Bacan
| Bacan | ||
|---|---|---|
| Location of Bacan | ||
| Waters | Moluccan Sea | |
| Archipelago | Bacan Islands | |
| Geographical location | 0 ° 37 ′ S , 127 ° 31 ′ E | |
|
|
||
| surface | 1 900 km² | |
| Highest elevation | 2111 m | |
| Residents | 13,000 6.8 inhabitants / km² |
|
| main place | Labuha | |
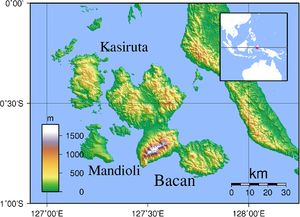
| Topographic map of the Bacan Islands | ||
Bacan is an Indonesian island in the Pacific . It is the largest of the Bacan Islands of the same name , a group of islands in the Moluccas archipelago .
Geography and inhabitants
Bacan is a densely forested, hilly and irregularly shaped island of volcanic origin. The southeastern peninsula , which is only separated from the northwestern part of the island by a small isthmus, is striking . The island is characterized by volcanoes, including the Amasing . In the lowland rainforest and in the mountain forest about 700 meters some life endemic bird species. The megachile pluto , the largest species of bee in the world, was discovered on Bacan in 1859 .
The island is about 20 kilometers off the coast of the southern peninsula of Halmahera Island . Bacan's land area amounts to around 1,900 km². The highest point is the Labua with about 2111 m above sea level. A 900 m high peninsula in the southeast is separated by an isthmus .
An estimated 13,000 people live on Bacan. The areas of the north and northeast coasts of Bacan are primarily populated. The largest place is Labuha , which is located in a bay on the west coast.
Economy and Transport
In the interior of the country, wood is felled that is exported. Rice and tobacco are grown for personal use. From Labuha there are boat connections to the island of Obi in the south and to Ternate in the north.