Hand hacksaw
The hand hacksaw is a hacksaw . It is used to cut materials and produce slots and incisions in workpieces . It is mostly used for metalworking at the workbench and for assembly work when the use of sawing machines is too complex or not possible. The hacksaw for metal consists of the saw bow and the saw blade.
Parts of the saw bow
The following parts are distinguished on the fixed saw bow:
- arc
- Tension lever
- Clamping nut
- Guide piece for clamping clamp
- Clamp with cross recess and retaining pin
- Staple clamp with cross recess and retaining pin
- notebook
The saw blade can be tightened and changed using the clamping and handle clamps. The saw blade must be clamped in such a way that the teeth point in the feed direction (forward).
Saw blades
So that the saw blade does not get stuck in the material, it is designed so that the saw slot produced is wider than the saw blade; the saw blade cuts itself free and does not get stuck in the material, this is known as a free cut. There are three different types of saw blades for this:
Wavy saw blade : The saw teeth run in slight curves (waves).
Compressed saw blade : The saw teeth are a little wider at the tips.
Set saw blade : the saw teeth are bent alternately to the left and right.
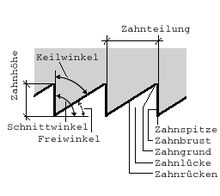
Angles on the saw teeth
The angles are called α (alpha, clearance angle ), β (beta, wedge angle ) and γ (gamma, rake angle - it influences chip formation). Most of the time, all three angles are positive (i.e., α + β + γ <90 °); at over 90 ° one speaks of a negative rake angle.
The saw blade should be selected depending on the nature of the material:
When sawing hard materials, the teeth penetrate the material poorly; few and small chips arise. For this reason, saw blades are used with a small tooth pitch, i.e. many teeth per unit length (specified as teeth per inch ; 1 inch = 25.4 mm).
When sawing soft materials, the teeth easily penetrate the material; many and large chips arise. A large chip space (space between the teeth) is required so that the saw can penetrate the soft material well. For this reason, saw blades with a large tooth pitch, i.e. few teeth per unit of length, are used.
When sawing soft materials such as plastic, saw blades with few teeth and a small wedge angle are used. This is used for better chip evacuation, since large chips accumulate more quickly with soft materials. Hard materials, on the other hand, are sawed with a saw blade with a large wedge angle. This allows the tool to withstand greater loads.