Central South African Railways
| Central South African Railways | |
|---|---|
|
CSAR tank locomotive
| |
|
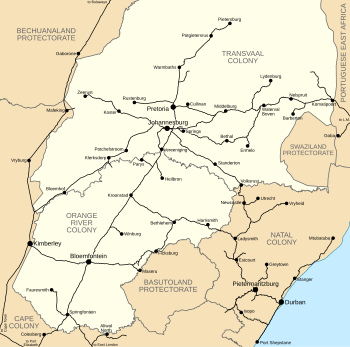
Rail network of the Central South African Railways in 1910,
shortly before the establishment of the South African Union | |
| Gauge : | 1067 mm ( cape track ) |
The Central South African Railways (CSAR) were a short-lived railway company in what is now South Africa and one of the predecessor railways of the later South African Railways .
history
During the Second Boer War , the conquered railways of the South African Republic ( NZASM and PPR ) and the Orange Free State ( OVGS ) were placed under military control as Imperial Military Railways (IMR). The supervisory authority was Lieutenant Colonel Sir Percy Girouard , originally from Canada , who had previously run the railways in Sudan . After the war, in 1902, the IMR became the Central South African Railways, with Percy Girouard keeping the line.
In the eight years of its existence, Deutsche Bahn developed six of its own locomotive series to supplement the locomotives taken over from its predecessor, including two of the Pacific classes, which are comparatively rare in South Africa , a mallet articulated locomotive, the largest South African tank locomotive and a cogwheel locomotive .
After the founding of the South African Union in 1910, the CSAR were merged with the Cape Government Railways (CGR) and the Natal Government Railways (NGR) to form the South African Railways (SAR).
literature
- Leith Paxton, David Bourne: Locomotives of the South African Railways . C. Strui (Pty) Ltd., ISBN 0-86977-211-2