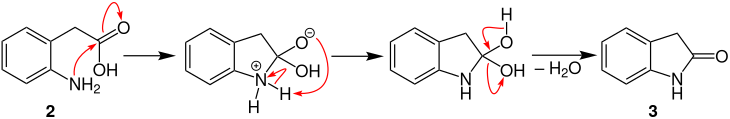Baeyer oxindole synthesis
The Baeyer oxindole synthesis , named after the German chemist Adolf von Baeyer , is a name reaction from the field of organic chemistry and was first described in 1878. The Baeyer oxindole synthesis enables the preparation of oxindole from o -nitrophenylacetic acid.
Overview reaction
By reducing the nitro group and subsequent ring closure, the oxindole is formed from o -nitrophenylacetic acid:
The reduction of the nitro group can be carried out with various reagents such as Sn / HCl, Zn / H 2 SO 4 or Fe / CH 3 COOH.
Reaction mechanism
The following mechanism is described in the literature:
In the first step, o -nitrophenylacetic acid ( 1 ) is reduced to o -aminophenylacetic acid ( 2 ). The reduction is similar to the Béchamp reduction .
In the second step there is a ring closure between the amino group and the carbon atom of the carboxy group . The oxindole ( 3 ) is formed by proton shifting and subsequent elimination of water ;
further reading
- Ward C. Sumpter: The Chemistry of Oxindoles. In: Chem. Rev. 37, 1945, pp. 443-479, doi: 10.1021 / cr60118a003 .
Individual evidence
- ^ Adolf Baeyer: Synthesis of Oxindole. In: Ber. German Chem. Ges. 11, 1878, pp. 582-584, doi: 10.1002 / cber.187801101153 .
- ↑ a b c Zerong Wang: Comprehensive Organic Name Reactions and Reagents , Wiley, 2009, ISBN 978-0-471-70450-8 , pp. 144-146.