Hachimoji DNA
The Hachimoji DNA (from Japanese 八 Hachi "eight", 文字 moji "letter (s)") is a deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), which in contrast to the naturally occurring DNA eight instead of four nucleic contains. Four of the bases are natural and correspond to those of DNA, four are added synthetically and do not occur in natural DNA. An advantage of such an eight-base DNA system could be an improved ability to store digital data, in addition, the researchers hope to discover how extraterrestrial life could develop with an alternative DNA.
construction
Natural DNA is a molecule made up of two chains that form a double helix and that carries the genetic information of all known living organisms and many viruses in the form of genes . DNA and ribonucleic acid (RNA) are nucleic acids and in addition to proteins , lipids and complex carbohydrates ( polysaccharides ), these nucleic acids are one of the four main types of macromolecules that are essential for all known life forms. The two strands of DNA are called polynucleotides because they consist of simpler monomeric units called nucleotides . Each nucleotide consists of one of four nitrogenous nucleobases ( cytosine [C], guanine [G], adenine [A] or thymine [T]), a sugar called deoxyribose, and a phosphate group . The nucleotides are linked in a chain by covalent bonds between the sugar of one nucleotide and the phosphate of the next, which leads to an alternating sugar-phosphate backbone. The nitrogenous bases of the two separate polynucleotide strands are linked according to the rules of base pairing (A with T and C with G) with hydrogen bonds to double-stranded DNA with elongated, orthogonal, base pairs.
Hachimoji DNA, on the other hand, is similar to natural DNA, but differs in the number and type of nucleobases. For the formation of this synthetic DNA, nucleobases are used that do not occur in nature and are more lipophilic than natural bases, and are combined to form a standard double helix that is formed regardless of the sequence of the bases used. Due to the new sequence of the nucleotides, synthetic Hachimoji genes are formed using appropriately developed enzymes , which in turn form aptamers from synthetic Hachimoji RNA.
The following new bases appear in the Hachimoji DNA:
| base | Surname | Structural formula |
|---|---|---|
| P | 5-aza-7-deazaguanine |
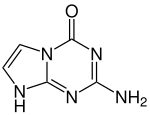
|
| B. | Isoguanine |

|
| rS | Isocytosine |

|
| dS | 1-methylcytosine |

|
| Z | 6-amino-5-nitropyridin-2-one |

|
S binds to B and Z binds to P to form base pairs. dS is used in the formation of DNA, rS for RNA. Together with the four naturally occurring base pairs in DNA and RNA, the resulting Hachimoji DNA contains eight different bases and four different base pairs.
An enzyme ( T7 - polymerase ) was conducted by researchers for the in vitro adapted transcription of DNA into Hachimoji Hachimoji RNA, the chemical activity in the form of a green-emitting fluorophore ( fluorochrome generated).
See also
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d Shuichi Hoshika, Nicole A. Leal, Myong-Jung Kim, Myong-Sang Kim, Nilesh B. Karalkar, Hyo-Joong Kim, Alison M. Bates, Norman E. Watkins Jr., Holly A. SantaLucia, Adam J. Meyer, Saurja DasGupta, Joseph A. Piccirilli, Andrew D. Ellington, John SantaLucia Jr., Millie M. Georgiadis, Steven A. Benner: Hachimoji DNA and RNA: A genetic system with eight building blocks. Science 363 (6429) February 22, 2019; Pp. 884-887. doi : 10.1126 / science.aat0971 .
- ↑ Daniela Albat: DNA with eight letters. Scinexx, February 22, 2019.
- ^ A b Carl Zimmer : DNA Gets a New - and Bigger - Genetic Alphabet. . In: The New York Times , February 21, 2019. Retrieved February 22, 2019.
- ↑ Bello Dumé: Hachimoji DNA doubles the genetic code . In: Physics World , February 22, 2019.
