Balaban reaction
The Balaban reaction is a name reaction in organic chemistry that was named after its Romanian discoverer Alexandru Balaban (* 1931).
Overview reaction
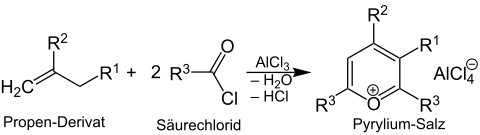
A propene derivative is reacted with a carboxylic acid chloride in the presence of a Lewis acid (e.g. AlCl 3 ). A pyrylium salt is formed :
Instead of a carboxylic acid chloride can also be a carboxylic anhydride are used.
Reaction mechanism
The following complex mechanism is suggested by Theophil Eicher et al. suggested:
In the first step, the acid chloride reacts with the C = C double bond of the propene derivative to form a carbenium ion . The splitting off of a proton then leads to an enol which, together with a further equivalent of the acid chloride, produces a carbenium ion again. The pyrylium salt is then formed with elimination of water .
modification
In a preparatively advantageous variant of the balaban reaction, alcohols or haloalkanes are used to produce the propene derivative in situ .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d Theophil Eicher, Siegfried Hauptmann, Andreas Speicher: The Chemistry of Heterocycles, Wilex-VCH, 2012, ISBN 978-3-527-32868-0 , p. 302.