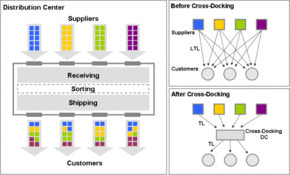
Cross docking
The term cross-docking or Kreuzverkupplung denotes a Warenumschlagsart at which goods from the supplier (sender) before picking come. This means that the storage process and the associated activity of the inventory warehouse are no longer necessary.
The conceptual opposite of cross docking is the sorted delivery, storage and subsequent picking of goods in a warehouse .
aims
Objectives of cross-docking :
- Reduction of storage costs
- Reduction in the number of process steps
Cross-docking variants
- One-stage system
- The suppliers pick the goods (also called logistical units ) based on the final recipient (branches or end customers). In the one-step system, the goods are forwarded “as if they were packed by the sender” to the final recipient via one or more transfer points. The prerequisite for this is that the sender labels the goods (usually on a pallet basis) - that is, specifies the corresponding end recipient directly on / on the goods. This process is also known as pre-allocated cross-docking (PAXD) .
- Two-stage system (also called transshipment )
- The suppliers pick based on the transshipment point or cross-docking point. In the two-stage system, the logistic units are routed unchanged only to the transfer point. At the transhipment point, the actual transhipment into new logistic units takes place, which are addressed to the end customer from this point in time. This process is also known as Break-Bulk Cross-Docking (BBXD) .
- Multi-level system
- A multi-level system includes further process steps in addition to the actual re-picking. These can be, for example, the packaging of articles or so-called value added services . The two-stage system can therefore only be seen as a special case of the multi-stage system.
See also
literature
- LH Harps: Crossdocking for savings . In: Inbound Logistics . May 1996.
- K. Wagar: The Logic of Flow-Through Logistics . In: Supermarket Business . June 1995.
- M. Stickel: Planning and control of cross-docking centers . Universitätsverlag Karlsruhe, 2006, ISBN 978-3-86644-084-5 .
- Daniel M. Harnisch: Cross-Docking Functionalities with SAP®: Optimization Potential in the Distribution Process . VDM Verlag Dr. Müller, 2011, ISBN 978-3-639-30968-3 .
Web links
Commons : Cross-docking - collection of images, videos and audio files
- ECR Europe
- ECR Europe (Germany)
- Bundling instead of being bundled: The fight for system leadership. ( Memento from September 1, 2004 in the Internet Archive ) - Ute Wagner, Frankfurt am Main (PDF, 53 kB)