Methylprednisolone
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
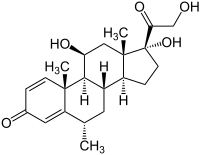
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Methylprednisolone | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 22 H 30 O 5 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white to almost white, polymorphic and crystalline powder |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | |||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | |||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | |||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 374.47 g · mol -1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
232.5 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
practically insoluble in water (120 mg l −1 at 25 ° C), sparingly soluble in ethanol , sparingly soluble in acetone and dichloromethane |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Methylprednisolone is a synthetic glucocorticoid that can be used as a drug orally , intravenously and dermally (on the skin).
Effects and areas of application
Methylprednisolone has a decongestant and anti-inflammatory effect and is used, among other things, to treat allergic and autoimmune diseases , skin diseases and as an accompanying medication in cancer and pain therapy . The intravenous dosing is described in anaphylactic shock , brain edema , to boost therapy for multiple sclerosis , severe asthma attack and status asthmaticus applied and a few other life-threatening conditions.
In the USA, methylprednisolone is administered nationwide for spinal cord injuries at a dose of 30 mg / kg in the early acute phase. The aim is to reduce cytotoxic edema , inflammation and the release of glutamate and free radicals. In Europe, it is not used in all centers for this indication because of the increased rate of complications ( wound infection , gastric bleeding , pancreatitis , pneumonia ) .
A study published in 2016 compared the intratympanic administration of methylprednisolone for the treatment of Menière's disease with the traditional use of gentamicin . While gentamicin can effectively reduce dizziness attacks in the context of Menière's disease, administration of the active ingredient leads to partial or complete hearing loss in more than 20% of cases. The administration of methylprednisolone produced an equally effective reduction in attacks of vertigo by 87%, but without impairing hearing performance.
Side effects
The most important side effects of methylprednisolone include nausea and vomiting with high doses, with long-term use, weight gain through to trunk obesity , cataracts , osteoporosis , diabetes mellitus and psychoses . Since the sudden discontinuation of long-term therapy (longer than three to four weeks) can lead to secondary Addison's disease , the therapy must be gradually terminated in these cases.
Dosage forms and trade names
Finished medicinal products with methylprednisolone are available in tablet form, as infusion and injection solutions for systemic treatment and as creams, ointments, emulsions and solutions for topical application on the skin.
Advantan (D, A, CH), Depo-Medrol (CH), Medrol (CH, P), Methypred (D), Metysolon (D), M-Predni (D), Predni M (D), Solu-Medrol ( CH), Urbason (D, A), Prednol (Ty), various generics (D)
Depot-Medrol (CH)
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b European Pharmacopoeia Commission (Ed.): European Pharmacopoeia 5th Edition . tape 5.0-5.8 , 2006.
- ↑ a b c d Entry on methylprednisolone in the ChemIDplus database of the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM)
- ↑ Data sheet 6α-Methylprednisolone ≥ 98% from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on May 29, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Schwab JM et al., Acute spinal cord injury: Experimental strategies as a basis for future treatments , in Deutsches Ärzteblatt , 101/2004, pp. A-1422, B-1183, C-1137.
- ↑ Mitesh Patel, Kiran Agarwal, Qadeer Arshad, Mohamed Hariri, Peter Rea: Intratympanic methylprednisolone versus gentamicin in patients with unilateral Ménière's disease: a randomized, double-blind, comparative effectiveness trial . In: The Lancet . tape 388 , no. 10061 , December 3, 2016, ISSN 0140-6736 , p. 2753-2762 , doi : 10.1016 / S0140-6736 (16) 31461-1 , PMID 27865535 ( thelancet.com [accessed October 23, 2019]).
- ↑ M. Menière: intratympanic administration of methylprednisolone as effective as gentamicin . In: ENT news . tape 47 , no. 4 , August 1, 2017, ISSN 2198-6533 , p. 17-17 , doi : 10.1007 / s00060-017-5484-9 .