DEMC
The differential mobility analyzer ( DEMC , Differential Electrical Mobility Classifier) classifies charged particles according to their electrical mobility in the electrical field. The name DEMC is used according to ISO 15900 for the already existing abbreviation DMA (DMA, Differential Mobility Analyzer ).
Working principle
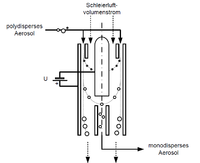
Charged particles (unipolar or bipolar) are deflected within an electric field. This principle is used within a DEMC for the classification of particles. The function of a cylindrical DEMC (ring electrode) is explained below, as shown in the adjacent figure. A polydisperse, charged aerosol is fed into the DEMC. In parallel, a sheath air flow is guided along the inner electrode. An electric field is created between the inner electrode and the earthed outer jacket. If the particles get into this field, they are deflected in the direction of the electrode. The deflection depends on the charge and the projected area of the particles, as well as on the geometry and the operating parameters of the DEMC. Only particles of a certain size can leave the DEMC (monodisperse aerosol) through the outlet at a given voltage.
Types
Cylindrical DEMC
Cylindrical DEMCs have an inner electrode and an outer, grounded jacket.
Planar DEMC
Planar DEMCs are rectangular and have the following advantages over cylindrical DEMCs:
- Simpler structure (no centric alignment of the electrode required, uncomplicated components)
- uniform electric field
application
Classification
Pure DEMCs are used to cut size-dependent fractions of charged particles (<1000 nm) or ions from an aerosol. In research, they are used to generate aerosols with defined particle sizes. Both the width of the particle size distribution and the particle size can be varied as desired. These aerosols are z. B. used for:
- Calibration of particle measurement technology
- Characterization of particle measurement technology (e.g .: counting efficiency, classification accuracy)
- Development of new particle measurement technology
Particle size analysis
If the DEMC is combined with a concentration measuring device such as a condensation particle counter ( CPC ) or an electrometer , it is referred to as a DMAS (Differential Electrical Mobility Analyzer System) according to ISO / FDIS 15900: 2009.
literature
- ↑ ISO 15900: 2009: Determination of particle size distribution - Differential electrical mobility analysis for aerosol particles, 2009
- ↑ E. Hontañón, M. Alonso, A. Rivero, D. Fuentes and E. Ramiro. A nano-DMA of rectangular planar plates, European Aerosol Conference 2009, Karlsruhe, Abstract T011A02