Radio module
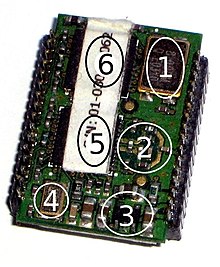
1: quartz oscillator
2: balun
3: linear regulator
4: quartz oscillator
5: transceiver
6: microcontroller
In electrical engineering, a radio module is an assembly made up of radio receivers and / or transmitters or transceivers and the associated control components (usually a microcontroller ). The microcontroller establishes the connection between the user interface (analog or digital values: serial or parallel data) and the radio protocol , encrypts the data if necessary and ensures the transmission (error-free, correct addressee, no manipulability or susceptibility to interference).
The high-frequency part of the module takes on the mixing , filtering and amplification as well as the demodulation or modulation . These procedures are increasingly being solved digitally. Radio modules often have their own antenna.
The user of a radio module does not have to worry about the radio transmission, in particular not about compliance with the national limit values (bandwidth, channel allocation, transmission power), he only needs to know one command set for controlling the radio module.
A radio technology such as Bluetooth , WLAN or ZigBee results from a specified encapsulation of several protocols on different levels .
Radio modules are often plug-in cards for a motherboard. The contacts are used for power supply and data communication.
The use of radio modules can, on the one hand, reduce the development costs of devices with radio technologies; on the other hand, different applications and regions can be served by only changing or equipping the radio module required for the respective radio standard. The main assembly remains the same, which lowers production costs due to larger quantities.
On the other hand, there are manufacturers who specialize in radio modules who manufacture large quantities and thus can better pass on the high development costs.
literature
- Markus Krauße, Rainer Konrad: Wireless ZigBee networks . Springer Fachmedien, Berlin / Heidelberg 2014, ISBN 978-3-658-05820-3 .
- Erik Bartmann: Discover the electronic world with Raspberry Pi. O'Reilly Verlag, Cologne 2013, ISBN 978-3-95561-109-5 .
- Mario Gongolsky, Niels Gründel: WLAN internet radios . Test - Ratgeber - Kaufberatung, Norderstedt 2010, ISBN 978-3-8391-5027-6 .