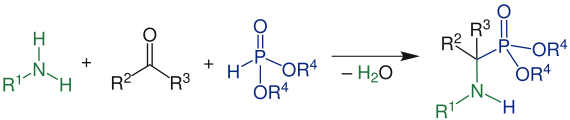
Kabachnik Fields reaction
The Kabachnik-Fields reaction is a multicomponent reaction in which an aldehyde (R 2 = H, R 3 = H or organyl group ), an amine (R 1 = H, organyl group), and a phosphonic acid derivative ((R 4 = H, organyl group) , (R 5 = H, organyl group)), to be converted to an α-aminophosphonate . The reaction was independently discovered in 1952 by Martin Israilewitsch Kabachnik and Ellis K. Fields .
mechanism
In the first step, the amine attacks the aldehyde on the carbonyl carbon atom. This creates a zwitterion, which reacts to the imine by rearranging a hydrogen atom ( tautomerism ) and then splitting off water . In the next step, the phosphonic acid derivative is added to the imine . After a further transfer of a hydrogen atom, the α-aminophosphonate is ultimately formed.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Martin I. Kabachnik, T. Ya. Medved: Новый метод синтеза сс-аминофосфиновых кислот (A new method for the synthesis of α-amino phosphonic acids) . In: Doklady Akademii Nauk SSSR . tape 83 , 1952, pp. 689 .
- ↑ Ellis K. Fields: The synthesis of esters of substituted amino phosphonic acids . In: Journal of the American Chemical Society . tape 74 , no. 6 , 1952, pp. 1528–1531 , doi : 10.1021 / ja01126a054 .
- ^ Zerong Wang: Comprehensive Organic: Name Reactions and Reagents. Wiley Verlag, 2009, ISBN 978-0-471-70450-8 , pp. 1588-1591.