Solar eclipse of December 24, 1992
| Solar eclipse of December 24, 1992 | |
|---|---|
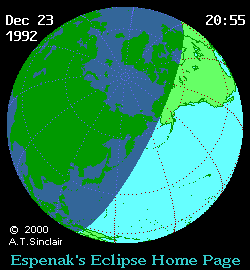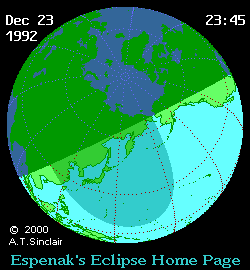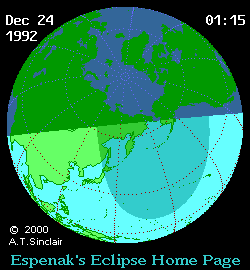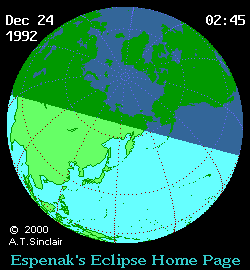 Course of the penumbra on the earth's surface |
|
| classification | |
| Type | Partially |
| area | Northeast Asia , North Pacific , Alaska |
| Saros cycle | 151 (13 of 72) |
| Gamma value | +1.0712 |
| Greatest eclipse | |
| place | Chukotka (Eastern Siberia) |
| location | 65 ° 42 ′ N , 155 ° 42 ′ E |
| time | December 24, 1992 00:30:42 UT |
| size | 0.8418 |
The partial solar eclipse of December 24, 1992 could be observed in Northeast Asia and in the Northeast Pacific. However, in mainland Asia, with the exception of the Kamchatka Peninsula, this happened early in the morning during sunrise. In Japan, however, the complete eclipse could be observed in the morning hours. While over 60 percent of the solar disk was covered by the moon from the northern main island of Hokkaidō , it was only a third on the southern main island of Kyūshū . Sunset observation was possible in southwest Alaska. Also noteworthy is the fact that the locations of the maximum eclipse of the partial solar eclipses that followed one another on December 24, 1992 and May 21, 1993 were only 300 km apart in Chukotka .
This solar eclipse belongs to the young Saros cycle 151, which will include a total of 72 eclipses. Saros 151 started on August 14, 1776 with a small partial solar eclipse in northwestern Canada. The first eclipses are 18 partial eclipses in the northern hemisphere of the earth. This is followed by 6 annular , 1 hybrid and 39 total solar eclipses . The conclusion is formed by 8 partial eclipses in the Antarctic . The cycle ends October 1, 3056.