Memel
|
Memel Njemen (middle and upper reaches), Lithuanian Nemunas , Russian Неман , Belarusian Нёман , Polish Niemen |
||
|
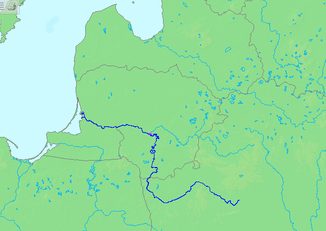
Course of the Memel |
||
| Data | ||
| Water code | RU : 01010000112104300000215 | |
| location |
Hrodsenskaja Woblasz , Minskaja Woblasz ( Belarus ), Lithuania , Kaliningrad Oblast ( Russia ) |
|
| River system | Memel | |
| Headwaters |
Belorussian ridge a little southwest of Minsk 53 ° 15 ′ 10 ″ N , 27 ° 18 ′ 21 ″ E |
|
| Source height | 176 m | |
| muzzle |
Curonian Lagoon west of Šilutė ; Atmata estuary: Coordinates: 55 ° 20 ′ 12 " N , 21 ° 14 ′ 50" E 55 ° 20 ′ 12 " N , 21 ° 14 ′ 50" E |
|
| Mouth height | 0 m | |
| Height difference | 176 m | |
| Bottom slope | 0.19 ‰ | |
| length | 937 km | |
| Catchment area | 98,200 km² | |
| Drain |
MQ |
678 m³ / s |
| Left tributaries | Shchara , Šešupė , Swislatsch , Selvyanka , Ussa , Moltschad , Ross , Serwetsch , Loscha | |
| Right tributaries | Merkys , Neris , Nevėžis , Dubysa , Jūra , Minija , Western Berezina | |
| Big cities | Hrodna (Belarus), Kaunas (Lithuania) | |
| Medium-sized cities | Druskininkai , Alytus , Sovetsk | |
| Small towns | Jurbarkas | |
| Communities | Birštonas | |
| Navigable | A hydrofoil operates from Kaunas to Nida | |
|
In the past, the Memel was also an important waterway |
||
|
The Memel in Hrodna , Belarus |
||
|
The Memel near Druskininkai , Lithuania |
||
|
The Memel near Jurbarkas , Lithuania |
||
|
View from the high bank of the Memel in Veliuona to the river |
||
The Memel ( Lithuanian Nemunas , Belarusian Нёман (Njoman), Russian Неман (Neman), Polish Niemen ) is a 937 km long river that flows from Belarus via Lithuania into the Curonian Lagoon and the Baltic Sea . In one section it marks the Lithuanian border with Belarus, and on the lower reaches the border with the Russian Kaliningrad Oblast .
etymology
The name "Memel" may derive from the Curonian-Lithuanian: memelis, mimelis (quieter, slower, more silent) Lithuanian mēms (mute, speechless).
The name Memel used to be used mainly for the lower reaches of the river, flowing through Prussian Lithuania , between Smalininkai (Schmalleningken) and the junction of the Gilgestrom near Tilsit (64 km). From there on, the main stream was referred to as the soot stream (35 km), from the village of Ruß , where it branches off again into a pronounced estuary delta , as Atmath (13 km) - today, however, the name Memel or the Lithuanian equivalent of Nemuna in use. For the river section in Belarus and Lithuania, the Polish designation Njemen or Niemen was also used in German .
In ancient writings, such as the Geographike Hyphegesis by Claudius Ptolemy , a river called Rhubon (also Rhudon ; Greek: Ῥούβωνος ἐκβ) is mentioned, which in historical research is occasionally equated with the Memel, but by other authors also with the Daugava .
A similarly named river ( Mēmele , or Nemunėlis in Lithuania) has its source in northern Lithuania and flows through Latvia towards the Riga Bay . Possibly the river name belongs to the so-called old European hydronymy , which encompasses language families ; a name parallel would then also be the small left tributary of the Main Mümling in the Odenwald , whose first Roman-Latin document is Nemaninga .
In ancient times, the river was part of the Amber Road trade route from the Baltic Sea to the Mediterranean .
In Lithuanian, the Memel (or the Nemunas ) is also referred to as the "father of the Lithuanian rivers", which in addition to the power of the river and the like. a. This is also due to the fact that almost the entire national territory (apart from a strip of land on the northern border and in the extreme northwest) is located in the Memel Basin and is thus drained via the Memel and its tributaries - which means that almost every Lithuanian Running waters ultimately flow into the Nemunas.
course
The Memel rises in Belarus on the Belarusian ridge a little southwest of Minsk .
From there it initially flows west to Hrodna . It then turns in a predominantly northerly direction towards Lithuania, breaking through the Baltic Ridge and then flowing west again from Kaunas . Directly in front of Kaunas, it is dammed for a hydroelectric power station on the Kaunasser Sea . The old town of Kaunas lies at the mouth of the largest tributary, the Neris . Shortly after Jurbarkas , the Memel from Smalininkai becomes the border river between Lithuania and the Kaliningrad region . The Memel Basin has a size of 97,928 km².
The Memel forms an estuary delta . After an estuary ( Matrossowka , English Gilgestrom, Prussian gilus, gilin, gillis (deep), Lithuanian Gilgė or Gilija ) branches off to the southwest at Sowjetsk / Tilsit , the main stream to Rusnė marks the further course of the border, where it branches off again several times and the actual Memel Delta , now designated as a protected area, begins. The Atmata (Prussian at , von, aus, her, Prussian mat to swivel), the northernmost branch of the estuary is the main stream and official waterway , the southernmost arm, the Skirvytė (Prussian skirti divide, separate, separate, separate, mark, Prussian wistit , swirl ) forms the further boundary. All arms flow into the the Baltic Sea belonging Curonian Lagoon .
At a headland opposite the mouth of the Atmata on which VENTES Ragas , Lithuania is important Vogelwarte .
Hydrology
An average of 20 km³ of water flows into the Curonian Lagoon from the Memel per year - about 41–45% in spring, 15–18% in summer, 19–22% in autumn and 17–21% in winter. The flow velocity is 1 m / s, at high tide up to 1.5–1.8 m / s.
icing
In December, the Memel regularly freezes over. The ice cover grows to 40–70 cm before it breaks up again between the end of January and March. Due to strong river meanders and an uneven gradient, ice accumulation regularly forms , which can often trigger large floods .
Spring flood
The beginning of the spring flood falls statistically on March 19, reaches its peak after six to nine days and lasts 16 days - however, the range of fluctuation is high; the longest known flood lasted 51 days. In the Memel estuary, the flood situation can be aggravated by backwater due to the later breaking up of the ice in the lagoon and possibly as a result of unfavorable winds, so that even today regular, sometimes devastating floods occur, especially in the lower reaches and in the Memel Delta.
The Memel Delta is often isolated from the outside world due to its island location - especially since the broken ice that is now drifting also hinders a connection by boat. The condition in which it is no longer possible to cross the ice , but not yet cross the water , is so common that it has its own name: The Schaktarp.
shipping
The Memel is hardly used as a waterway , although it is a large river that is navigable at least as far as Kaunas . At least freight traffic does not take place to a relevant extent; at most traffic with pleasure boats and excursion boats. Continuous navigation beyond Kaunas has not been possible since the construction of the Kaunasser Sea dam .
In earlier times the river was not consistently developed into a waterway, although the first attempts were made to clear stones from the fairway as early as 1350 and again in 1553. There are still dangerous shallows in numerous places. Above all, the emerging competition from the railroad made its importance as a transport route wane. Today it does not meet the requirements of modern freight shipping.
In the past, however, there was a brisk freight transport on the Memel; first written evidence goes back to the 13th century. Canal construction projects, through which there were connections to other river systems, testify to the former importance. As early as 1765/68, the Oginski Canal was built to connect the rivers of Memel and Dnepr , and in 1839 the Augustów Canal was used to connect to Biebrza and the Vistula . The König-Wilhelm-Kanal and the Friedrichsgraben-System are also to be mentioned (which opened a connection to the Frischen Haff via the estuary Gilge and the Pregel ).
In addition to the transport of agricultural products, rafting was particularly important . The wood felled on the upper reaches of extensive forest areas was transported to the mouth as firewood and, above all, as timber, where it was partially pre-processed and further distributed via the former centers of Königsberg and Memel / Klaipėda - from the local wooden port by sea across the Baltic Sea, sometimes even as far as shipped to England . Rusnė / Ruß in the Memel Delta was an important trading center for the timber trade. After the First World War , the timber trade practically came to a standstill.
Important cities
On the Memel are u. a. these cities:
At the mouth of the Curonian Lagoon , through which the Memel finally flows into the Baltic Sea, there is also the city of Klaipėda , which itself was called Memel at the time of German rule .
Germany song
The Memel is mentioned in the first stanza of the Deutschlandlied as a German border:
In 1841 the lyricist August Heinrich Hoffmann von Fallersleben roughly outlined the area, which he considered to belong to Germany because of the German-speaking population living there, by specifying these waters. In the east, East Prussia was one of them. Its north and east borders were stable for more than 400 years ( Treaty of Melno Sea , 1422). There the Memel offered itself as a demarcation, although German was also spoken north of it. He did not think of a clear language border , the area along the river was at that time Baltic German area, and the concept of language nationalism only came into effect towards the end of the 19th century.
As a result of the Treaty of Versailles , the Memel actually became a border from 1920, as the areas to the right of the river were separated and placed under a mandate from the League of Nations (see Memelland ). This demarcation has been reflected since 1945 in the border between Lithuania and the Kaliningrad region .
The Memel was also mentioned in the folk song Zogen once five wild swans (words transferred from Karl Plenzat, Weise traditional):
Five young girls, slim and beautiful, once grew up on the Memel beach.
history
In July 1807 between Emperor Napoleon I , Tsar Alexander I and King Friedrich Wilhelm III. The peace of Tilsit was concluded on a raft on the Memel .
In the Peace Treaty of Versailles the Memel was declared an international river together with the Danube , Elbe and Oder . This means that all people and goods on the river had to be treated equally regardless of the nationality or the flag of the ship.
literature
- Erich von Lojewski : In the murmur of the Memel Stream…. Local folk tales from Tilsit and the Memel area . J. Reyländer, Tilsit 1931.
- Erich von Lojewski: The Memel Witch. Legends and wondrous stories from East Prussia . Verlag Möller, Rendsburg 1956.
- Uwe Rada : The Memel. Cultural history of a European river. Siedler Verlag, Berlin 2010. ISBN 978-3-88680-930-1 .
- AE Preuss: Prussian country and folklore or description of Prussia . Koenigsberg i. Pr. 1835, pp. 40-49.
- Johann Christian Wutzke : First contribution to the knowledge of the Memel river, from its origin to the division into the Ruß and Gilge rivers and to its discharge into the Curonian Lagoon . In: Contributions to the customer of Prussia . Volume 3, Issue 2, Königsberg 1820, pp. 89-121.
- Johann Christian Wutzke : Second contribution to the knowledge of the Memel Current, as a commercial waterway from Russia to Prussia, namely from Grodno to Schmalleningken . In: Contributions to the customer of Prussia . Volume 3, Issue 3, Königsberg 1820, pp. 221–241.
- Johann Christian Wutzke : Third contribution with regard to the passage over the Memel river from Grodno, up to the division into Ruß and Gilge and the discharge into the Curonian Lagoon . In: Contributions to the customer of Prussia . Volume 3, Issue 4, Königsberg 1820, pp. 281-292.
Web links
Remarks
- ↑ Historical sources show that boats drifted on the town hall square in Kaunas in 1715, 1811, 1829, 1855 and 1906. Probably the strongest flood disaster occurred in Kaunas in 1946, on the upper reaches around Druskininkai and Birštonas in 1958.
- ↑ There is no lock or similar at the dam. This suggests that at the time of planning, at least this section was of little importance as a shipping route. In today's flooded section there were two of the most dangerous shoals, the "Devil's Bridge" (Guoga) and the "Kamadulenserin" (Kamandulė).
- ↑ The Venta-Dubysa Canal , which was also part of this project and was supposed to connect the Memel with the Ventspils port (the actual “goal” of the Augustów Canal project), was not completed.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Article Memel in the Great Soviet Encyclopedia (BSE) , 3rd edition 1969–1978 (Russian)
- ↑ a b Memel in the State Water Register of the Russian Federation (Russian)
- ↑ Diercke, Weltatlas, 1982/83, p. 82.
- ↑ Gottlieb August Wimmer: History of the geographical voyages of discovery on water and on land. Volume 1, Vienna 1838
- ^ W. Smith: Dictionary of Greek and Roman Geography. London 1854
- ↑ a b c d e Nemunas / Memel water travel route; State Office for Tourism at the Ministry of Economy of the Republic of Lithuania, 1st edition 2007
- ↑ Schaktarp - GenWiki. In: wiki-de.genealogy.net. Retrieved September 4, 2015 .
- ↑ Stand Up Paddling: When there is a flood, tractors pull the cars on trailers through the water . In: The time . ( zeit.de [accessed on September 4, 2015]).
- ↑ Peace Treaty of Versailles. June 28, 1919. Chapter III. Articles 331, 332.