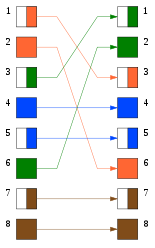
Cross cable
As a crossover cable , crossover cable , cross linked cable or crossover cable referred to in the computer network technology ( LAN ) technique, a four- or eight-wire twisted pair , wherein in a the two RJ45 connectors certain cable cores are reversed ( engl . to cross : to cross). While a straight through network cable connects computers to switches , a crossover cable can be used to connect two computers (or two switches) directly to one another. With the spread of Auto-MDI-X , crossover cables are no longer necessary, as network devices with this standard recognize the pair of send and receive lines and automatically connect correctly internally. With 1000BASE-T connections, crossover cables are unnecessary, since every pair is identified there and any assignments work.
construction
The Ethernet media types 10BASE-T and 100BASE-TX each use a pair of wires for the sending direction and one for the receiving direction. In order for a connection to be established, the wire pairs must be connected in such a way that the sending wire pair of one device is connected to the receiving wire pair of the other device. In the case of network components such as repeaters , hubs , bridges or switches , the crossover is provided internally in the RJ45 connection sockets and is referred to as MDI-X . The computer and switch are therefore connected by straight twisted pair cables with the same assignment on both sides (the same positions on both plugs are connected to one another). With 10BASE-T and 100BASE-TX, this is either EIA / TIA-568A or B on both sides .
If two computers are to be connected directly with a cable, the pairs of wires carrying the signal must be crossed in the cable. This can be achieved by assigning one of the two connectors differently. No connection is established without the crossing of the wire pairs. Instead of a crossover cable, you can also use a straight cable with a crossover adapter to cross the wire pairs.
Before Auto-MDI-X was widespread, most hubs and switches had an uplink port that was not crossed internally and could be connected to a normal MDI-X port of another switch with a straight cable. When using a crossover cable, the uplink port was not necessary and two MDI-X ports could be connected to one another.
For comparison, the two connector ends of an uncrossed patch cable .
variants
The cross cable is available in 3 variants:
10BASE-T and 100BASE-TX Ethernet
Here only two wire pairs are used / crossed (1-2 and 3-6). Since not all wire pairs are used for transmission in these standards, not all wire pairs have to be connected or crossed.
This means that in a crossed cable of this type, the twisted wire pairs 1-2 and 3-6 are crossed with 3-6 and 1-2, the assignment of wire pairs 4-5 and 7-8 is not important.
100BASE-T4 Ethernet
100BASE-T4 Ethernet is somewhat common in the USA because it can also be used with older CAT-3 cables. However, four wire pairs are then used for transmission, so all four wire pairs must be crossed.
In principle there are two bundles of four in this cable, the one known from 10BASE-T and 100BASE-TX (1-2 and 3-6) and additionally the wire pairs 4-5 and 7-8, which are connected or crossed in the same way become.
This means that the twisted wire pairs 1-2, 3-6, 4-5 and 7-8 are connected with 3-6, 1-2, 7-8 and 4-5, precisely in this arrangement and with this twist.
1000BASE-T Ethernet
At least CAT-5 cables are required here; analogous to 100BASE-T4, all four wire pairs are in operation here, so the crossed cable should correspond to the 100BASE-T4 type. However, cross cables are no longer necessary with 1000BASE-T, practically all interfaces (LAN cards, switches, etc.) automatically recognize the respective situation with 10 and 100 Mbit / s connections and switch the pin assignment accordingly (Auto-MDI- X, see Medium Dependent Interface ). In the case of gigabit connections, crossover cables are irrelevant, since all pairs are automatically assigned in the physical medium attachment sublayer. In this way, switch-switch or PC-PC connections can be made with any cables.
The pin assignments can be found in article RJ45 .
Manufacturing, electrical details
Cross cables can be manufactured relatively easily yourself according to the above assignment.
If the cables are manufactured according to the 100BASE-TX standard, there is another frequent source of error in addition to the wrong cable quality ( Cat 5 or better is required). If the twisting with ISDN or 10BASE-T is still almost without influence due to the relatively low signal frequencies, it is of major importance at 100 Mbit / s.
Ethernet over twisted pair uses symmetrical, differential signals to minimize electromagnetic radiation and reduce common-mode interference . It is therefore important which wire pairs are twisted together. It works as follows: If one wire of the pair of wires changes to a positive voltage, the voltage on the other wire changes to an equally high negative voltage - the resulting electromagnetic fields cancel each other out. In any case, with 100BASE-TX pins 1 and 2 must form a twisted wire pair, the same applies to the wire pair on pins 3 and 6 (with 100BASE-T4 cables, pins 4-5 and 7-8 also form twisted pairs). Furthermore, all wires of a wire pair should be exactly the same length, and the twisting may only be missing or removed on a short piece of cable (max. Approx. 1.5 cm). [Receipt?]
Only expensive radio frequency cable testers or some suitable Gigabit Ethernet network cards can detect these types of errors. Simple LED testers, on the other hand, work with direct current and therefore do not show which wire pairs are twisted. This also applies analogously to 10BASE-T cabling, whereby incorrectly placed wire pairs are far less disturbing here.
Auto crossover
Since 1999, many devices have been able to detect which lines have to go where and assign the corresponding pair themselves, so that crossed and uncrossed cables can be used equally. To do this, the devices switch between the channels while they are sending and receiving until they receive connection data and then stop switching. Auto-crossover was standardized with IEEE 803.2ab-1999, Section 40.4.4 (Automatic MDI / MDI-X configuration).
See also
Web links
swell
- ↑ a b crossover cable. WEKA Fachmedien GmbH , accessed on August 19, 2017 .
- ↑ Wolfram Gieseke: The great PC lexicon. 16th edition. Data Becker, Düsseldorf 2011, ISBN 978-3-8158-3083-3 , p. 518 (keyword network cable ).
- ↑ a b IEEE 802.3 40.1.4 signaling
- ↑ https://www.iol.unh.edu/sites/default/files/knowledgebase/ethernet/Auto-Crossover_White_Paper.pdf M. Hersh: Auto-Crossover White Paper; PDF file in English