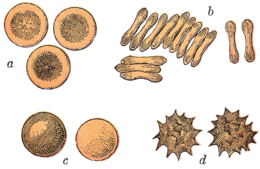
Echinocyte
As echinocytes or Datura cells deformed are red blood cells refer to operations where the biconcave has passed into a spherical shape, and - in contrast to Sphärozyt - have numerous (10-30) blunt projections so that they at Datura remember.
Echinocytes can exist as artifacts from drying and shrinking processes as well as from the action of hypertonic solutions , fatty acids or certain drugs. Echinocytes can also develop when stored blood is due to the decrease in ATP and the influence of the lysolecithin that forms . They then have no diagnostic significance.
Diseases associated with the formation of echinocytes are liver disease (especially with coexisting renal failure ), phosphate deficiency , pyruvate kinase deficiency, phosphoglycerate deficiency, aldolase deficiency, decompression sickness , hemolytic uremic syndrome , Abetalipoproteinemia and burns . It can also develop from other deformed erythrocyte forms such as spherocytes or acanthocytes .
literature
- Barbara J. Bain, Dieter Huhn: Roche basic course in hematological morphology . Georg Thieme Verlag, 1997, ISBN 3-89412-299-4 , pp. 58-60.