way that is easily detached from it in the finished object.
- Rafts, skirts, brims (d .: flat foundations, aprons, edges): The printing of the first object layer, which is in contact with the printer bed, has some peculiarities, including problems with the object adhering to the substrate, unevenness, smooth deposition of the first amounts of filament and more. The slicer can automatically add some detachable structure to minimize these problems. Common types of these basic structures are skirts (a single band around the base of the object without touching it), brims (multiple lines of filaments around the base of the object until they touch but not underneath), and rafts (multiple layers of Material forming a removable base over which the object will be printed).
Programs
There are numerous slicer applications out there, some of which are free and open source. Some of the most commonly used are:
- Ultimaker Cura ( GNU LGPL )
- PrusaSlicer ( GNU AGPL )
- Slic3r ( GNU AGPL )
- KISSlicer (proprietary)
- ideaMaker (proprietary)
- REALvision (proprietary)
supporting documents
- ^ Brian Evans: Practical 3D Printers: The Science and Art of 3D Printing . apress,, ISBN 978-1-4302-4393-9 .
- ↑ Keon Aristech Boozarjomehri: 3D Printing at School and Maker Spaces: Project Learning with 3D printing . Cavendish Square ,, ISBN 978-1-6804-5016-3 .
- ↑ Liza gelding Kloski, Nick Kloski: Getting Started with 3D Printing: A Hands-on Guide to the hardware, software, and services behind the New Manufacturing Revolution . Maker Media, Inc ,, ISBN 978-1-6804-5020-0 .
- ↑ a b Slicer - RepRap ( en ) Retrieved September 15, 2018.
- ^ What is slicing software, and what does it do? ( en ) Retrieved September 15, 2018.
- ↑ Best 3D Slicer Software for 3D Printers of 2018 (Most are Free) | All3DP (en-US) . In: All3DP , June 1, 2018.