Swabian Rezat
| Swabian Rezat | ||
|
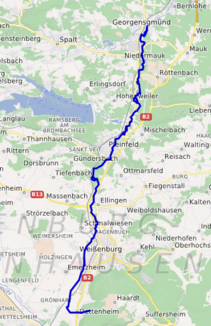
Course of the Swabian Rezat |
||
| Data | ||
| Water code | DE : 24212 | |
| location |
Foreland of the southern Franconian Alb
|
|
| River system | Rhine | |
| Drain over | Rednitz → Regnitz → Main → Rhine → North Sea | |
| source | on the eaves of the Franconian Alb near Dettenheim 48 ° 59 ′ 16 ″ N , 10 ° 57 ′ 37 ″ E |
|
| Source height | approx. 480 m above sea level NHN | |
| confluence | with the Franconian Rezat zur Rednitz in Georgensgmünd Coordinates: 49 ° 11 '17 " N , 11 ° 1' 20" E 49 ° 11 '17 " N , 11 ° 1' 20" E |
|
| Mouth height | 341.7 m above sea level NHN | |
| Height difference | approx. 138.3 m | |
| Bottom slope | approx. 4.2 ‰ | |
| length | 33.3 km | |
| Catchment area | 284.99 km² | |
| Discharge at the Mühlstetten A Eo gauge: 254.7 km² Location: 5.23 km above the mouth |
NNQ MNQ 1994–2012 MQ 1994–2012 Mq 1994–2012 MHQ 1994–2012 HHQ (April 13, 1994) |
372 l / s 531 l / s 2.11 m³ / s 8.3 l / (s km²) 22.4 m³ / s 55.4 m³ / s |
| Left tributaries | see below | |
| Right tributaries | see below | |
| Small towns | Weißenburg in Bavaria | |
| Communities | Ellingen , Pleinfeld , Röttenbach , Georgensgmünd | |
| Residents in the catchment area | 39,000 | |
|
The Heiligenbrücke in Ellingen over the Swabian Rezat |
||
The Swabian Rezat is the 33.3 km long, right and southern source river of the Rednitz in Middle Franconia . It flows in the Bavarian districts of Weißenburg-Gunzenhausen and Roth . It belongs to the river system of the Rhine and is , hydrographically seen, a tributary of the Rednitz as the less water-rich of the two source rivers of the Rednitz - its left and western source river is the longer and more water-rich Franconian Rezat .
Only 2 km after its source it touches a valley watershed in the course of the main European watershed . This was overcome in the 8th century by the Karlsgraben to connect the Danube with the Rhine .
etymology
The name Rezat comes, like the river name Rednitz, from the Celtic Radantia , which means river. In the year 793 the river was first mentioned as "Radentia", in 1327 it was called "Redentz", 1387 as Retzend, 1500 as "Regnizwesserli", 1503 as "Rednitz", 1571 as "Retzet", in the 16th century as " Bairisch "or" Ober Retzach "and 1726 as" Ober Rezat ". The year 1715 is often mentioned as the first mention of the river as "Swabian Rezat", but the name already appears in a dissertation from 1702.
The addition "Swabian" is explained by the fact that the Rezat comes from the south and thus from a dialect area that already has clear Swabian features. It serves to clearly differentiate it from the Franconian Rezat. The fact that the name of the river comes from the fact that the imperial city Weißenburg belongs to the Swabian League of Cities is probably incorrect.
geography
source
The source of the Swabian Rezat is about 480 m above sea level. NHN in the area of the city of Weißenburg in Bavaria , about 900 m east of Dettenheim an der Talsteige der Straße von Haardt down. It rises here in a short side valley in the natural area of the Upper Altmühlalb of its northward moving main valley, which itself starts at the side of the valley axis of the Altmühl flowing to the Danube .
course
A few hundred meters after its source, the Swabian Rezat flows through Dettenheim and has been routed underground to the western end of the town since the canalization in 1962/1963. Then it runs a short distance directly on the watershed and turns north here. In the same flat meadow area, at an altitude of about 420 m , about 100 m to the left of it, rises a body of water that flows through the remains of the historic Fossa Carolina with a slight gradient to Altmühl , just under 2 km away .
A little later, the Swabian Rezat is fed by the runoff from a sewage treatment plant. It initially runs through the flat reed and then passes the Weißenburg core city in the west. Immediately after Weißenburg it reaches its longest tributary from the east, the Felchbach . This is where the valley begins to deepen. Your further course leads through Ellingen and Pleinfeld northwards. Then she takes the from the Great Brombachsee coming Brombach and happened several mills and the villages Mühlstetten and Niedermauk , two districts of the municipality Röttenbach in the district Roth.
confluence
Finally, the Swabian Rezat unites between the eponymous capital of the Georgensgmünd municipality on the left and its Petersgmünd district on the right opposite at 341.7 m above sea level with the Franconian Rezat coming from the south-west, which is much longer and has a richer catchment area, to the indirect Main tributary Rednitz .
Catchment area
The Swabian Rezat drains an area of 285.0 km² . Your catchment area has roughly the shape of a triangle with a southern tip near the origin near Dettenheim. The highest point is 635.7 m above sea level. NHN high peaks of Laubbichel east of Wülzburg on the southeastern watershed.
There the catchment area, viewed in terms of its natural surroundings , has a share in the eaves of the southern Franconian Jura , more precisely, in its subspaces (from southwest to northeast) Weißenburger Alb , Anlauteralb and Anlauter-Braunjura funnel . Most of the rest of the southern part of the catchment area lies in the adjoining natural area foreland of the southern Franconian Jura , of which the upper Rezattal and the low hills and mountains to the east are in the lower area of the foreland of the Weißenburger Alb , while the areas to the left and west of the valley belong to the lower area of Weimersheimer Platte . Below Ellingen, the river changes over to the Middle Franconian Basin . From there, the valley and the rest of the right catchment area belong to the confluence with the sub-area of Rother sand plates , while the left-hand catchment area is divided into the sub-areas of the southern foreland of the Spalter hill country (with Brombachgrund) in the south, southern Spalter hill country in the northwest and north and a gusset of the eastern foreland of the Spalter hill country near the mouth on the left the Rezat.
The water rivals outside are in turn in the southeast across the Albtrauf of the Treuchtlinger Schambach , some dry valleys and finally the Anlauter , all of which drain towards the Altmühl . After descending from the Alb plateau, the Scheide moves, initially over the Frankenalb-Zeugenberg Schloßberg ( 606.7 m ), before, among other things, the tributaries of the upper Roth, approximately northwest to the confluence with the Franconian Rezat; here the Rednitz catchment area borders on the outside. The northern watershed west of the mouth borders the lower catchment area of the Franconian Rezat , which also competes in the northwest via its right tributary Erlbach near Höfstetten. The western and southwestern watershed runs against the upper Altmühl and its smaller left tributaries.
The Brombachsee , one of the largest reservoirs in Central Europe, is located in the catchment area .
Tributaries
The more important tributaries of the Swabian Rezat are listed from the origin to the confluence:
| Surname | GKZ | location | Length in km |
EZG in km² |
Mouth | Mouth height in m above sea level NHN |
Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kühlenbach | right | ≈ 2.0 | ≈ 3.9 | to Dettenheim | 416 | ||
| Hammerstadtgraben | Left | ≈ 4.2 | near Emetzheim | 408 | Upper course: Wöhrbach | ||
| Weimersheimer Bach | Left | ≈ 4.5 | ≈ 5.5 | near Weissenburg | 404 | ||
| Rohrbach | right | ≈ 7.7 | ≈ 12.1 | near Ellingen - Bräumühle | 394 | Bösbach → Rohrbach | |
| Felchbach | 242122 | right | 15.4 | 40.1 | at Ellingen-Bräumühle | 393 | Flurbach → Felchbach |
| Himmelreichgraben | Left | ≈ 1.1 | ≈ 0.7 | after the Bräumühle in their mill ditch | 393 | ||
| Mittelbühlgraben | Left | ≈ 4.2 | ≈ 6.1 | shortly before Ellingen | 389 | ||
| Riedgraben | Left | ≈ 2.5 | ≈ 1.6 | in Ellingen | 387 | ||
| Hörleinsgraben | Left | ≈ 3.5 | ≈ 4.3 | on the northern edge of Ellingen | 386 | ||
| Ottmarsfelder Graben | right | ≈ 3.0 | ≈ 4.9 | at Ellingen- Zollmühle | 384 | Seiserbach → Ottmarsfelder Graben | |
| Walkershöfer Weihergraben | Left | ≈ 1.3 | ≈ 1.2 | at Ellingen-Zollmühle | 381 | ||
| Front Troppelgraben | Left | ≈ 3.8 | ≈ 3.2 | in front of Ellingen- Lauterbrunnmühle | 381 | ||
| Rear drip trench | Left | ≈ 2.1 | ≈ 2.1 | at the Lauterbrunnmühle | 376 | ||
| Banzerbach | 242124 | Left | 9.1 | 20.0 | before Pleinfeld | 375 | Weihergraben → Buxbach → Banzerbach |
| Arbach | right | 6.6 | in northern Pleinfeld | 373 | |||
| Iglseebach | right | 4.3 | Pleinfeld- Prexelmühle | 365 | |||
| Brombach | 242126 | Left | 17.0 | 67.3 | at Pleinfeld- Mäusleinsmühle | 364 | |
| Red moat | right | 3.4 | at Pleinfeld- Mackenmühle | 361 | |||
| Kühbach | Left | 1.6 | near Röttenbach - Mühlstetten | 356 | |||
| Rottenbach | right | shortly after Röttenbach | 352 | ||||
| Maukbach | right | near Röttenbach- Niedermauk | 349 | ||||
| Stöckachgraben | right | near Georgensgmünd - Petersgmünd | 345 |
- The Fossa Carolina , a left branching channel to the Altmühl, formerly belonged to the river system . But today it is no longer associated with the Rezat. The runoff from the remains of the canal leads to the Altmühl .
- The Flurgraben is an alluvial ditch of the Swabian Rezat .
Localities
Places on the Swabian Rezat are:
|
|
Flood
As with all slow-flowing rivers, there is an acute flood risk along the Swabian Rezat , which is particularly high in winter due to melting snow or prolonged rainfall. The highest discharge ever measured was 55.4 m³ / s on April 13, 1994, which corresponds to an annuality of well over 50 years. From 60 m³ / s, the Swabian Rezat is referred to as a 100-year flood.
Function of water regulation
After major hydraulic engineering work, the Swabian Rezat now conducts water together with other bodies of water from the rain-rich south of Bavaria to the rain-poor north of Bavaria. For this purpose, the Brombachsee with its three parts Großer Brombachsee , Kleiner Brombachsee and Igelsbachsee as well as the Altmühlsee on the Altmühl supplying the water were created from the 1970s . In the event of flooding at the Gern Altmühl level near Ornbau , water is supplied to the Altmühlsee via the Altmühl feeder. There it is temporarily stored and, if the level is exceeded, it is transferred to the Kleiner Brombachsee via the Altmühlüberleiter . From there, the water first flows over the Großer Brombachsee and the Brombach into the Swabian Rezat, at Georgensgmünd into the Rednitz and then on to Nuremberg, before reaching the Main via the Regnitz . In this way, water that would flow via the Altmühl into the Danube without human intervention is diverted into the river system of the Rhine-Main area via the European main watershed if necessary . The building project was decided by the Bavarian State Parliament on July 16, 1970 at the initiative of MP Ernst Lechner and completed in the late 1990s.
Carolina fossa
The landscape in the headwaters of the Swabian Rezat has become known historically and touristic through the Fossa Carolina . Already Charlemagne wanted, according to tradition, the main European watershed between the catchment areas of the Danube and the Rhine , among other things, on the ridges between the Swabian Rezat and Altmühl runs, overcome by a canal.
Hydraulic structures
Mills
Mills on the Swabian Rezat were or are among others:
bridges
The bridges over the Swabian Rezat include (viewed downstream):
- Heiligenbrücke in Ellingen
- Nepomuk Bridge in Pleinfeld
literature
- Johann Kaspar Bundschuh : Retzat . In: Geographical Statistical-Topographical Lexicon of Franconia . tape 4 : Ni-R . Verlag der Stettinische Buchhandlung, Ulm 1801, DNB 790364301 , OCLC 833753101 , Sp. 480-481 ( digitized version ).
- Werner A. Widmann: Franconian + Swabian Rezat: River valleys in Franconia. Majer, Leutershausen 1989, ISBN 3-922175-28-7 .
Web links
- Course and catchment area of the Swabian Rezat on: BayernAtlas of the Bavarian State Government ( information )
- Level in the main area: Weißenburg / Swabian Rezat (at theBavarian flood news service), on hnd.bayern.de
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Map services of the Federal Agency for Nature Conservation ( information )
- ↑ a b List of brook and river areas in Bavaria - Main river area, page 37 of the Bavarian State Office for the Environment, as of 2016 (PDF; 3.3 MB)
- ↑ Flood news service of the Bavarian State Office for the Environment ( information ) (queried on February 22, 2016)
- ↑ Directory of brook and river areas in Bavaria - Main river area of the Bavarian State Office for the Environment, as of 2016 (PDF; 3.3 MB)
- ↑ Water names in the Weißenburg-Gunzenhausen district, Mfr., In: Blätter für Oberdeutsche Namenforschung , 44th year, p. 94, Munich 2007
- ^ Dissertatio historico-critica de Chronici Halberstadensis . 1702. p. 60 ( digitized version )
- ↑ Ulf Beier: Weißenburger Flurnamenbuch. From Galgenberg to the Kingdom of Heaven (Weißenburger Heimatbücher Volume 4), Weißenburg i. Bay. 1995. p. 429
- ↑ Bavaria Atlas: Rezatquelle and Altmühl
- ^ Franz Tichy : Geographical Land Survey: The natural spatial units on sheet 163 Nuremberg. Federal Institute for Regional Studies, Bad Godesberg 1973. → Online map (PDF; 4.0 MB)
- ↑ Ralph Jätzold: Geographical land survey: The natural space units on sheet 172 Nördlingen. Federal Institute for Regional Studies, Bad Godesberg 1962. → Online map (PDF; 3.9 MB)
- ↑ Flood events (at Rednitz and Rezat), on hopla-main.de
- ↑ Flood characteristics (from Rednitz and Rezat), on hopla-main.de
- ↑ History of the Brombachses
- ^ Grand failure: The "Karlsgraben" between the Rhine and the Danube , Neue Zürcher Zeitung , July 24, 2014