Baclofen
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1: 1 mixture of ( R ) -form (left) and ( S ) -form (right) |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Baclofen | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 10 H 12 ClNO 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 213.66 g · mol -1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
189–191 ° C or 206–208 ° C ( polymorphism ) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| pK s value |
3.9; 9.6 |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
poorly soluble in water; very heavy in ethanol ; soluble in dilute mineral acids and in alkali hydroxide solutions |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Baclofen is a drug from the group of muscle relaxants . It is used to treat spasticity in spinal cord injuries and multiple sclerosis .
Chemical-physical properties
Baclofen is a white, odorless crystalline powder, slightly soluble in water, very slightly soluble in methanol, and insoluble in chloroform . It is also practically insoluble in acetone and diethyl ether . Chemically, it is a chiral derivative of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). The racemate of Baclofen is used pharmaceutically . When heated to over 50 ° C., baclofen splits off water and cyclizes to the lactam 4- (4-chlorophenyl) pyrrolidin-2-one. This reaction can even be detected in aqueous solution.
presentation
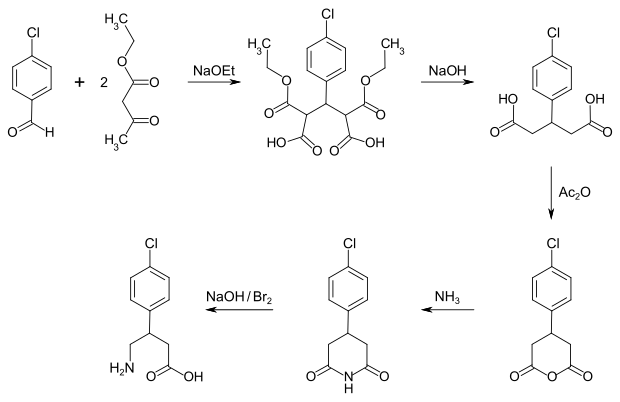
There are two different ways to synthesize baclofen. By condensing 4-chlorobenzaldehyde with two molecules of acetoacetic ester , followed by saponification and decarboxylation, a substituted glutaric acid is obtained. Dehydration then leads to cyclic anhydride , which is then reacted with ammonia to form glutarimide. The reaction with an alkaline solution of bromine yields baclofen in a Hofmann rearrangement .
A second synthetic route starts from ethyl 4-chlorocinnamate . This is reacted with nitromethane in a nitro Michael addition in the presence of a base to form β- (4-chlorophenyl) -γ-nitrobutyric acid ester. The reduction with hydrogen in the presence of Raney nickel gives a β- (4-chlorophenyl) -γ-aminobutyric acid, which leads to baclofen after ester saponification.
effect
Baclofen acts as a specific agonist at the GABA B receptors of the synapses and nerves of the mammalian spinal cord . Without constant control from the brain, the spastic reflex mechanisms predominate in the spinal cord. These can be so severe in sick people that they wake up from sleep and feel severe pain.
Baclofen acts on the reflex arcs of the spinal cord. It can mimic the natural antispastic effect of GABA, especially on the so-called Renshaw cells . The dose required for intrathecal administration varies, but is much smaller than for oral administration.
The substance does not work on the GABA receptor in the fruit fly .
As a GABA receptor agonist, baclofen has a similar effect to the muscimol of the toadstool .
Pharmacokinetics
The substance is completely absorbed after oral administration. Their plasma half-life is three to four hours. Most of the drug is excreted unchanged through the kidneys. The main metabolite is 3- (4-chlorophenyl) -4-hydroxybutanoic acid, which is formed to a small extent and which itself has no effect.
Overdose
As a result of a baclofen overdose, symptoms such as nausea, vomiting , weakness, dizziness , difficulty breathing, altered pupils, low blood pressure ( hypotension ), decreased heart rate ( bradycardia ) and decreased body temperature ( hypothermia ) may occur. The occurrence of comas has also been observed.
Therapeutic use
Baclofen was originally developed as a drug to treat epilepsy . It was first synthesized by chemist Heinrich Keberle in 1962 at what was then Ciba , which patented the active ingredient in 1968. The anti-epileptic efficacy was not present (baclofen rather lowers the seizure threshold and is contraindicated in epilepsy), but the antispastic effect was useful.
Spasticity
Baclofen is approved for the treatment of severe chronic spasticity in multiple sclerosis, after injuries to the spinal cord or cerebral genesis, which cannot be successfully treated with standard therapy. Baclofen was and is still administered orally with varying degrees of success . In seriously ill children, however, the oral dose required is so large that the side effects limit the therapy and, as a result, intrathecal administration is a therapeutic option . For intrathecal administration, a baclofen solution is infused directly into the cerebrospinal fluid . Intrathecal administration is necessary in spasticity patients because only a very small amount of the orally administered substance reaches the site of action on the nerves of the spinal cord and therefore only high oral doses with corresponding side effects are available as an alternative.
Intrathecal administration is primarily chosen for patients with multiple sclerosis who have severe painful spasms that cannot be controlled by oral baclofen or other drugs. A test dose is given to demonstrate effectiveness. If the test dose is successful, a catheter is placed intrathecally through which a computer-controlled implanted pump delivers the drug as long-term therapy. The pump's reservoir can be refilled from the outside through the skin. The disadvantage of the pump system is its price of 20,000 euros and the complex implantation and maintenance, so that a strict patient selection is necessary.
alcoholism
The French cardiologist Olivier Ameisen undertook a successful self-experiment with high-dose baclofen for the treatment of alcohol addiction , the course of which was published in 2005 in the journal “Alcohol and Alcoholism” . He makes his experiences accessible to a broader public in the biographically based book “The End of My Addiction” , which has meanwhile been published in several languages .
An international systematic review published in 2019 came to the conclusion that baclofen is a promising drug for the treatment of alcohol abuse in moderate to severe cases. B. in terms of the ideal duration of treatment and the risks associated with the combination of alcohol and baclofen.
An overview of the potential mechanisms of action of baclofen in alcohol use disorders (AUD) was published by Renaud de Beaurepaire.
In France, baclofen has also been approved for the treatment of alcohol dependence by the National Agency for the Safety of Medicines and Health Products (ANSM) since October 2018 . This was preceded in 2014 by a provisional, three-year approval for the medical prescription.
In Germany, a doctor's prescription for the treatment of alcoholism is currently only possible in off-label use and is quite controversial.
Other uses
Baclofen may also be able to reduce episodes of reflux, regurgitation, and pH-metrically the phases of pH values below 4.0 in reflux oesophagitis (GERD), a double-blind study showed.
The importance of the GABA B receptors for the development of anxiety has been examined in various studies and, in this context, the effect of baclofen on anxiety and depression has been demonstrated in animal experiments.
Baclofen is also given for persistent hiccups .
Commercial preparations
Lebic (D), Lioresal (D, A, CH) and generics (D, CH); Baclocur (F)
Web links
- Intrathecal Baclofen Therapy (for MS). (February 4, 2012 memento on the Internet Archive ) Cleveland Clinic Information Center. June 15, 2001
- Entry on Baclofen in Flexikon , a Wiki of the DocCheck company
Individual evidence
- ^ The Merck Index. An Encyclopaedia of Chemicals, Drugs and Biologicals. 14th edition. 2006, ISBN 0-911910-00-X , p. 159.
- ↑ a b c d e f Entry on Baclofen. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on July 23, 2019.
- ↑ Entry on Baclofen at TCI Europe, accessed on February 16, 2020.
- ↑ Safety data sheet for Baclofen at LGC Standards. Retrieved March 14, 2020 .
- ↑ Data sheet (±) -Baclofen at Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on April 30, 2017 ( PDF ).
- ^ H. Keberle, JW Faigle, M. Wilhelm: GAMMA-AMINO-BETA- (PARA-HALOPHENYL) -BUTYRIC ACIDS AND THEIR ESTERS. U.S. Patent 3,471,548.
- ↑ H. Keberle, JW Faigle, M. Wilhelm: US Patent 3634428.
- ↑ F. Uchimaru, M. Sato, E. Kasasayama, M. Shiamuzu, H. Takashi: JP Patent 45016692.
- ↑ M. Mezler et al: Cloning and functional expression of GABA (B) receptors from Drosophila. In: Eur J Neurosci. 13 (3), 2001, pp. 477-486. PMID 11168554 .
- ↑ S. Dzitoyeva include: gamma-aminobutyric acid B receptor 1 mediates behavior-Impairing actions of alcohol in Drosophila: adult RNA interference and evidence pharmacological. In: Proc Natl Acad Sci USA . 100 (9), 2003, pp. 5485-5490. PMID 12692303 ; PDF (free full text access).
- ↑ Michael Freissmuth, Stefan Offermanns (Hrsg.): Pharmacology and Toxicology: From the molecular basis for pharmacotherapy . Springer, Heidelberg 2012, ISBN 978-3-642-12353-5 , pp. 256 ( limited preview in Google Book Search).
- ↑ Perumal Yogeeswari, Jegadeesan Vaigunda Ragavendran, Dharmarajan Sriram: An Update on GABA Analogs for CNS Drug Discovery. ( Memento from June 16, 2010 in the Internet Archive ) (PDF). In: Recent Patents on CNS Drug Discovery. 1, 2006, pp. 113-118.
- ^ O. Ameisen: Complete and prolonged suppression of symptoms and consequences of alcohol-dependence using high-dose baclofen: a self-case report of a physician. In: Alcohol and Alcoholism. 40 (2), March / April 2005, pp. 147-150.
- ↑ Olivier ants: La derniére verre. Éditions Denoël, 2008, ISBN 978-2-207-25996-2 . German edition The end of my addiction. published by Kunstmann 2009–2013, ISBN 978-3-88897-901-9 .
- ↑ R. de Beaurepaire et al .: The Use of Baclofen as a Treatment for Alcohol Use Disorder: A Clinical Practice Perspective In: frontiers in Psychiatrie. January 2019, Article 708.
- ^ R. de Beaurepaire: A Review of the Potential Mechanisms of Action of Baclofen in Alcohol Use Disorder In: Frontiers in Psychiatrie. October 2019, Article 506
- ↑ L'ANSM octroie une autorisation de mise sur le marché pour une utilization du baclofène dans l'alcoolo-dépendance - Communiqué . Press release of the French Medicines Agency of October 23, 2018.
- ↑ Une recommandation temporaire d'utilisation (RTU) est accordée pour le baclofène - Point d'information. ANSM, March 14, 2014.
- ↑ Is alcohol addiction curable after all? In: pta forum. Issue 16/2014,
- ↑ Alcohol cessation - no use of high-dose baclofen (LIORESAL, generics) in ALPADIR study In: arznei-telegramm, at 48, 2017, p. 63.
- ↑ MJ Crossentino, K. Mann, SP Armbruster, JM Lake, C. Maydonovitch, RKH Wong: Randomized Clinical Trial: The Effect of Baclofen in Patients With Gastro-Oesophageal Reflux. In: Alimentary Pharmacology and Therapeutics . 35 (9), 2012, pp. 1036-1044.
- ↑ JF Cryan, K. Kaupmann: Don't worry "B" happy !: a role for GABA-B receptors in anxiety and depression. In: Trends in Pharmacological Sciences . 26, 2005, pp. 36-43.
- ↑ C. Mombereau et al .: Genetic and pharmacological evidence of a role for GABA (B) receptors in the modulation of anxiety and antidepressant-like behavior. In: Neuropsychopharmacology . 29, 2004, pp. 1050-1062.
- ↑ PERSISTENT HOSPITALITY - RATIONAL AND IRRATIONAL - arznei telegram. Retrieved June 23, 2017 .