Hopper excavator
A hopper dredger is a sea-going self-propelled Laderaumsaugbaggerschiff with which the dredged material (solid material, more specifically: a soil-water mixture) by towing heads of the river bed and / by a suction head and a suction pipe in the cargo space (Hopper tank . Engl hopper = loading , Bunker) is pumped in the ship. The water serves as a transport medium and for the most part flows outboard again during the charging process.
Working method
Hopper excavators work with the help of one or more centrifugal pumps .
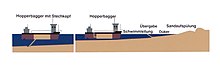
At the lower end of a suction line, which is attached to the side of the ship, there are so-called tow heads. These loosen the sediment at the bottom of the river, which is pumped into the hold as dredged material when driving slowly forward.
The water pumped into the hold is drained through an overflow so that only solid dredged material remains in the hold. After the end of the dredging process, the dredged material is transported to folding points and folded or flushed there.
use
Hopper dredgers are used to deepen fairways and for maintenance dredging in bodies of water. They are only suitable for easily detachable sediments and soils, i.e. usually sand.
They are also used for beach wash-ups on Sylt and Norderney . Here they pick up the sand on the open sea and use pipes to flush a water-sand mixture onto the beach as a coastal protection.
The largest hopper dredgers are the two ships of the Cristóbal Colón class . The Crestway is in use in German waters.
Web links
- The hopper excavator MS NORDSEE from May 17, 2016 by Peter Pospiech , accessed on August 1, 2017
Individual evidence
- ↑ Different Types of Dredgers Used in the Maritime Industry. In: Marine Insight. July 29, 2019, Retrieved August 31, 2019 (American English).
- Jump up the beach on Norderney. State Office for Water Management, Coastal Protection and Nature Conservation, July 12, 2019, accessed on August 31, 2019 .